Double-cladding optical fiber temperature sensor
A temperature sensor, double-clad optical fiber technology, used in thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that optical fiber temperature sensors cannot be widely used, cannot directly interpret sensing data, and demodulate signals. High cost , to achieve the effect of simple structure, flexible design and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
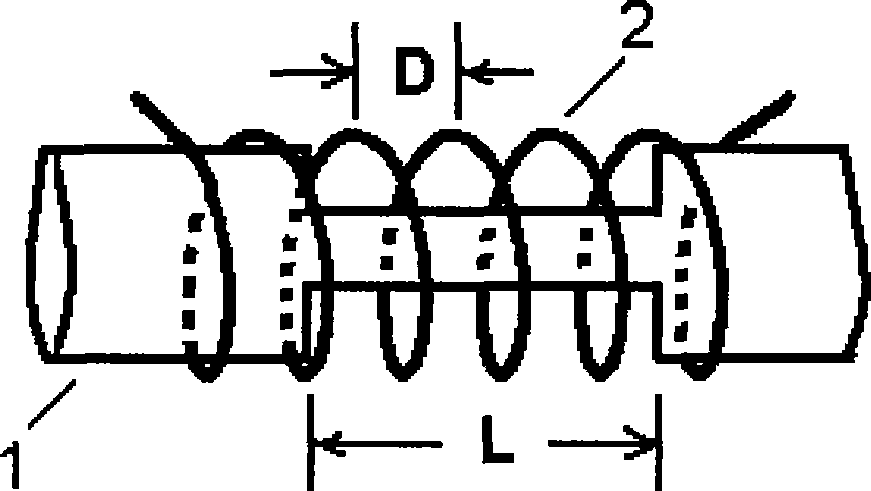
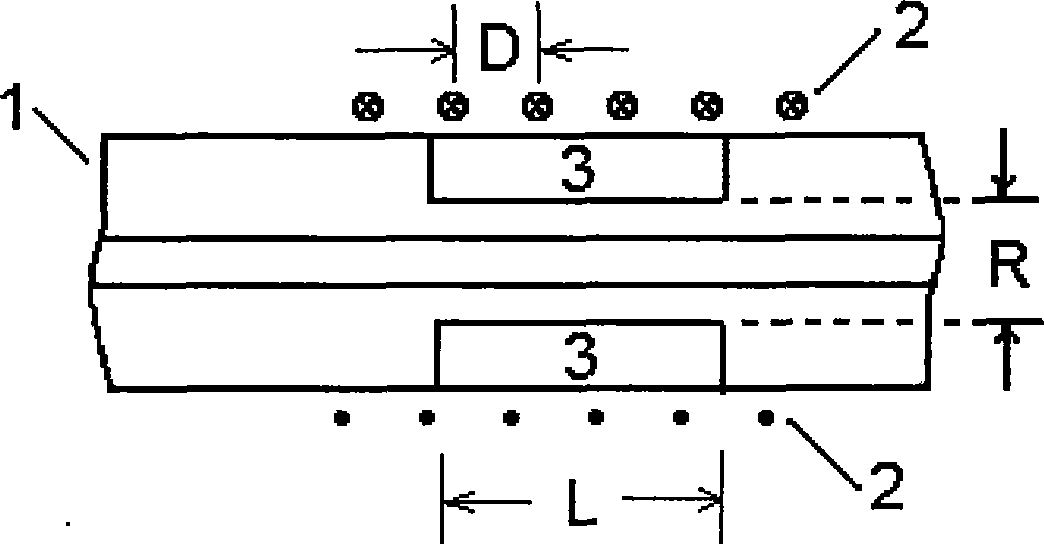
[0016] The structure of the present invention is as figure 1 and figure 2 shown by figure 1 and figure 2 It can be seen that the step-type optical fiber 1 adopts Corning SMF-28e. The length of the sensing section in the optical fiber 1 is L as shown in the figure, and the outer diameter of the inner cladding is R as shown in the figure. A metal wire with a diameter of 0.13mm is wound into a solenoid 2, the pitch D of which is 0.3mm, and its inner diameter is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the optical fiber 1, so that the optical fiber 1 can just pass through it, and its length is greater than L, which is taken in this embodiment 9mm. The outer cladding layer 3 is made of polymer material OE-4110 produced by Dow Corning Company. Its thermo-optic coefficient is equal to 0.0003, and its refractive index for a wavelength of 1554nm is 1.4600 at a temperature of 22°C. Using the table-top stabilized light source, table-top optical power meter, and digital electroni...
