Laminated film photovoltaic device with plasmon structure and application thereof
A plasmonic and thin-film photovoltaic technology, applied in the direction of photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., can solve the problems that the crystal growth speed cannot be too fast, microcrystalline silicon cannot be formed, and the production rate is reduced, so as to reduce the production rate. Cost, increase in element efficiency, effect of increase in absorption length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
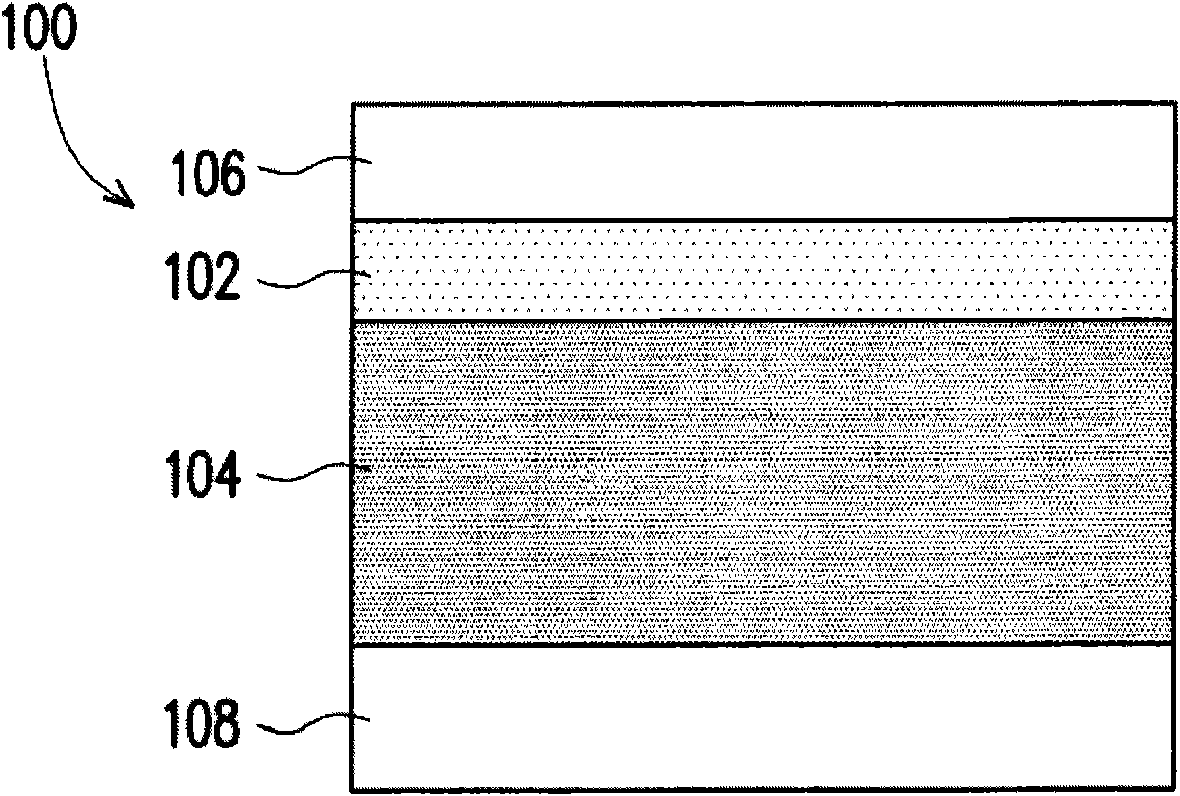
