Construction method and use of Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene expression library
A Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene expression technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problem of not reflecting the Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen, and achieve high throughput, low operation cost and high coverage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
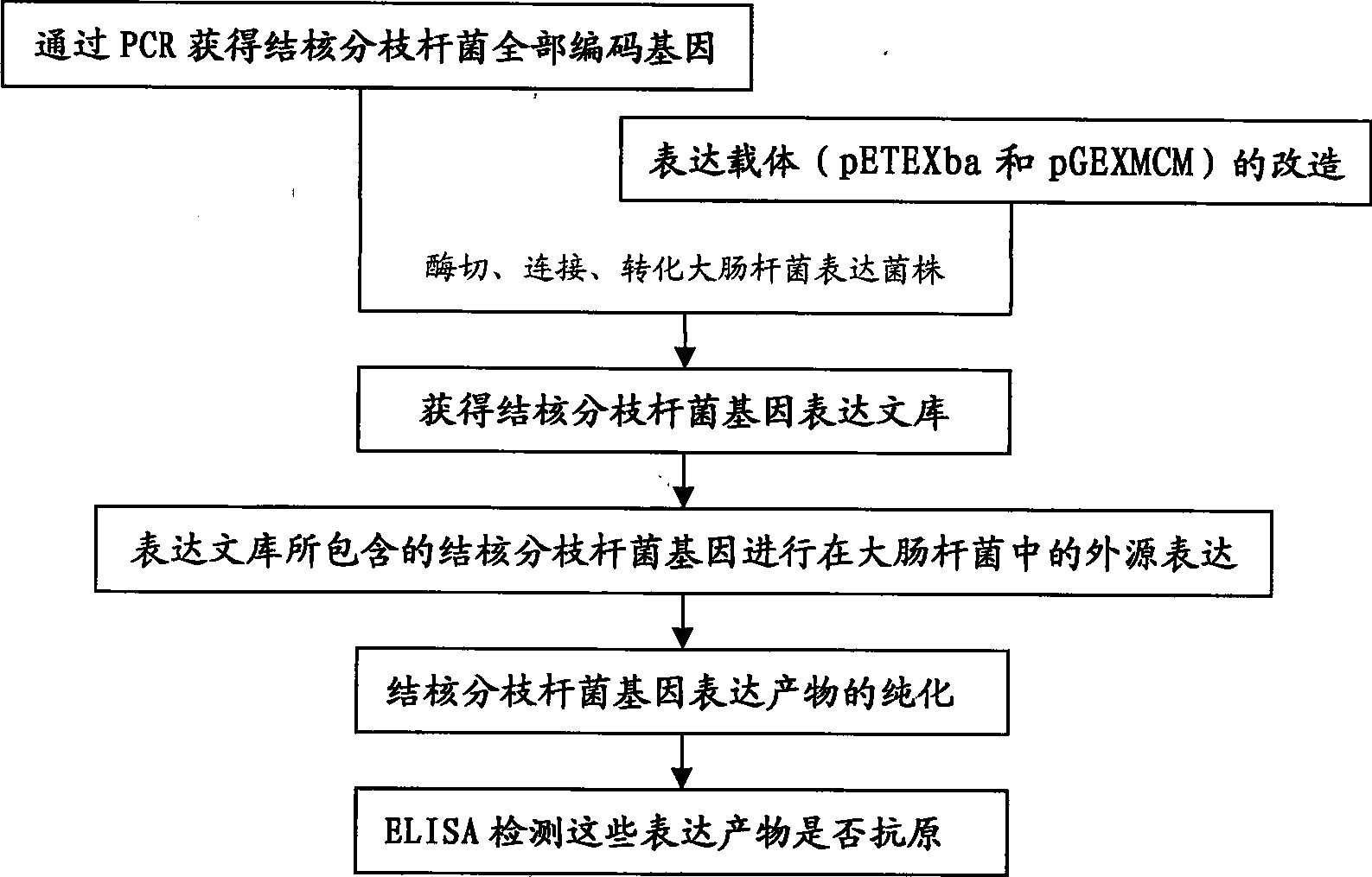
[0057] Embodiment 1: PCR amplification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene
[0058] Using the total genome DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (accession number: NC000962) as a template, the genome coding gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was amplified with primers designed according to the nucleic acid sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome provided by GenBank.
[0059] The primer design method of the coding gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: according to the restriction site inside the coding gene, select the restriction site combination that does not have inside the gene (EcoRI and XbaI, EcoRI and XhoI, NotI and XbaI, NotI and XhoI, BamHI and XhoI), take 20bp from the front and back of the coding gene to design primers, and adjust the GC content of the upstream and downstream primers to achieve consistency through the change of the terminal protection bases. The specific primers are as follows (taking 24 pairs of primers as an example):
[0060] R1325cf: A...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Embodiment 2: Transformation of expression vector pETEXba
[0116] (1) Eliminate the XbaI cleavage site on the commercially available pET28a (purchased from Novagen) vector by the method of end-filling modification (for specific methods, refer to the method of using T4DNA Polymerase of Takara Company), and obtain an intermediate vector named pET28a -△X;
[0117] (2) The intermediate vector pET28a-ΔX obtained in step (1) is digested with restriction endonucleases NdeI and XhoI;
[0118] (3) The cdc62 gene (Genebank ID: 1455035) of the extreme thermophilic archaea S. solfataricus was used as the first vector gene of the transformation vector. Amplified from the genome of the extreme thermophilic archaea S. solfataricus by PCR (forward primer 14bEcoR-f: GCGCGG CATATG A GAATTC ATGAGTGATATAATTGATGAG, reverse primer 14hEcoR-r: ATATGA CTCGAG TACTCCAGAGATCAGCAAACCT, the underline is the restriction site) obtained from the cdc62 gene fragment containing NdeI and XhoI rest...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Embodiment 3: Transformation of pGEX-4T-1 expression vector
[0126] (1) The mini-chromosome maintenance-like gene (mini-chromosome maintenance-likegene, MCM, Genebank ID: 1455038) of the extreme thermophilic archaea S. solfataricus was used as the original vector gene of the transformation vector. By PCR (forward primer Trgada-f: GAGC GAATTC GTTGGAAATTCCTAGTAAAC, reverse primer Adapter-r: GGATGG CTCGAG TCTAGACTAGACTTTTTGTAACAT, the underline is the restriction site) method to amplify the 2.0 kb MCM gene from the genome of the extreme thermophilic archaea S. solfataricus. Since there are two BamHI restriction endonuclease recognition sites inside the MCM, the fragment was fully digested with BamHI to form a fragment with a deletion of 844 bases. Subsequently, the fragment was treated by the end-filling modification method (for specific methods, refer to the T4DNA Polymerase usage method of Takara Company) to form a 1.2kb MCM mediator gene containing EcoRI and XhoI r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com