Method for generating high-frequency ultrasonic waves based on dielectric body superlattice
A high-frequency ultrasonic and superlattice technology, applied in the directions of sound-producing instruments, fluids using vibration, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as ineffective separation, and achieve convenient multi-frequency multi-directional ultrasonic output, easy impedance matching, and simple structure. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Fabrication of electroacoustic transducing media using tetragonal structural acoustic superlattice (cutting LiTaO in the z direction 3 example). A layer of uniform gold or silver electrodes is prepared respectively on the upper and lower x-y surfaces of the crystal by coating, vapor deposition or ion sputtering. Connect to the network analyzer, measure the reflection coefficient of the sample under the z-direction alternating electric field (this coefficient is related to the resonance frequency), follow the instructions attached Figure 4 , to get a series of reflection peaks, the appearance of each peak corresponds to a reciprocal lattice vector of a specification, the reflection intensity can represent the resonance intensity, and the frequency is the frequency of the excited ultrasonic wave.
Embodiment 2
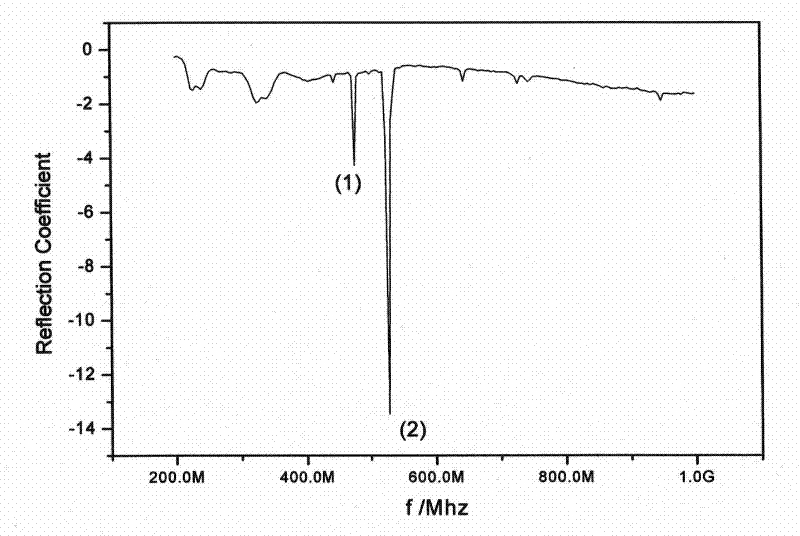
[0033] Fabrication of electroacoustic transducing media using tetragonal structural acoustic superlattice (cutting LiTaO in the z direction 3 example). The difference from Example 1 is that a layer of uniform gold or silver electrodes is prepared on two opposite y-z surfaces of the crystal by coating, vapor deposition or ion sputtering respectively. Connect to the network analyzer, measure the reflection coefficient of the sample under the x-direction alternating electric field (this coefficient is related to the resonance frequency), follow the instructions attached figure 2 , it can be observed that the ultrasonic waves excited by the x-direction reciprocal lattice vector have the greatest intensity under the x-direction electric field.
Embodiment 3
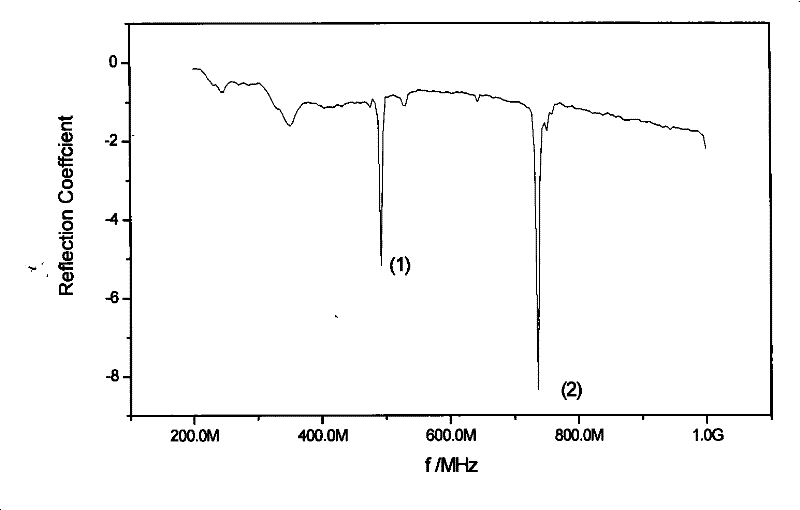
[0035] Fabrication of electroacoustic transducing media using tetragonal structural acoustic superlattice (cutting LiTaO in the z direction 3example). The difference from examples 1 and 2 is that a layer of uniform gold or silver electrodes is prepared on two opposite x-z surfaces of the crystal by coating, evaporation or ion sputtering respectively. Connect to the network analyzer, measure the reflection coefficient of the sample under the y-direction alternating electric field (this coefficient is related to the resonance frequency), follow the instructions attached image 3 , it can be observed that the ultrasonic waves excited by the reciprocal lattice vector in the y direction have the greatest intensity under the alternating electric field in the y direction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com