Method for removing heavy metallic salt in industrial wastewater by utilizing shells
A technology for industrial wastewater and heavy metal salts, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor resistance to the impact of running water and easy loss, unsolved metal recovery methods, and difficult desorption of adsorbed metals. , to achieve the effect of short adsorption time, good natural sedimentation performance and good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
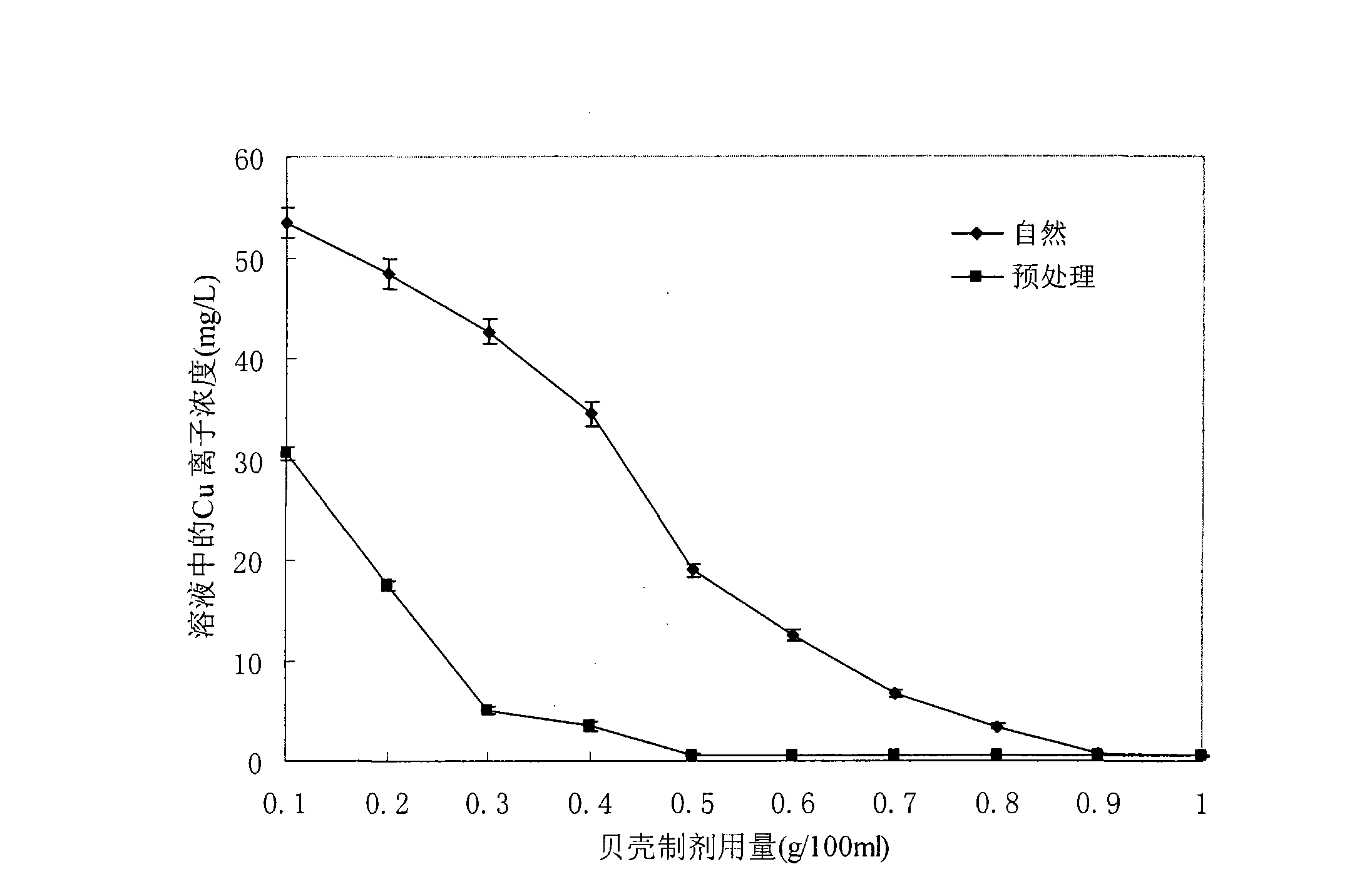
[0029] Embodiment 1: shell preparation consumption is to Cu 2+ Remove the effect of the effect
[0030] Generally, the experimental steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) 100mL initial Cu 2+ Cu with a concentration of 100mg / L 2+ The heavy metal salt solution (initial pH 5) was placed in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and a certain amount of shell preparation (see figure 1 ), at 32°C for 2 hours on a 200rpm shaker.
[0032] (2) Remove the adsorbed solution from the Erlenmeyer flask, pour it into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4800 rpm for 5 minutes (Beckman centrifuge, Germany), and take the supernatant.
[0033] (3) adopt the standard method of Perkin-Elmer Company to measure residual Cu with atomic absorption instrument (Beijing General Analysis General, TAS-990) 2+ concentration.
