Fault line selection method for resonant grounded power distribution system by pattern spectrum
A technology of power grid fault and line selection method, which is applied in the direction of fault location, electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., and can solve problems such as unsatisfactory line selection effect, low voltage level, and low desire for line selection protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
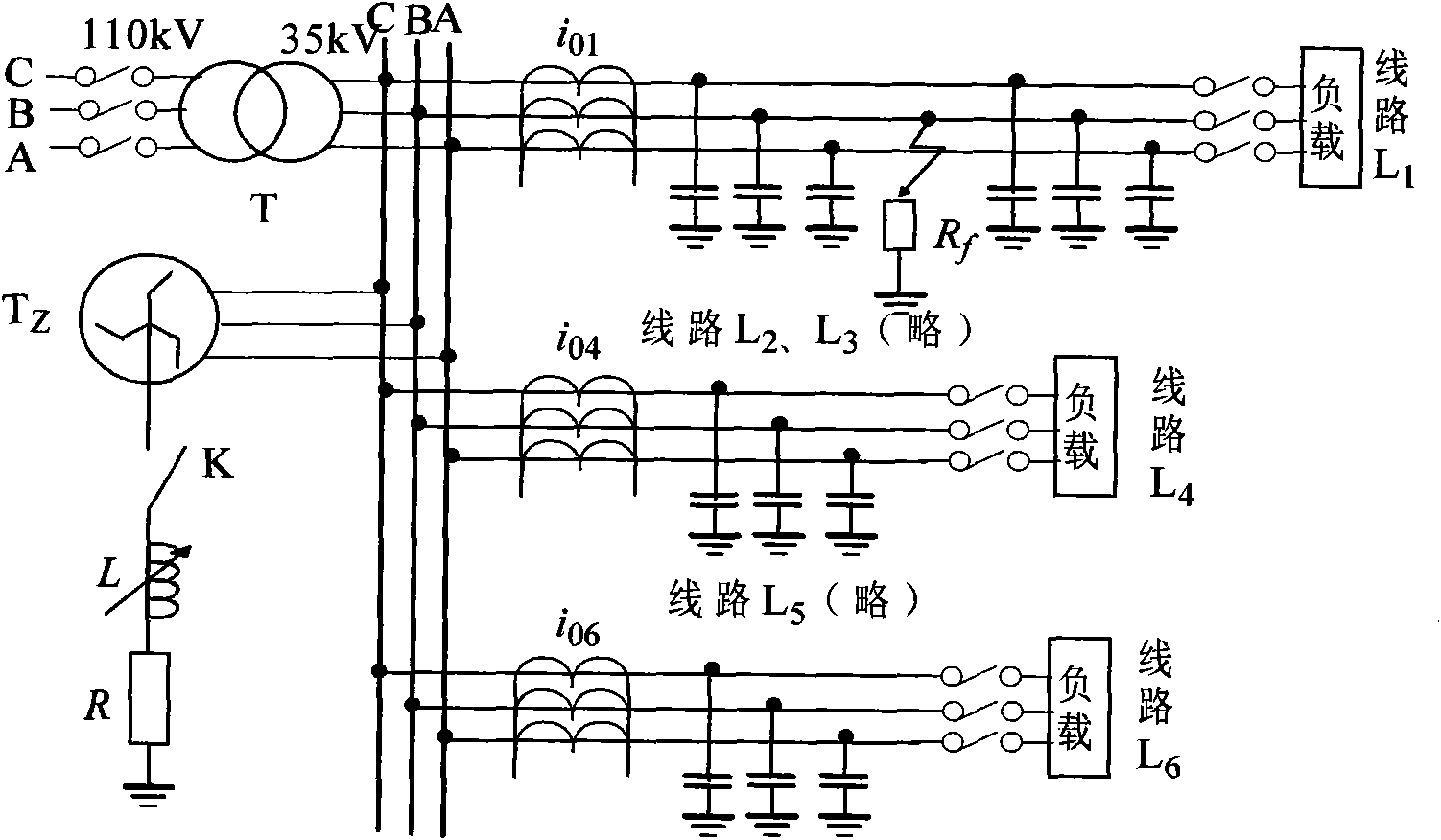
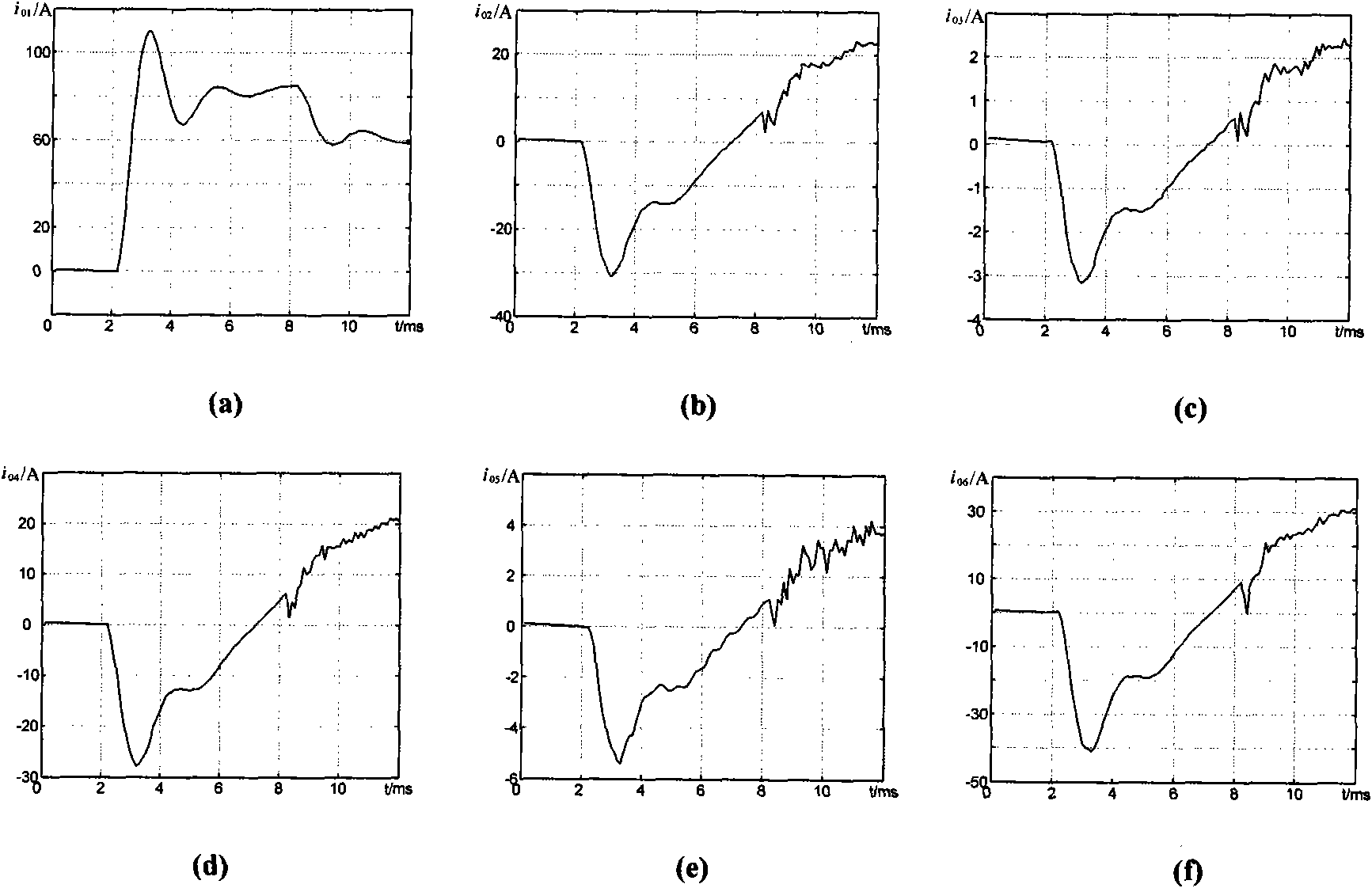
[0042] use as figure 1 The single-phase-to-earth fault network of the resonant grounded power grid shown, its line L 1 A single-phase ground fault occurs 2km away from the first section, the fault closing angle is 90°, and the sampling frequency is 10kHz. figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a phase-to-ground fault network of a 110kV / 35kV resonant ground grid with 6 lines. The neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer is grounded through the series resistance of the arc suppression coil, and the LSJC-35 current transformer is used. The line adopts overhead line (L 1 , L 3 , L 5 ), wire-cable hybrid line (L 4 ) and cable lines (L 2 , L 6 ), where the overhead line adopts JS 1 Rod type, LGJ-70 type conductor, the span is 80m, and the cable line adopts YJV23-35 / 95 type cable. figure 1 Among them, T is the step-down transformer, Tz is the Z-shaped transformer, K is the switch, L is the inductance of the arc suppression coil, R is the series resistance of the arc sup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com