Process for producing osteocalcin-containing extract
A technology of extract and osteocalcin, which is applied in the field of preparing extracts containing active osteocalcin, can solve the problem of no effective use of bone residues and the like, and achieve the effect of saving cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
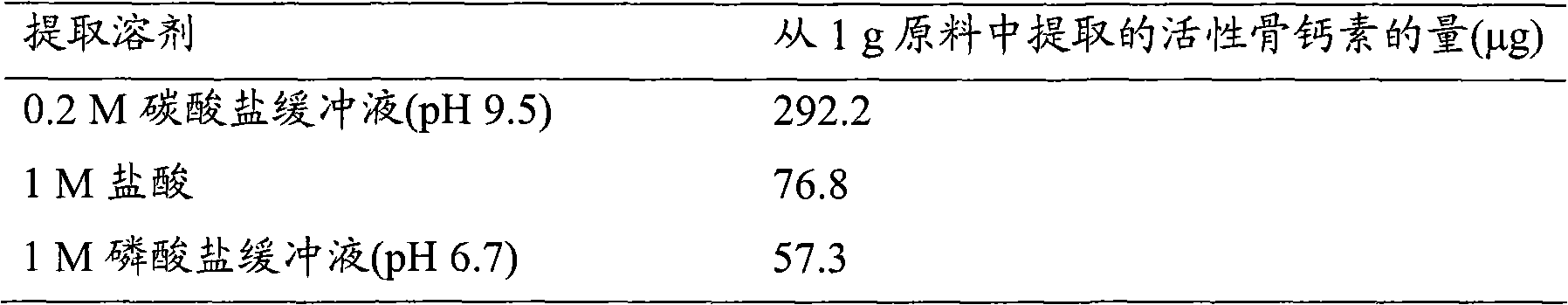
Study on Solvents for Extracting Active Osteocalcin from Porcine Bone(1)
Prepare the extraction solvent as follows. 0.2M carbonate buffer (pH 9.5): 0.275 g of sodium carbonate (NACALAITESQUE, INC.) and 0.62 g of sodium bicarbonate (NACALAITESQUE, INC.) were dissolved in distilled water to make 50 mL. 1M Hydrochloric acid: 45.7 mL of distilled water was mixed with 4.3 mL of hydrochloric acid (NACALAI TESQUE, INC.). 1 M phosphate buffer (pH6.7): 7.1 g disodium hydrogen phosphate (NACALAI TESQUE, INC.) was dissolved in distilled water to make 50 mL; 6.8 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate (NACALAI TESQUE, INC.) was dissolved in distilled water , to make 50 mL, and then mix the two solutions to adjust to pH 6.7. Then, 10 mL of each extraction solvent was added to 3 g (wet weight) of the mixer-milled bone extract extraction residue (cooked bone) of raw pig bone using hot pressurized water, and the mixture was extracted at 4° C. for 24 hours with stirring. After separating the extrac...
Embodiment 2
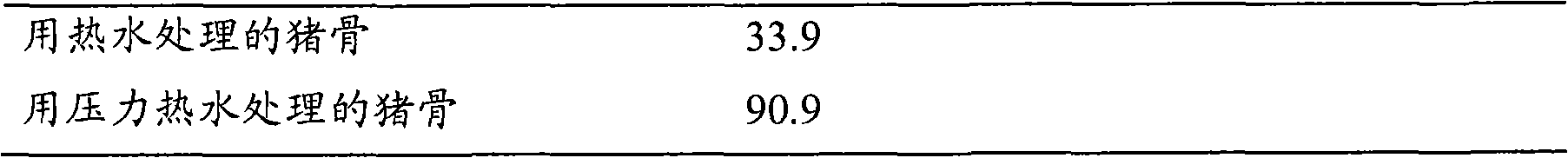
Study on the Raw Materials for Extracting Active Osteocalcin from Pork Bone
Raw pork bones were heated in how water (90° C.) for 30 minutes to obtain heating extraction solution 1 . Take out the remaining pork bones and grind them roughly. Then, the coarsely ground pork bones were further heated in how water (90° C.) for 30 minutes to obtain hot extraction solution 2 and hot water-treated pork bones. Then, the raw pig bone was heated in hot water under pressure (120° C.) for 5 hours to obtain the heating extraction solution 3 and the pig bone treated with hot water under pressure. Then, according to the same method as in Example 1, the extract was prepared, and the content of active osteocalcin in the extract was determined, except that 20 g (wet weight) was treated with hot water or 20 g (wet weight) was treated with Autoclaved hot water-treated pork bones were used as raw material bones, both of which were used after coarse grinding with a mixer, and 60 mL of 0.5 M carbona...
Embodiment 3
Study on Salt Concentration of Extraction Solvents Used for Extracting Active Osteocalcin from Porcine Bone
Various concentrations of carbonate buffer were prepared as follows. 1M carbonate buffer (pH 9.5): 1.375 g of sodium carbonate and 3.1 g of sodium bicarbonate were dissolved in distilled water to prepare 50 mL. The solution was diluted with distilled water to obtain a 0.05-0.5M carbonate buffer (pH 9.5). Then, according to the same method as in Example 1, the correlation between the concentration of carbonate buffer solution (pH9.5) and the extraction efficiency of active osteocalcin was studied. The results are shown in Table 3. As shown in Table 3, it was proved that although active osteocalcin was extracted at all tested concentrations, the extraction efficiency of active osteocalcin was particularly high in 0.1-1 M carbonate buffer solution (pH 9.5).
[0078]
table 3
[0079]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com