Glyoxalation of vinylamide polymer
A technology of vinyl amide and polyvinyl amide, applied in paper, textile and papermaking, non-fibrous pulp addition, etc., can solve problems such as limited application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
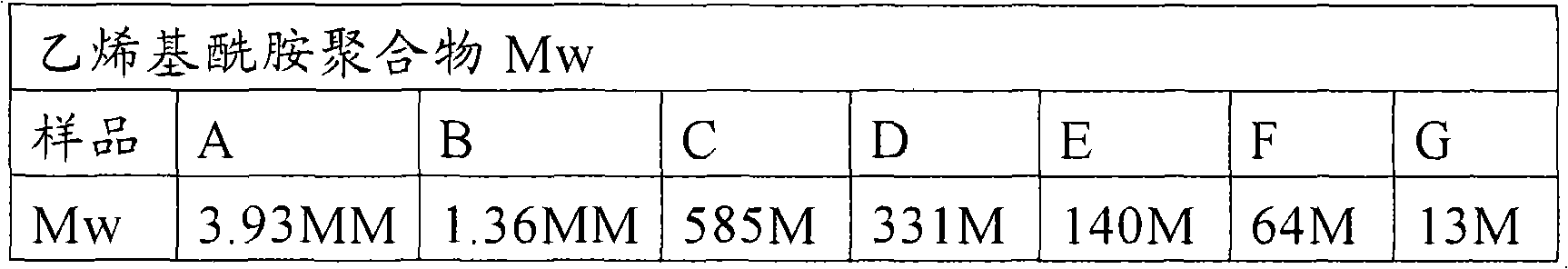
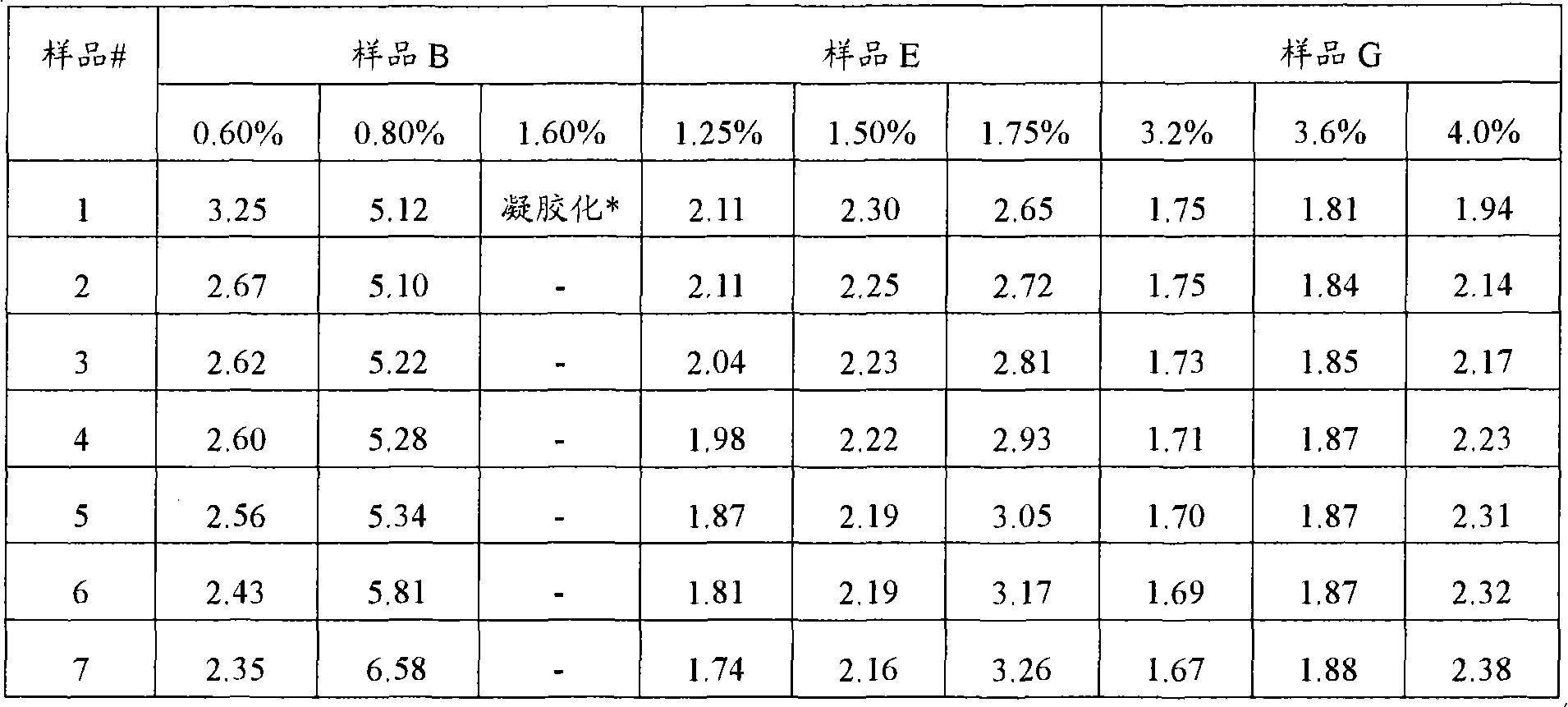
[0143] Determination of critical concentration of polyvinylamide with different Mw
[0144] A set of seven identical vinylamide polymers with different weight average molecular weights were synthesized. The seven polymers are all copolymers of 90% by weight acrylamide and 10% by weight DADMAC. The weight average molecular weights of these seven polymers are shown in the table below.
