Postweld heat welding method
A technology of thermal welding and welding, which is applied in the direction of welding accessories, heat treatment furnaces, heat treatment equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of affecting the metallurgical quality of the weld, low stress, and increasing the process, so as to save heating equipment, prevent stress corrosion cracking, Effect of improving fatigue life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
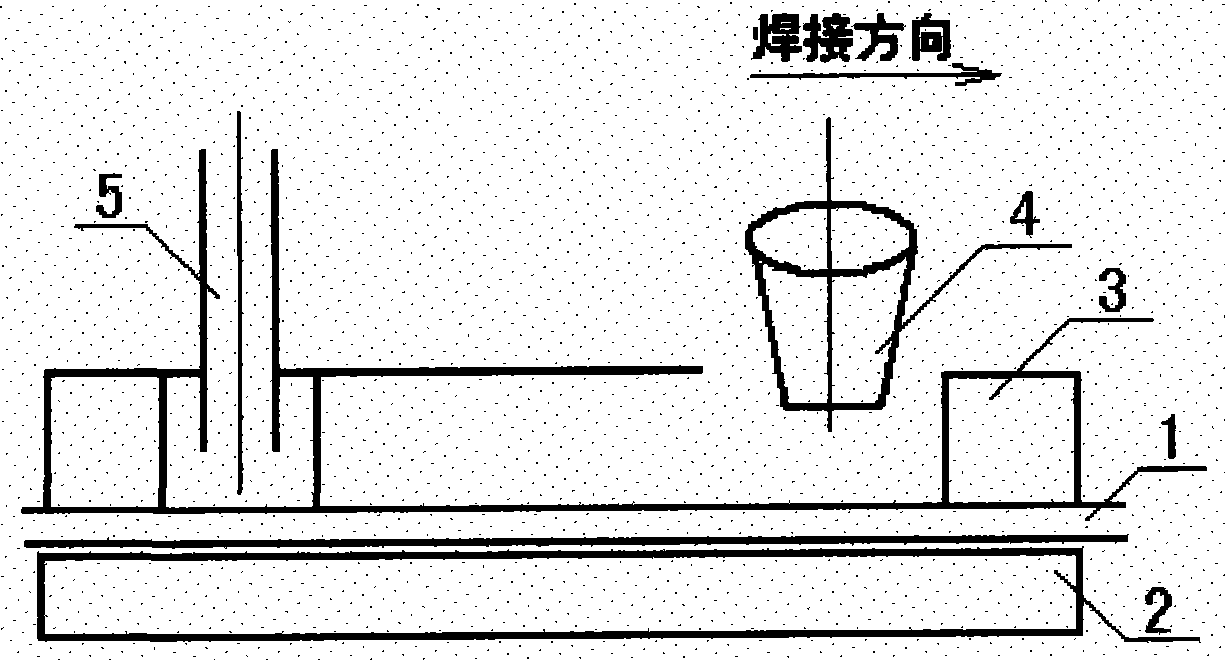
[0013] Example 1 Low-carbon steel plate is welded without stress after welding (the "mechanical melting point" of low-carbon steel is 600°C)
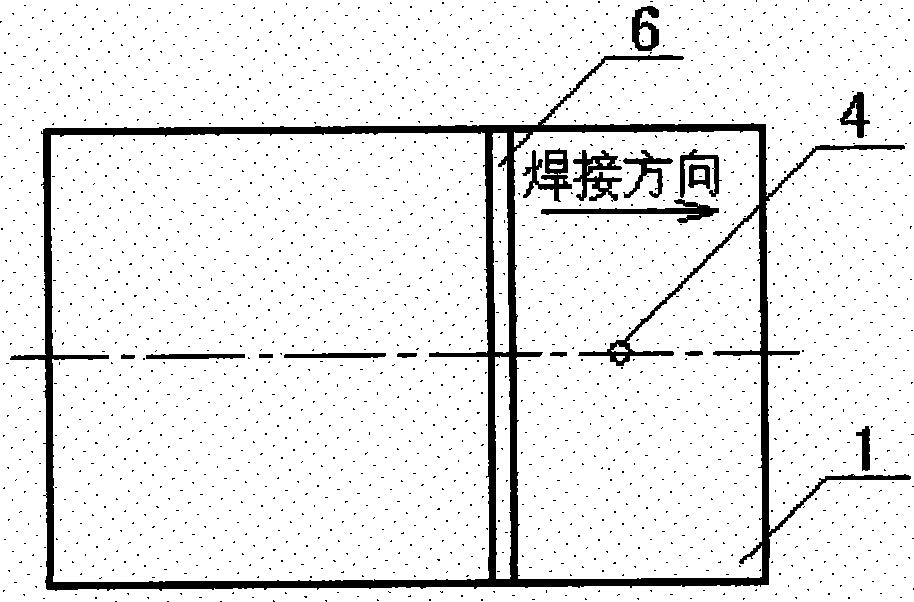
[0014] At 60 mm behind the welding heat source, the entire cross-section of the welded steel plate is subjected to post-welding heat with an oxygen-acetylene flame at a temperature of 610 ° C, and then naturally cooled.
[0015] There is no welding residual stress in the welding seam and near seam area of low carbon steel plate.
Embodiment 2
[0016] Example 2 LF6 aluminum alloy plate is welded without stress after welding (the "mechanical melting point" of LF6 aluminum alloy is 420°C)
[0017] At 70 mm behind the welding heat source, the entire cross-section of the welded aluminum alloy plate is subjected to post-welding heat with an oxygen-acetylene flame at a temperature of 440 ° C, followed by natural cooling.
[0018] There is no welding residual stress in the welding seam and near seam area of LF6 aluminum alloy plate.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Example 3 TC4 titanium alloy plate is welded without stress after welding (the "mechanical melting point" of TC4 titanium alloy is 800°C)
[0020] At 65 mm behind the welding heat source, the entire cross-section of the welded titanium alloy plate is subjected to post-welding heat with a linear laser beam at a temperature of 800 ° C, protected with argon gas, and then cooled naturally.
[0021] There is no welding residual stress in the weld seam and near seam area of TC4 titanium alloy plate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com