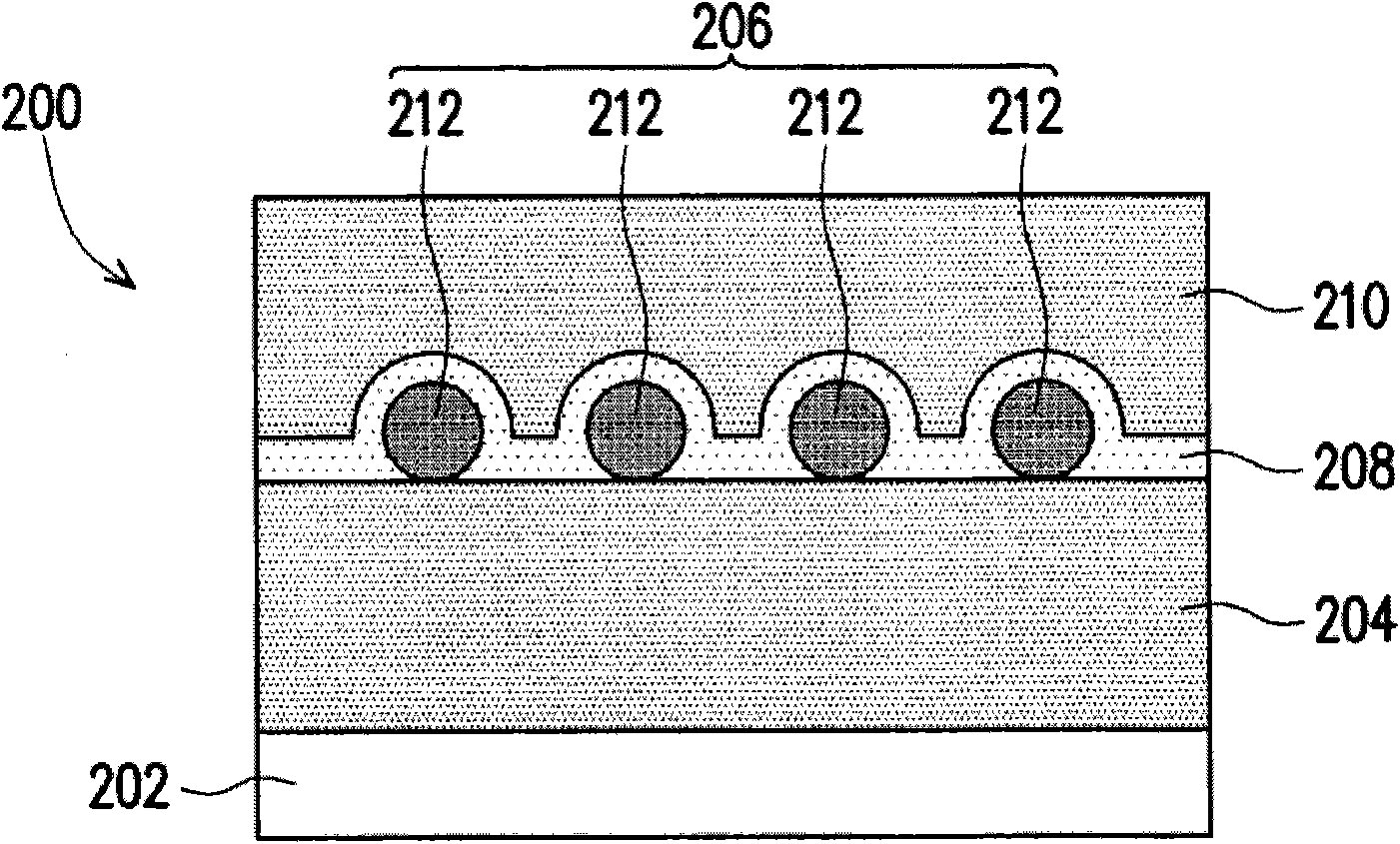
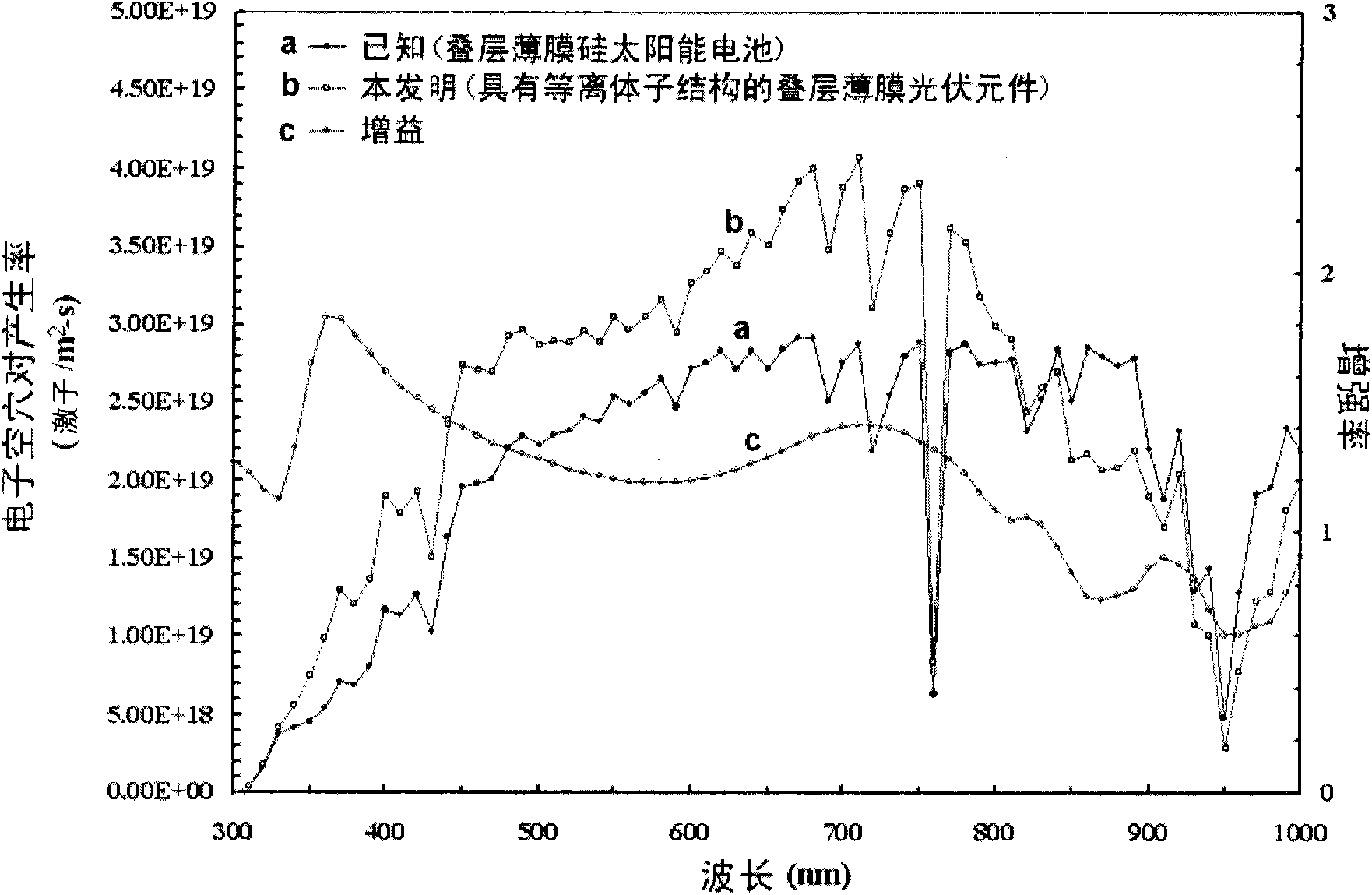
[0036] Plasmons are light or high-frequency electromagnetic waves interacting with metal free electrons, resulting in electron charge density oscillations. When resonance conditions occur, such plasmonic materials will produce extremely high extinction coefficients (extinction) and High-density strong near-field with very special optical properties. According to the Mie scattering theory, the extinction coefficient of metal ball particles with a size of more than 100 nanometers mainly comes from the scattering of the ball, and the heat loss caused by absorption is much lower than the contribution of scattering. This scattering characteristic is related to the material, size and shape of the metal particles, which will cause light to travel in different directions due to different wavelengths, and effectively control the behavior of metal particles, which will help the application of thin-film silicon solar cell light confinement technology . The present invention utilizes the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com