Method for improving reproductive speed of microbial strain
A microbial strain and speed technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of increasing microbial strains and reducing the efficiency of decomposing organic matter, and achieving the effects of increasing efficiency, improving reproduction speed, and decomposing organic wastes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 microbial strain
[0039]The microbial strain selection of the present embodiment has the bacterial classification that has registration number in American Type Culture Center (American TypeCulture Centre, ATCC) and the bacterial classification on Canadian Civil Substance List (Canadian Domestic Substance List, DSL), with To ensure its safety, it specifically includes the following strains: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ATCC14579, Bacillus cereus ATCC14579, Bacillus circulans ATCC9500, Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 12713, Bacillus megaterium ATCC 14581, Bacillus polymyxa ATCC 842, Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051, Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 13525 and Pseudomonas putida ( Pseudomonas Putida) ATCC 12633.
[0040] The microbial strains of the present embodiment take wheat bran and seaweed as carriers, and the total number of colonies is 1×10 8 ~1×10 10 cfu / g.
Embodiment 2
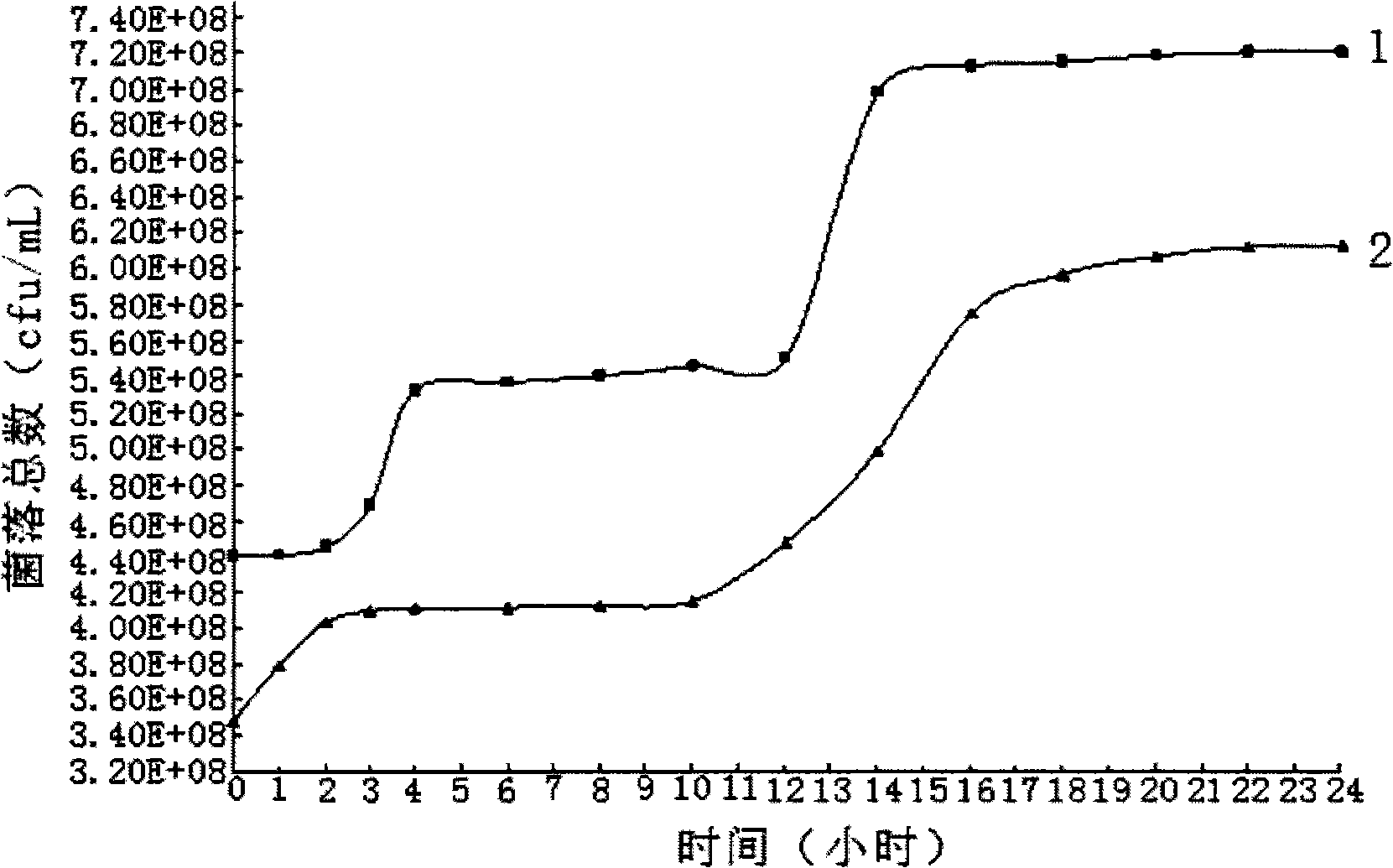
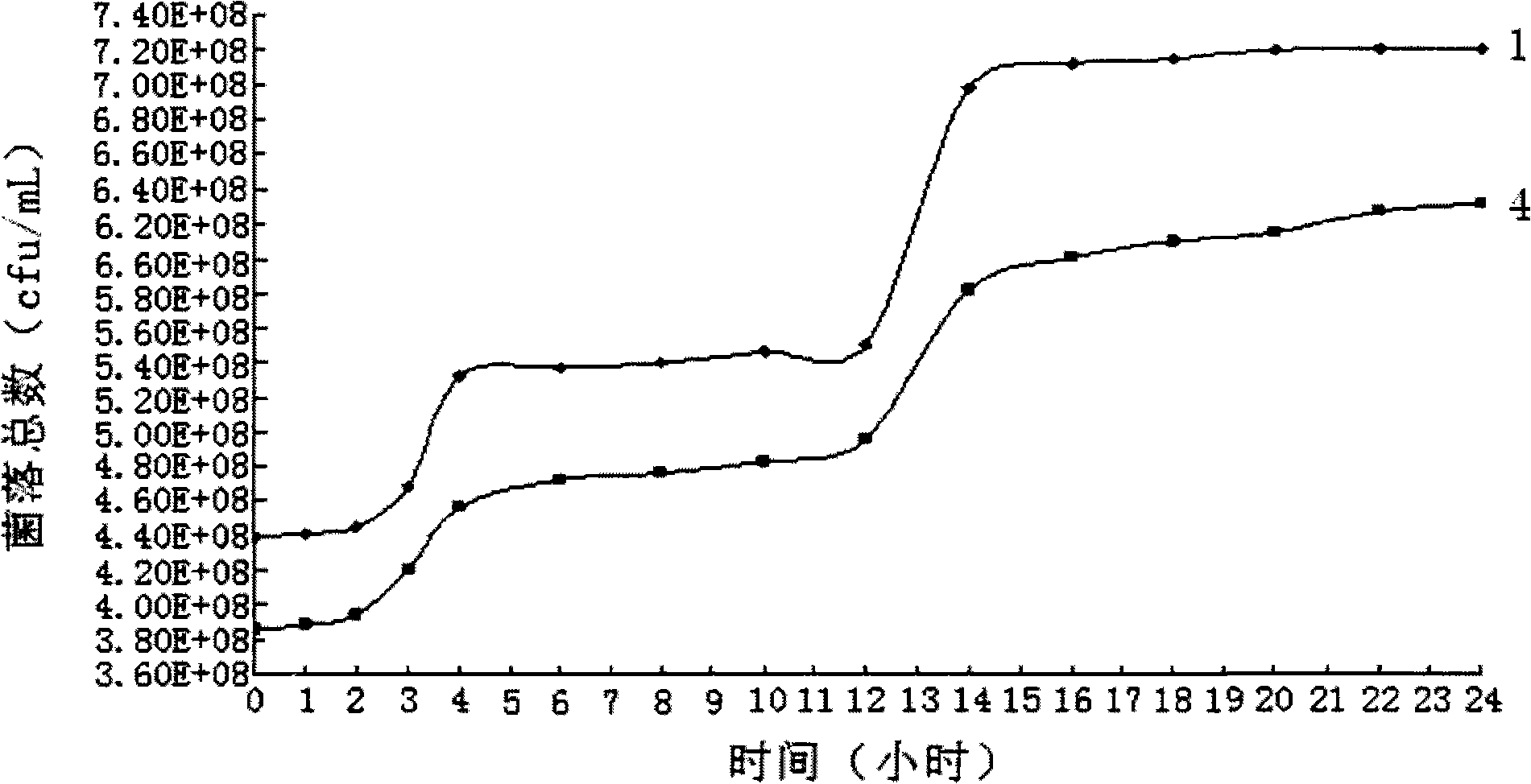
[0041] Embodiment 2 The propagation of microbial strains under the condition of containing Yucca extract and not containing Yucca extract respectively
[0042] In this embodiment, the yucca extract and humic acid are mixed together with the microbial strains in Example 1 for aerobic treatment. The yucca extract (wherein the steroid saponin mass percentage is 38.0%) is commercially available.
[0043] The specific operation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0044] (1) Weigh 10 mL of Yucca extract (wherein the steroid saponin is 3.8 g) and 3 g of humic acid are added to a 1000 mL beaker, then 990 mL of deionized water is added, and stirred evenly;
[0045] (2) Add the microbial strain of 10g embodiment 1 in the above-mentioned mixed solution, fully stir, and record as experimental group;
[0046] (3) Get another 1000mL beaker, add 1000mL deionized water to the inside, then add the microbial strain of 10g embodiment 1, fully stir, and record as the control group;
[00...