[0034] (4) With the "National Standard Sewage Comprehensive Discharge Standard of the People's Republic of China" (GB8978-1996) (see Table 1 below) as a reference standard, it is judged that the di...
Embodiment 2
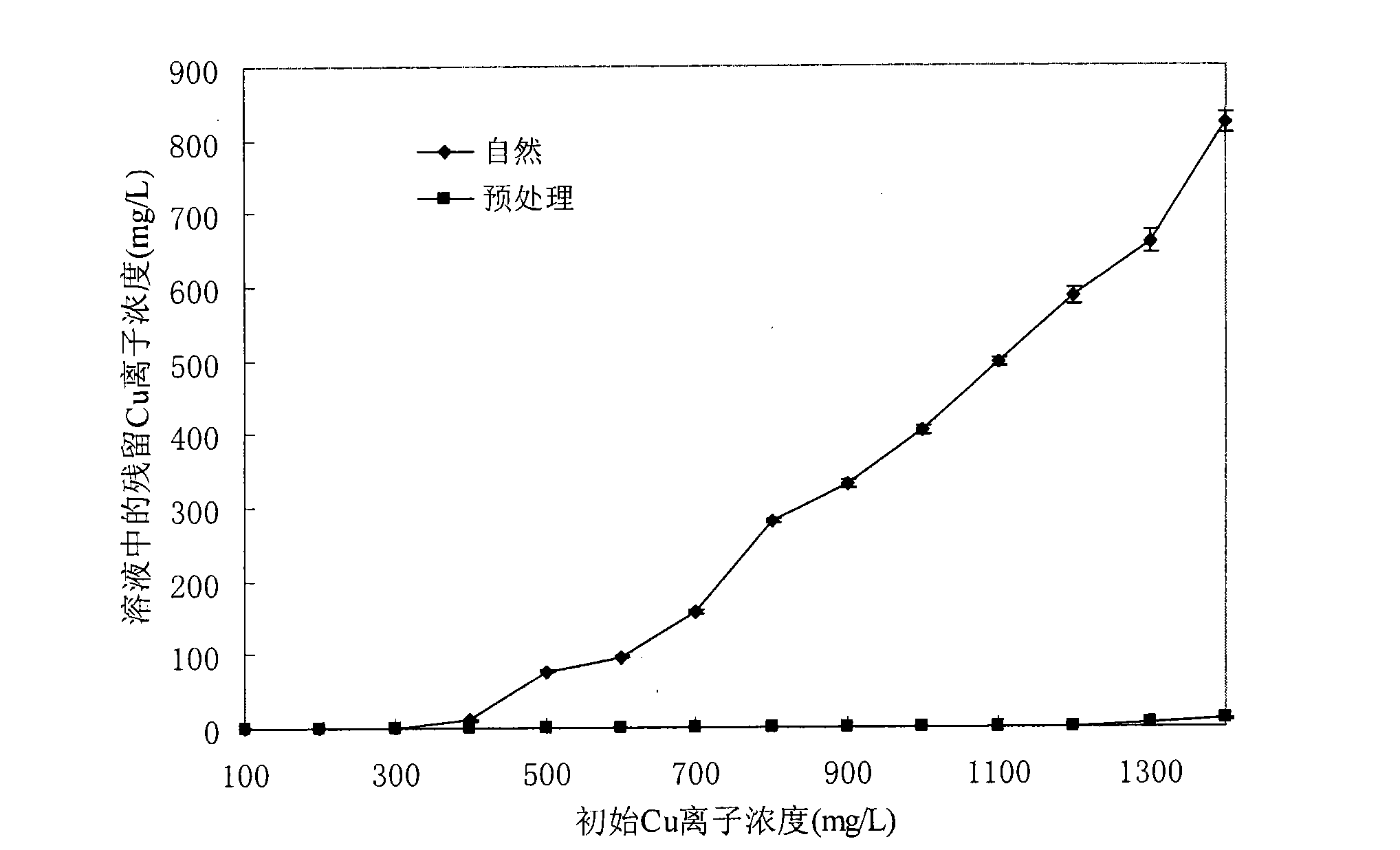
[0039] Example 2: Solution initial Cu 2+ Concentration vs. Cu 2+ Remove the effect of the effect
[0040] see figure 2 , in the detection solution the initial Cu 2+ Concentration on the removal of Cu by shell preparation 2+ In the experiment of the influence of effect, the consumption of natural shell preparation (◆) and pretreatment shell preparation (■) is 1g / 100ml, and the solution initial Cu 2+ The concentration was gradually increased, the initial pH of the solution was 5, and the solution was adsorbed on a shaking table for 2 hours at 32°C. Other experimental conditions were the same as those in Example 1. With the initial Cu 2+ When the concentration increases from 100mg / L to 400mg / L, the removal effect of natural shells can reach the national secondary emission standard for copper. When the initial Cu 2+ Concentration increased more than 400mg / L, the removal effect of natural shell preparations decreased significantly, and the residual Cu in the solution 2+ Th...