Embodiment 2~4
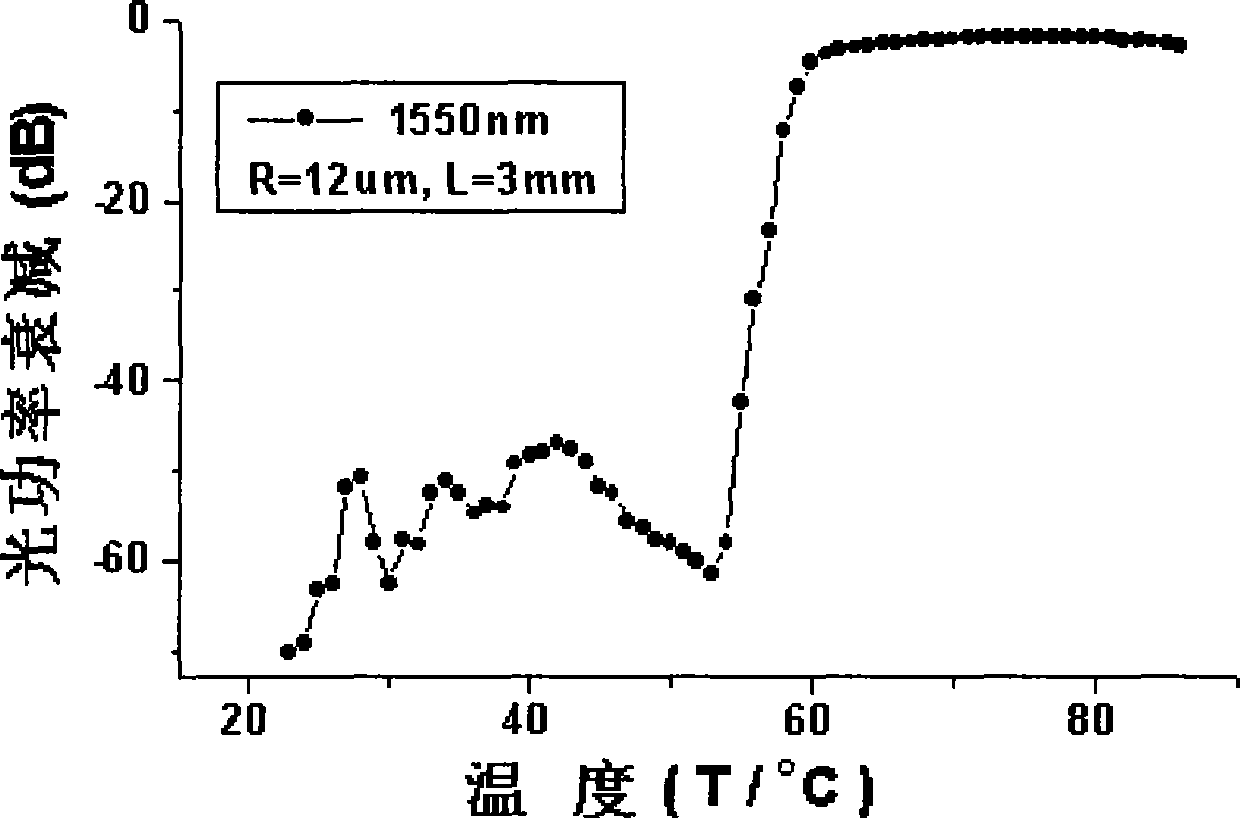
[0020] The difference from Example 1 is that the outer diameters of the inner cladding are respectively 13 μm, 16 μm and 20 μm, and the others are the same as in Example 1. The experimental curves of these 3 embodiments for the optical power loss of 1550nm wavelength as a function of temperature are shown in Figure 5 middle. The ranges of the steep loss change regions corresponding to Embodiments 2 to 4 are: -50dB, -43dB and -7dB respectively. From Figure 5 It can also be seen from the figure that the minimum optical power loss (ie, insertion loss) corresponding to Embodiments 2 to 4 are: -3.8dB, -1.7dB and -1.5dB, respectively. It can be seen from these two sets of data that the smaller the outer diameter of the inner cladding, the larger the range of the steep change region of optical power loss and the greater the insertion loss.
Embodiment 5
[0022] The difference from Example 1 is that the length of the sensing section is 5.6 mm, the outer diameter of the inner cladding is 13 μm, and the others are the same as in Example 1. The experimental curve of the sensor of this embodiment for the optical power loss of 1550nm wavelength as a function of temperature is shown in Figure 6 middle. The scope of the steep loss change region of this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 2. It can be seen that, when the length of the sensing section is changed from 3mm to 5.6mm, and other things are the same as in Embodiment 1, the range of loss variation remains unchanged.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com