Human body intestinal canal flora detection parting and quantitative reagent kit
A technology of intestinal flora and kits, which is applied in the fields of material stimulation analysis, microbial measurement/inspection, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult cultivation, no one is completely ideal, and inaccurate counting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
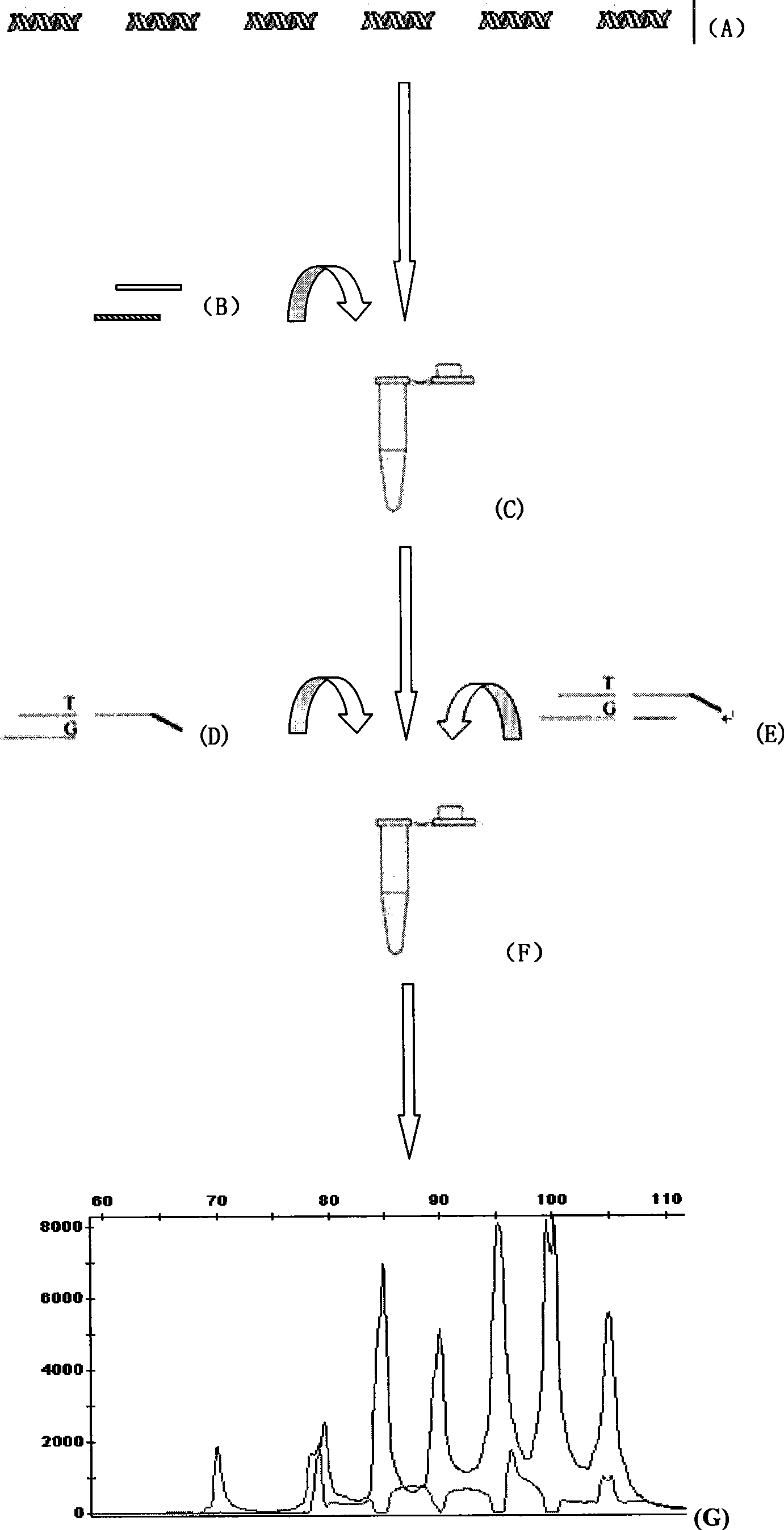
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Sample pretreatment and DNA extraction
[0072] experiment procedure:
[0073] (1) Pretreatment
[0074] Collect fresh fecal samples from healthy adults, each with a wet weight of about 4g, collect them in sterile plastic bags, and store them in a refrigerator at 4°C for no more than 12 hours. Add each stool sample into a test tube containing 6ml of sterile PBS buffer (0.05mol / L, pH7.4) and shake well for 5-10min, then centrifuge at 500rpm for 5min, and collect the supernatant. This step was repeated 3 times. Then the supernatant was centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 10 min, and the precipitate was collected and placed in an Eppendorf tube. The precipitate was suspended in 1 mL of double distilled water (ddH2O), and after mixing, it was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 5 min to collect the precipitate. The precipitate was dissolved in 200 μL of absolute ethanol (pre-cooled at -20°C), shaken and mixed, and then centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 2 minutes, and the supernatant was...
Embodiment 2
[0078] 16s rDNA universal primer, LDR and LCR probe design
[0079] experiment procedure:
[0080] The 16S rDNA sequence information of each bacterial genus was searched in Genebank, and more than 50 were found, and then compared together, the segments that were conserved at both ends and contained variable regions in the middle were found for design. In order to ensure the consistency of the PCR amplification efficiency and the specificity of the probes, the regions containing completely identical sequences at both ends and the intermediate variable regions with specific sequences for each bacterial genus were screened out. Universal primers were designed in the conserved regions at both ends to ensure that the primers were perfectly matched with the primer-binding sequences of each genus, and the specific sequences of each genus were compared in the middle variable region to design specific probes. In order to further ensure the consistency and effectiveness of the amplific...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Universal Primer Amplification of Standard DNA and Sample DNA
[0083] experiment procedure:
[0084] (1) The amplification system used for standard DNA and sample detection is the same.
[0085] (2) Universal primer: upstream, 5'-CAGGATTAGATACCCTGGTAGT-3'
[0086] Downstream, 5′-TTGCGCTCGTTGCGGGACTT-3′
[0087] (3) Amplification system (10 μL):
[0088] Upstream primer 0.5μmol / L
[0089] Downstream primer 0.5μmol / L
[0090] 10×Buffer 1×
[0091] dNTP 0.2mmol / L
[0092] Mg 2+ 2.0mmol / L
[0093] Taq polymerase 1U
[0094] Add water to 10 μL
[0095] (4) Amplification program:
[0096] 95℃15min
[0097] 94℃30s→55℃30s→72℃60s(40cycles)
[0098] 72℃7min
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com