[0145] Samples A, B, C and D were synthesized by heterogeneous suspension polymerization, and samples E, F and G were synthesized by aqueous solution polymerization.
[0146] The average molecular weight of samples A and B was measured using a DAWN multi-angle light scattering detector with a combined differential refractive index detector. In light scattering experiments, the amount of light scattered at a given angle is proportional to the weight-average molar mass and concentration. A secondary Zimm plot was used to generate molar mass data at a dn / dc (specific refractive index gain) value ...
Embodiment 1
[0183] A vinylamide polymer having a Mw of 100,000 formed from acrylamide and diallyldimethylammonium chloride in a 90 / 10 weight ratio was glyoxalated according to the invention. The glyoxalation reaction was carried out at 2 wt% solids with a concentration of about 1.7 wt% vinylamide polymer. The molar ratio of amide:glyoxal for the glyoxalation reaction is 4:1. The initial viscosity before glyoxalation was 4.05 cp. The viscosity after glyoxalation was 4.75 cp. The reaction was followed by monitoring turbidity. The starting turbidity was 4.4 NTU and the final turbidity was 13.1 NTU.
Embodiment 2
[0185] Example 2 is a glyoxalated polyvinylamide sold under the name BAYSTRENGTH 3000.
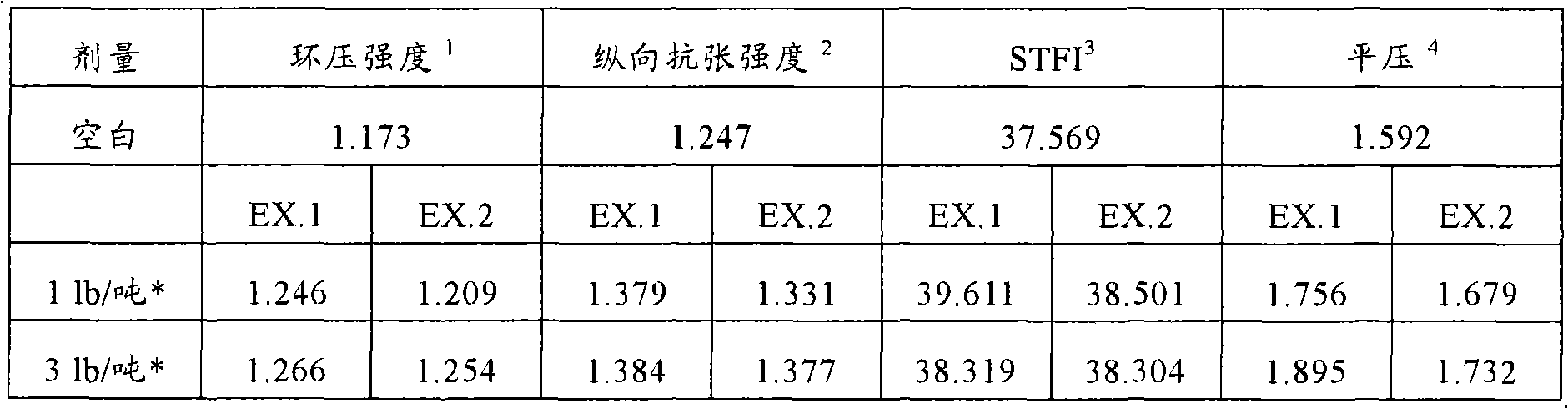
[0186] In order to demonstrate the effect of the glyoxalated product produced by the process of the present invention (Example 5) relative to the known glyoxalated vinyl amide polymer (Example 6), the two products were evaluated as dry strength The agent was applied to the paper furnish and resulted in the paper properties measured in Table 6 below.
[0187] The paper was produced on a 2-ply fourdrinier paper machine (15% top ply: 85% bottom ply) with Bellbond at a reel speed of 2100 ft / min. The furnish was 80% Kraft fibres, 20% OCC, 1% solids, furnish loading approximately 350 meq / l, conductivity 3000 microSiemens and pH 5.1 in the headbox.
[0188] Before the mixing paddle pump, the glyoxalated vinyl amide polymer (embodiment 1) and the conventional glyoxalated vinyl amide polymer (comparative example 2) formed by the inventive method were respectively added to In ingredients in thin s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com