Method for removing sodium sulfate and sodium chloride from lauryl sodium sulfate
A technology of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate, which is applied in the field of pharmaceutical adjuvant production, can solve the problems of high content of sodium sulfate and sodium chloride, and achieve the effect of reducing the content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
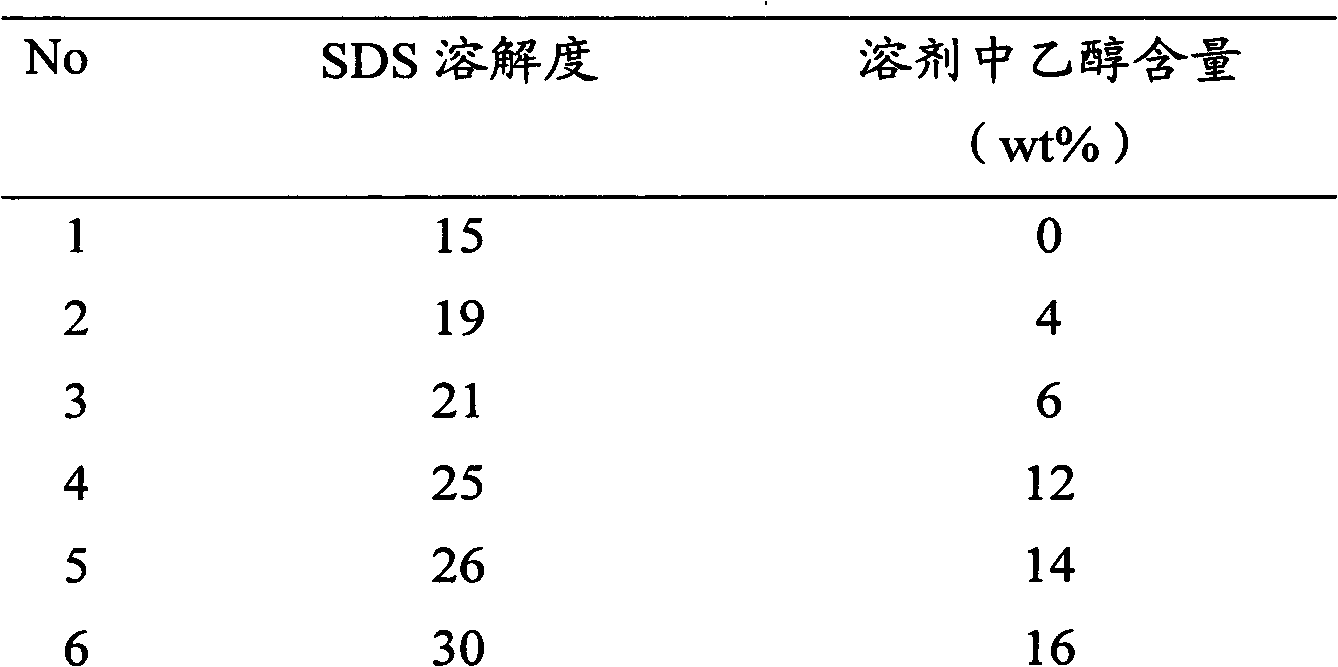
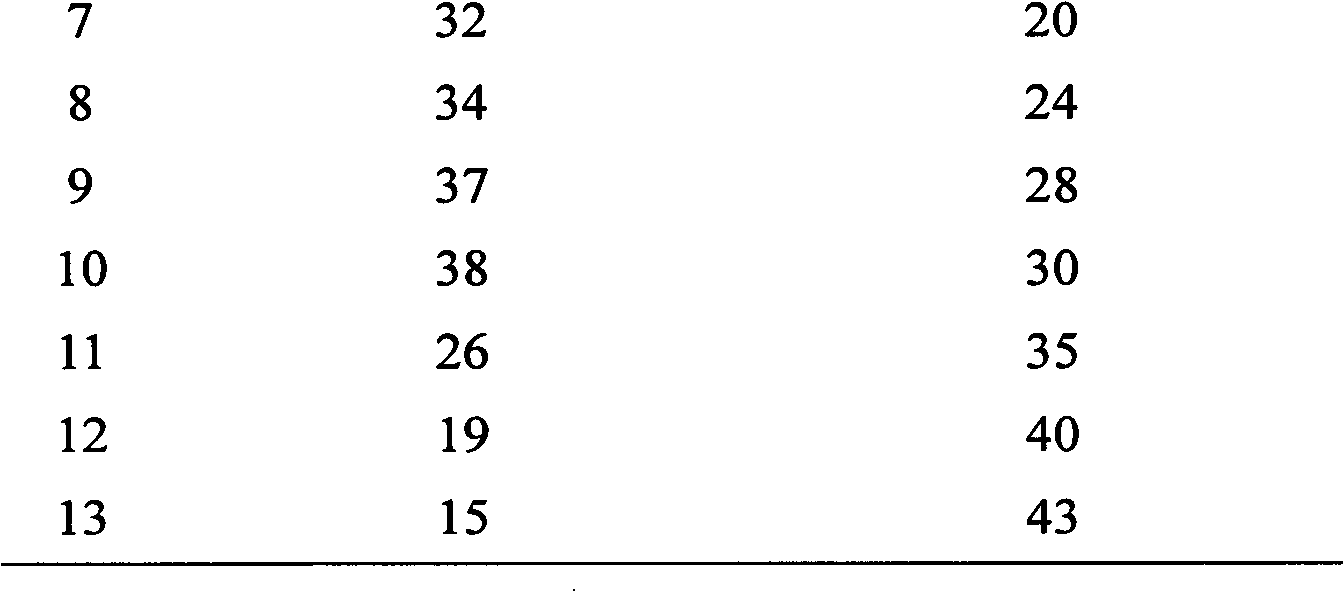
[0024] Dissolve 35 g of technical grade SDS in 70 g of ethanol-water solvent containing 30% ethanol. Stir for 30min, filter to remove insoluble matter. The solution was cooled to 0-1 °C over a period of 3 hours and held for 30 min. Filter to obtain powder. The powder was combined with the above insoluble matter, dried and weighed to obtain 3.2 g. The powder was fired with no weight loss. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure until the filtrate became a slurry. Finally, dry and remove water in a vacuum oven at 80° C. to obtain 30.7 g of the finished product. Detecting its sodium sulfate content is 2.1%, and sodium chloride content is 1.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com