Process and device for continuous ultrasound desulfurization of scrapped lead paste
A desulfurization process and desulfurization device technology, applied in the direction of dispersed particle separation, chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to meet the requirements of the results, poor operating environment, and influence on the stability of the operating process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
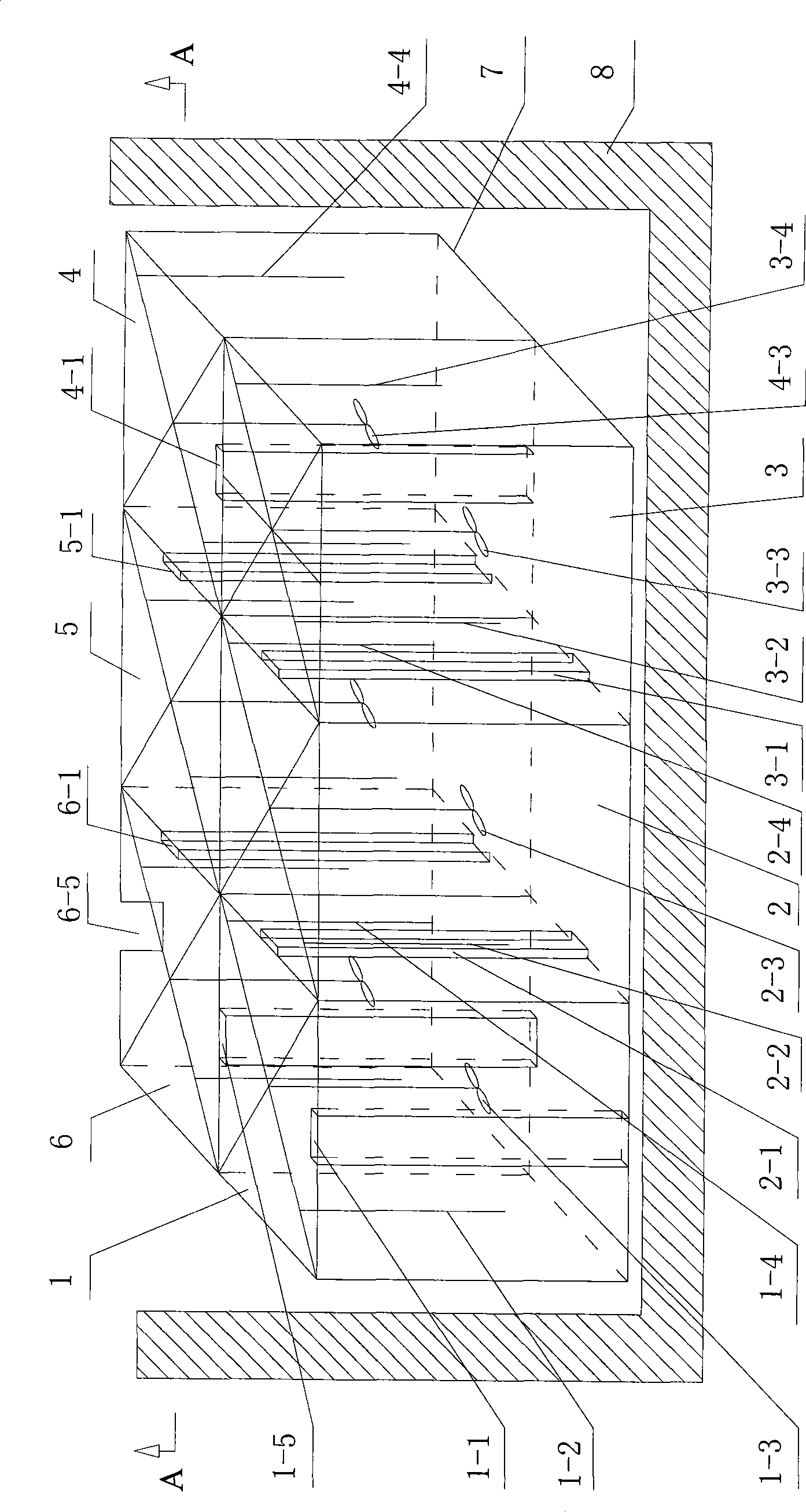
[0059] The continuous ultrasonic desulfurization process of waste lead plaster comprises the following steps:
[0060] 1). Take the waste lead plaster 1000g wherein the S content is 5.8% (mass) through determination, Na 2 CO 3 210g is continuously added in the waste lead plaster (the molar ratio of Na ions to S ions is 2.2:1);
[0061] 2). First, according to the Na ion: S ion ratio of 1.3:1, take Na 2 CO 3 (the remaining Na 2 CO 3 Add to each reaction chamber in batches); waste lead plaster, Na 2 CO 3 Together with water, make a fluid slurry with solid-liquid weight ratio S / L=3 / 4 in the pulping tank;
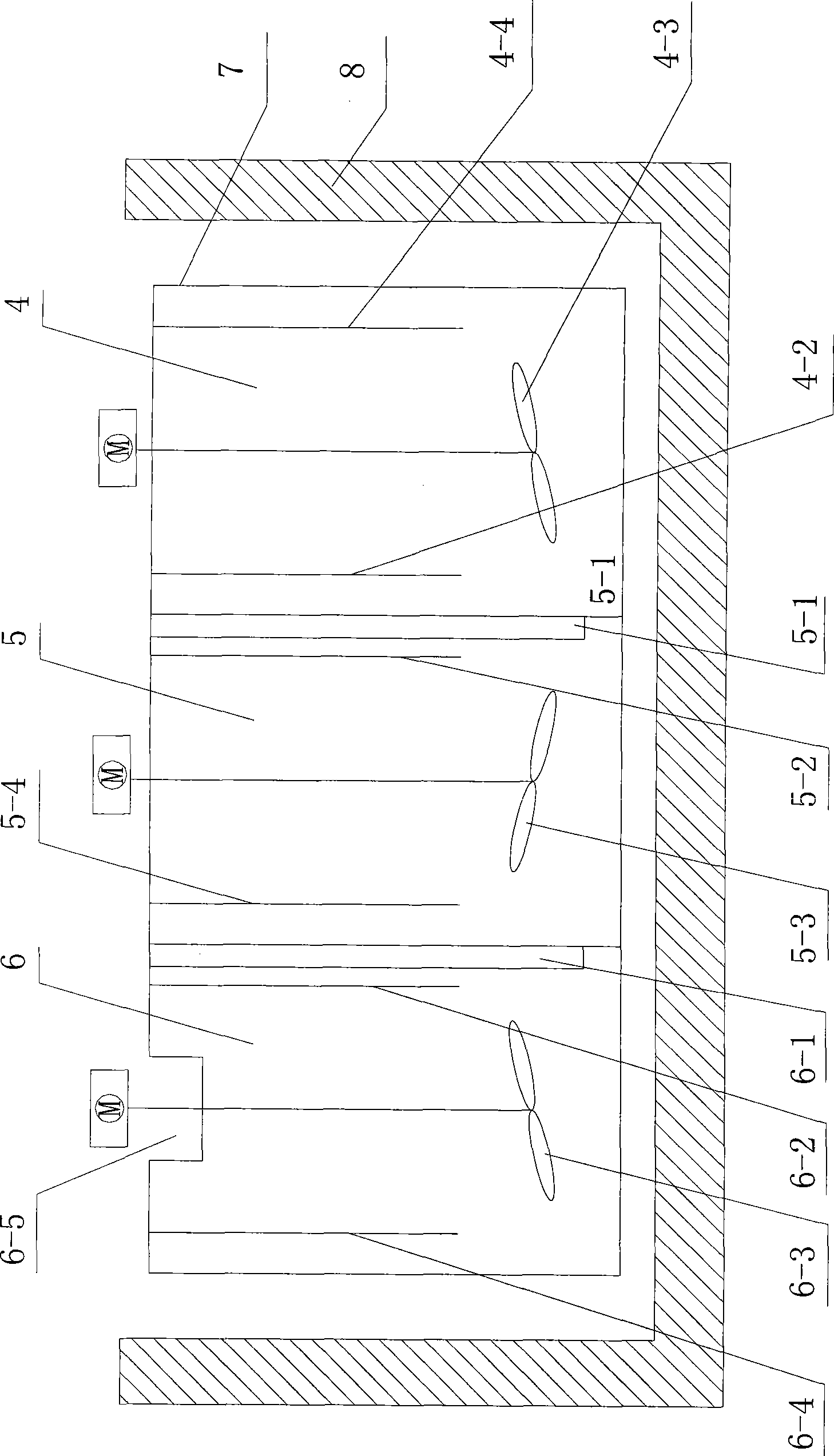
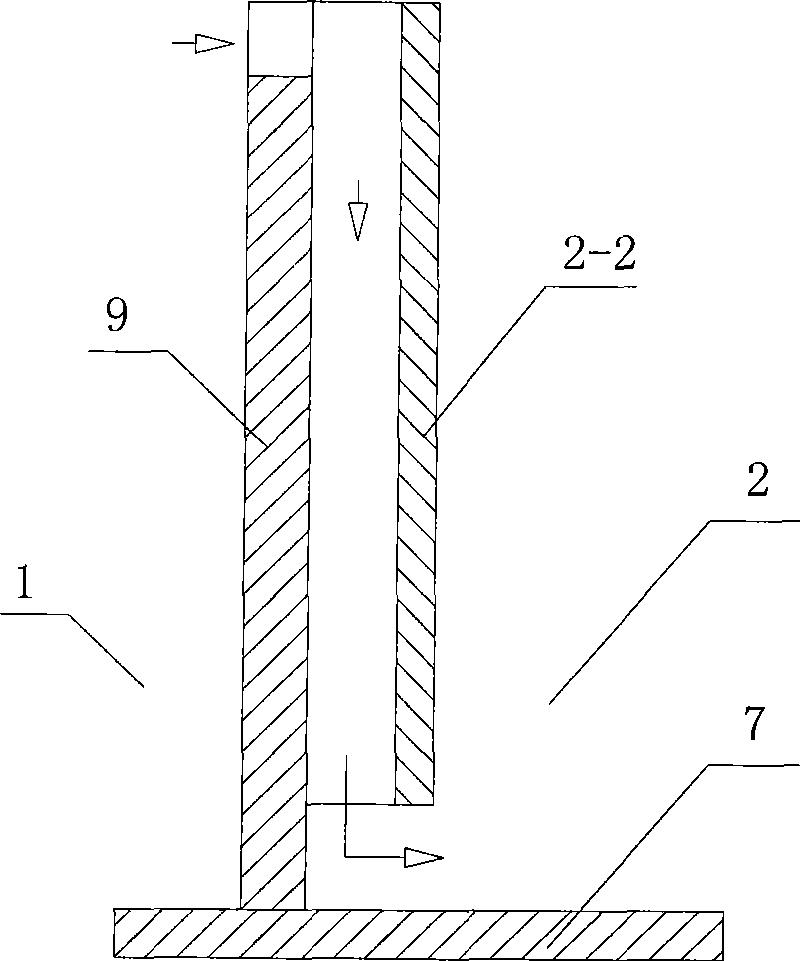
