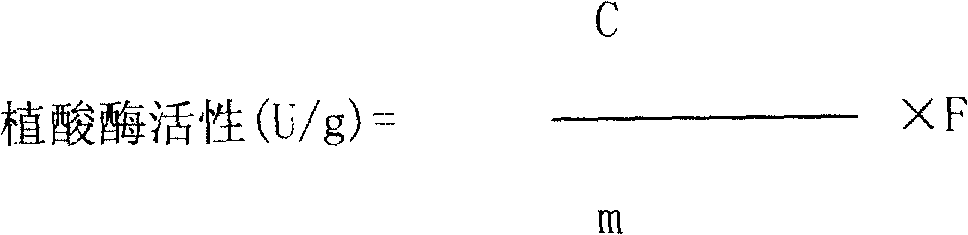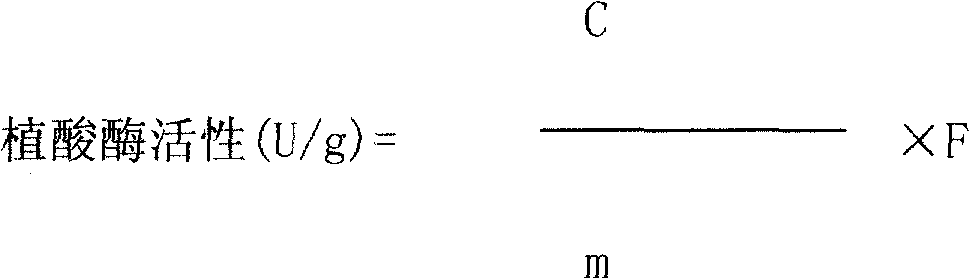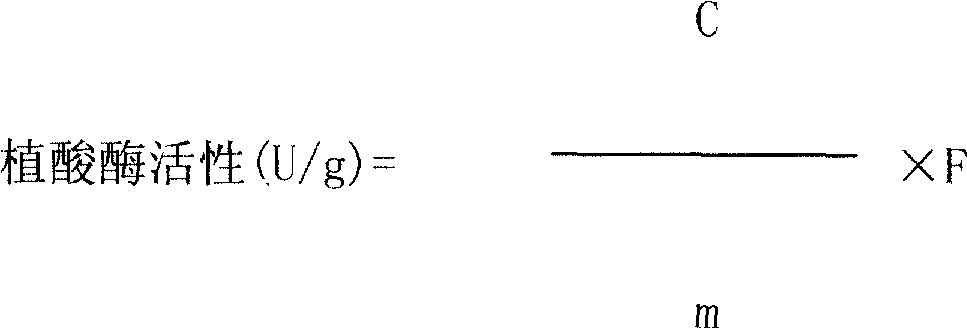Microdetermination method for phytase in feedstuff
A micro-measurement and phytase technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve problems such as low activity, large relative deviation of results, and complex components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0075] The present invention is illustrated below through a specific experimental determination process.
[0076] 1. Reagents and solutions
[0077] The reagents used in this standard refer to the third-grade water of analytical grade and in compliance with the provisions of GB / T6682, unless other requirements are specified.
[0078] 1.1 Acetate buffer I, CH 3 Concentration of COONa c=0.25mol / L: Weigh 34.02g of sodium acetate trihydrate into a 1000ml beaker, add 900ml of water and stir to dissolve, adjust the pH value to 5.00±0.01 with glacial acetic acid, then transfer to a 1000ml volumetric flask, and rinse with distilled water Make up to the mark. It is valid within 2 months when stored at room temperature.
[0079] 1.2 Acetate buffer II, CH 3 The concentration of COONa c=0.25mol / L: take 34.02g sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.5g bovine serum albumin (BSA) in a 1000ml beaker, add 900mL water and stir to dissolve, adjust the pH value to 5.00±0.01 with glacial acetic acid, T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com