Worm body membrane bound short peptide ZL-4 with specific target and anti-schistosome function and application thereof
An anti-schistosomiasis, membrane-bound technology, applied in the application, resistance to vector-borne diseases, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of unsafe use, toxic effects, low concentration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
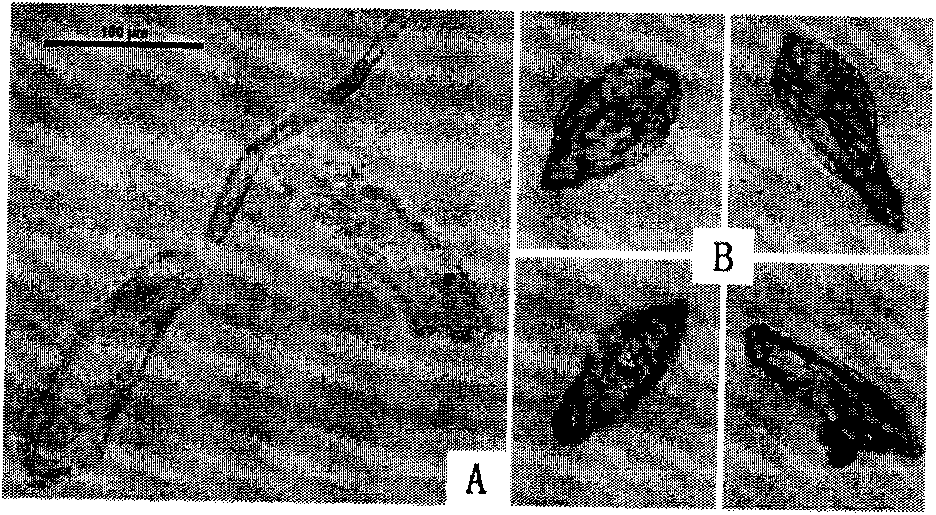
[0029] Embodiment 1: the screening of short peptide ZL-4 molecule
[0030] Differential panning of live worms of Schistosoma japonicum with random 12 peptide library of commercial phage: release and collect cercariae from Schistosoma-positive oncomelania snails according to conventional methods, wash aseptically, and divide into two parts: one part is used for reverse adsorption peptide library ; The other was prepared by repeated aspiration with a 6-gauge needle syringe to prepare mechanically decapitated larvae for panning peptide libraries. Panning method: first take 5.7×10 10 pfu phage and 500±20 cercariae were added to a 15ml test tube and shaken at 37°C for 150min, centrifuged to collect the phage supernatant that did not bind to the cercariae, and then washed by TBS-T centrifugation for 10 times to discard the unbound phage, and then used The bound phages were collected by PEG / NaCl precipitation, and 2 μl of infected Escherichia coli was taken for abundance determinati...
Embodiment 2
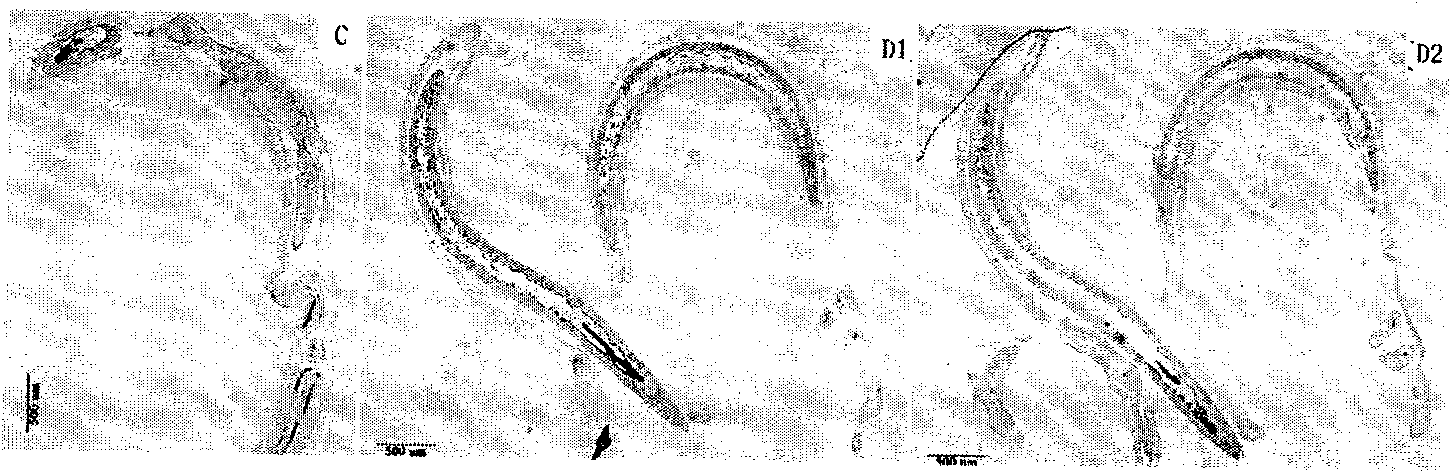
[0033] Example 2: Specific binding and insect resistance of short peptide ZL-4
[0034] 1. Proving that ZL-4 specifically binds to schistosomiasis, the following methods are used.
[0035] 1. Detection of the specific binding ability of ZL-4 molecule and schistosomiasis off-tailed juvenile worm: Experimental comparison proves that ZL-6, ZL-4 and ZL-1 molecular phage clones and M13KE (phage standard control) and schistosome off-tailed live Specific binding ability of juvenile worms: method: take Schistosoma japonicum cercariae, mechanically remove tails, count worms, divide them into 1, 2, 3, 4 tubes (about 500 tailed larvae in each tube), add ZL- 6. For the phages of ZL-4, ZL-1 and M13KE, shake gently at 37°C for 2 hours, then centrifuge to discard the supernatant, collect the worms and wash them with TBS-T for 10 times to discard unbound phages, and then use The bound phages were collected by PEG / NaCl precipitation, and 2 μl of infected Escherichia coli was taken for abundan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com