[0062] 3). Under the condition of ultrasonic waves, the fluid slurry enters the first reaction chamber from the lower end of the first reaction chamber (or called the first reaction tank) to heat and stir;
[0063] Then it is discharged from the overflow port of the upper end of the first reaction chamber, and enters the second reaction chamber from the lower end of th...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The continuous ultrasonic desulfurization process of waste lead plaster comprises the following steps:
[0077] 1). Get 1000g of waste lead plaster where the S content is 5.8% (mass) after measuring, add Na continuously in the continuous reactor 2 CO 3 200g (the molar ratio of Na ions to S ions is 2.07:1);
[0078] 2). First, according to the Na ion: S ion ratio of 1.4:1, take Na 2 CO 3 (the remaining Na 2 CO 3 Add to each reaction chamber in batches); waste lead plaster and Na 2 CO 3 Together with water, make a fluid slurry with a solid-liquid weight ratio S / L=0.7 in a pulping tank;
[0079] 3). Under the condition of ultrasonic waves, the fluid slurry enters the first reaction chamber from the lower end of the first reaction chamber to heat and stir;
[0080] Then it is discharged from the overflow port of the upper end of the first reaction chamber, and enters the second reaction chamber from the lower end of the second reaction chamber to heat and stir;
[...
Embodiment 3
[0093] The continuous ultrasonic desulfurization process of waste lead plaster comprises the following steps:
[0094] 1). Get 1000g of waste lead plaster where the S content is 5.8% (mass) after measuring, add Na continuously in the continuous reactor 2 CO 3 180g (the molar ratio of Na ions to S ions is 1.87:1);
[0095] 2). First, according to the Na ion: S ion ratio of 1.3:1, take Na 2 CO 3 (the remaining Na 2 CO 3 Add to each reaction chamber in batches); waste lead plaster and Na 2 CO 3 Together with water, make fluid slurry with solid-liquid weight ratio S / L=2 / 3 in the pulping tank;
[0096] 3). Under the condition of ultrasonic waves, the fluid slurry enters the first reaction chamber from the lower end of the first reaction chamber to heat and stir;
[0097] Then it is discharged from the overflow port of the upper end of the first reaction chamber, and enters the second reaction chamber from the lower end of the second reaction chamber to heat and stir;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com