A group of antigen epitope polypeptide and uses thereof
A technology of antigenic epitopes and polypeptide chains, applied in the field of molecular immunology, can solve the problem of small differences in antigenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Overlapping polypeptide fusion expression series of JEV E protein antigen polypeptide fragments and indirect ELISA screening of JEV E protein B cell antigen epitopes
[0040] According to the amino acid sequence of the E protein of JEV (SA14-14-2 strain), a series of 50 peptides in total were designed. These polypeptides overlap each other and cover the region of 1-402 amino acid residues of the JEV E protein, which contains the E protein domain. I (Domain I) and domain II (Domain II). According to the amino acid sequence of each polypeptide, a pair of DNA chains are designed and synthesized, and the DNA chains are inserted into the expression vector pGEX-6p-1 and GST for fusion expression. The series of recombinant proteins expressed in fusion and anti-JEV serum were analyzed by indirect ELISA to analyze the epitope of JEV E protein. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0041] The specific process is as follows:
[0042] Design the polypeptide sequence→synthesize ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Location of core sequence of antigen epitope
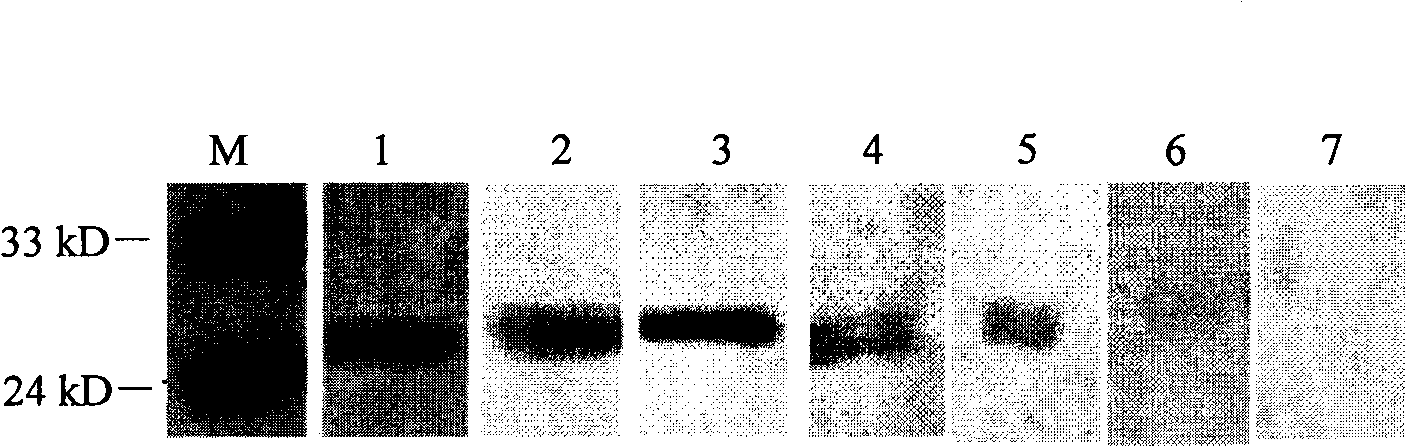
[0050] According to the preliminarily identified epitope sequence in Example 1, further design small fragment polypeptides, or design a series of polypeptides that are reduced by one amino acid residue from C-terminus to N-terminus and those that are reduced by one amino acid residue sequentially from N-terminus to C-terminus. A series of peptides were fused and expressed with JEV positive serum for Western blot analysis. The two ends were reduced to the point that the peptide fusion protein lost the ability to bind to JEV positive serum to determine the core sequence of the epitope. The reaction results are shown in Table 2.
[0051] Table 2 Indirect Western blot reaction results of peptide fusion protein and anti-JEV serum
[0052] serial number
Codename
GST fusion peptide sequence
Western blot test results
SEQ ID NO: 1
E1
FNCLGMGNRDFIEGAS
+++
SEQ ID NO: 51
E...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Mutation analysis of epitope core sequence
[0059] The epitope core sequence determined in Example 2 was compared with the E protein sequence of different strains of Japanese encephalitis and compared with the Meruo Valley Encephalitis Virus (MVEV), West Nile Virus (WNV), and Usutu Virus (Usutu Virrus, UV), Kunjin virus (Kunjin virus, KUN) and Dengue virus (Dengue Virus, DV) and other flavivirus E proteins were analyzed and compared by homology.
[0060] To compare the homology of the epitope core sequence determined in Example 2 with other viruses, first select short peptides of homologous sequences with a homology greater than 50%, which are SEQ ID NO: 64, SEQ ID NO: 95, SEQ ID NO :108 and SEQ ID NO: 124, after GST fusion expression, Western blot analysis of the reactivity with JEV positive serum, the reaction results are shown in Table 3.
[0061] Table 3 Western blot reaction results of peptide fusion protein and anti-JEV serum
[0062]
[0063]
[0064] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com