Embodiment 3
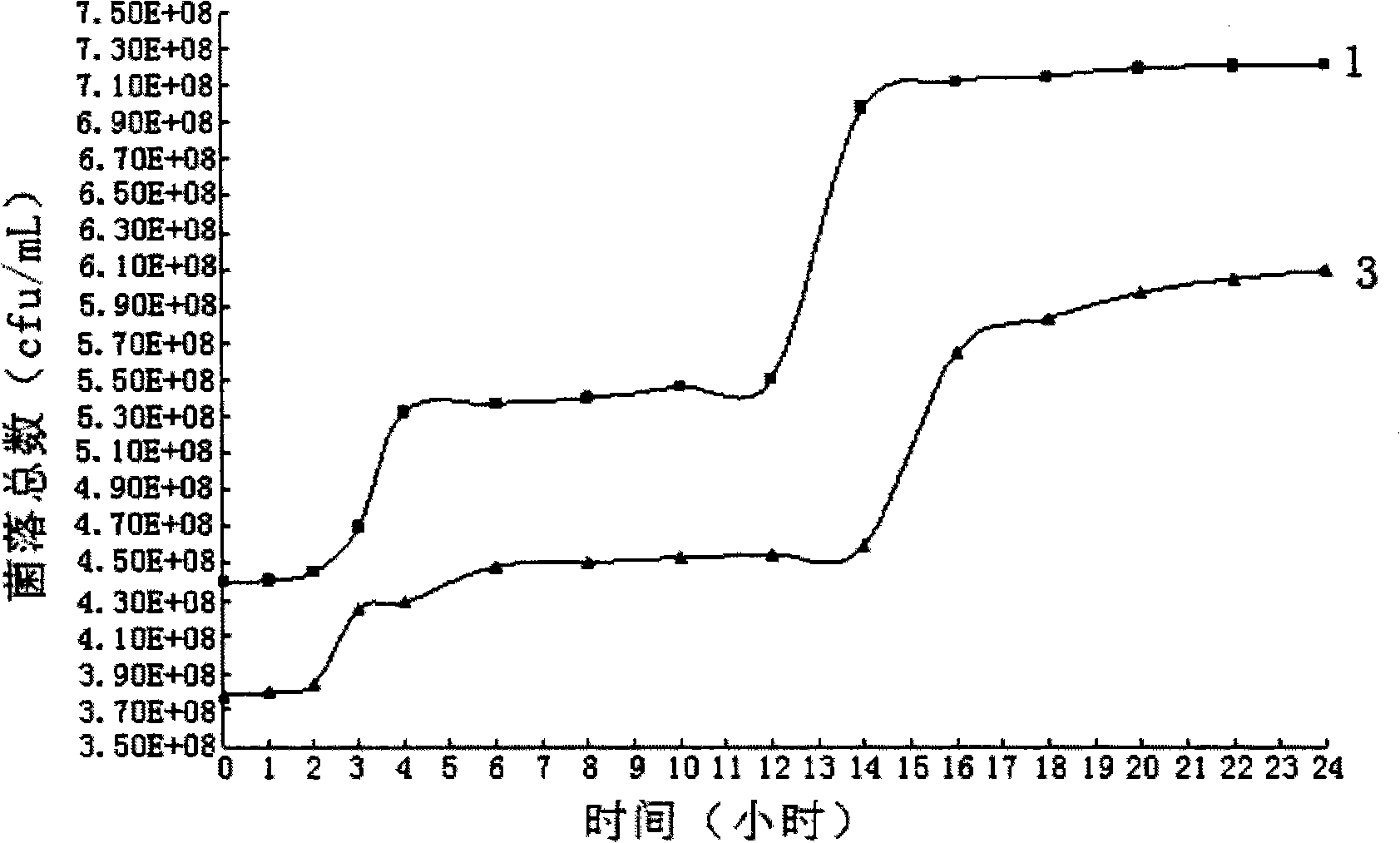
[0055] The reproduction of embodiment 3 microbial strains under aerobic / anaerobic state respectively
[0056] The present embodiment is divided into experimental group and control group, and experimental group adopts the experimental group prepared in embodiment 2, and its aerobic treatment is also with embodiment 2, and the preparation of control group is as follows:
[0057] (1) Weigh 10 mL of Yucca extract (wherein the steroid saponin is 3.8 g) and 3 g of humic acid are added to a 1000 mL beaker, then 990 mL of deionized water is added, and stirred evenly;
[0058] (2) Add the microbial strain of 10g embodiment 1 in above-mentioned mixed solution, fully stir, and record as control group;
[0059] (3) After the control group was stirred evenly, no aerobic treatment was carried out, and in the 24 hours when the experimental group was aerated, the control group remained in a static state;
[0060] (4) During the 24 hours when the experimental group was aerated, samples were t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com