Embodiment 3
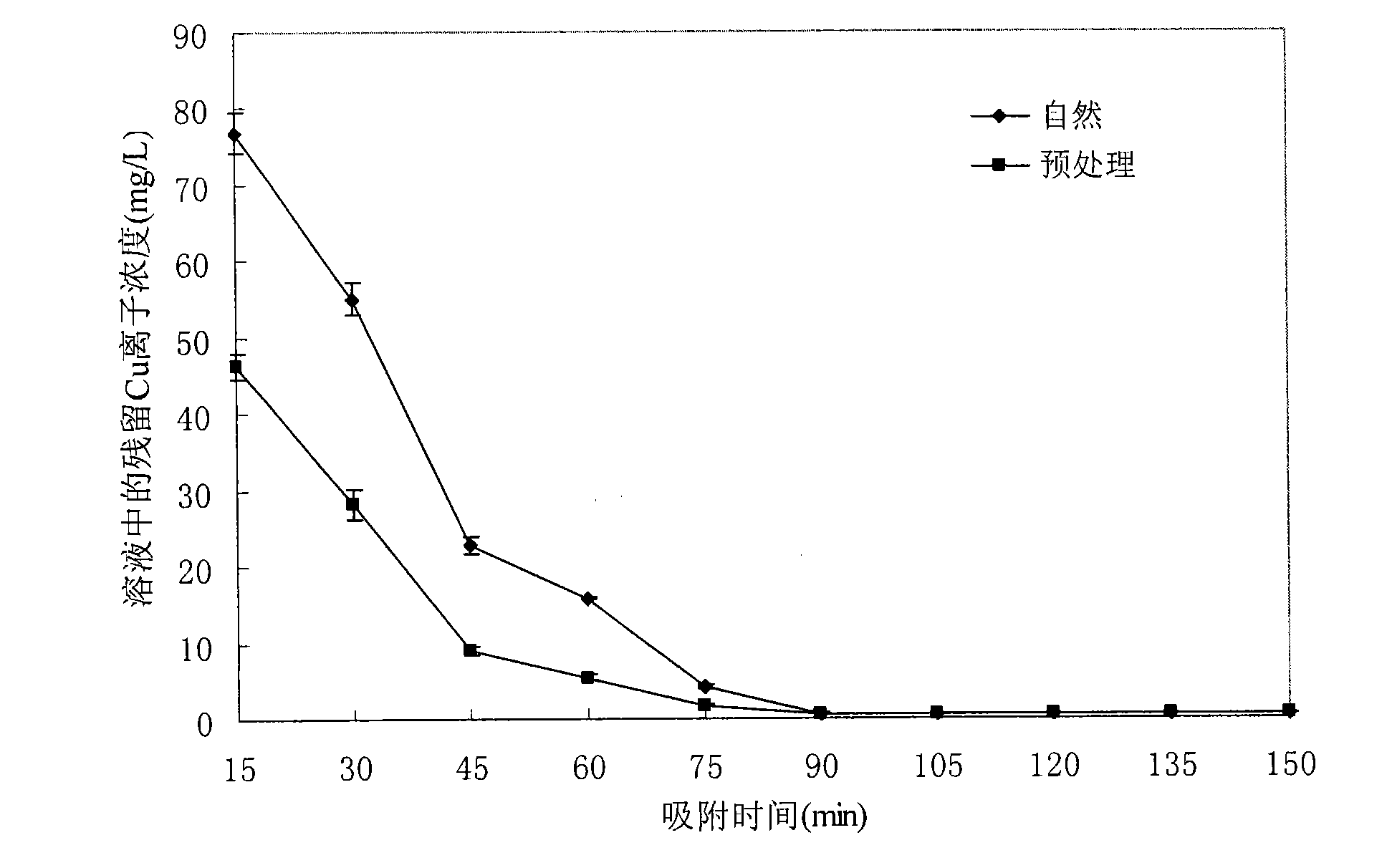
[0041] Example 3: Adsorption time on Cu 2+ Remove the effect of the effect
[0042] see image 3 , removal of Cu from shell preparations at detection of adsorption time 2+ In the experiment of the influence of the effect, the dosage of the natural shell preparation (◆) and the pretreatment shell preparation (■) are both 1g / 100ml, the initial pH of the solution is 5, and the initial Cu in the solution 2+ The concentration is 100mg / L, 32°C shaker adsorption, the adsorption time is from 15 minutes to 150 minutes, and the residual Cu in the solution is detected every 15 minutes 2+ Concentration, other experimental conditions are all identical with the experimental conditions of embodiment 1.
[0043]With the extension of adsorption time, the removal effect increased significantly. After the pretreatment shell preparation is adsorbed for 75 minutes, the removal effect can reach the national secondary emission standard for copper. However, no matter pretreatment or natural shel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com