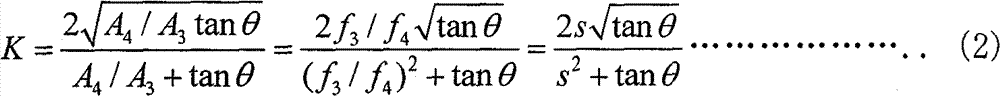Common-path radial shear interferometer based on four-step spatial digital phase-shift
A shearing interferometer and ring-direction shearing technology, applied in optics, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of environmental vibration sensitivity, low measurement accuracy, and low contrast of interference fringes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
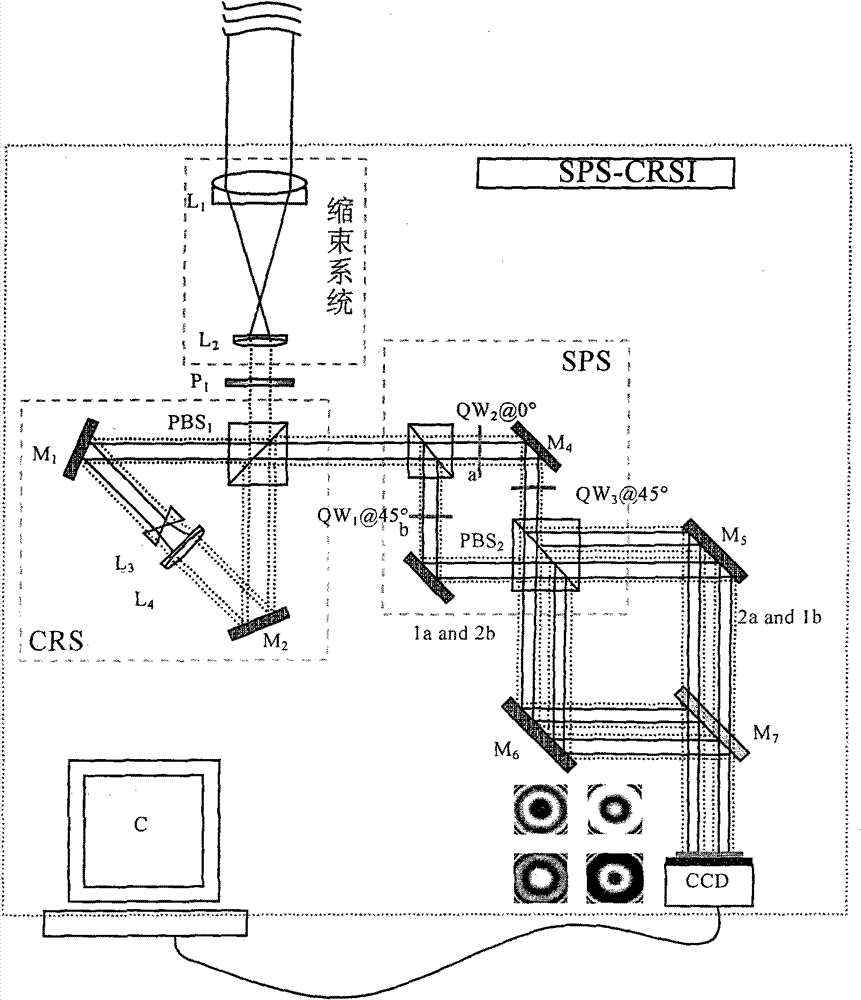
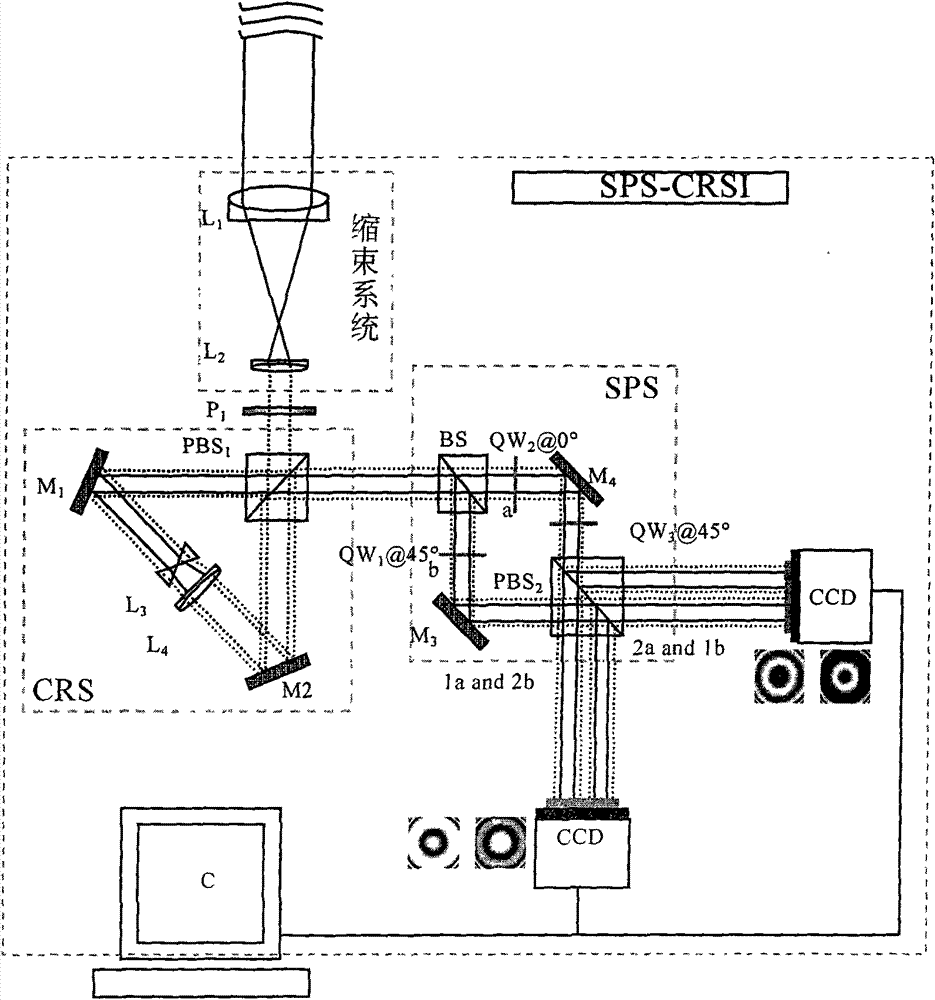
[0047] like figure 1 As shown, the distorted beam enters the common optical path direction shearing interferometer based on four-step spatial phase shifting, and the beam aperture is transformed by using the beam shrinking system. The lens L 1 , L 2 The focal lengths are f 1 and f 2 , the incident distorted beam aperture is A 1 , then the reduced beam aperture A 2 , and A 2 =A 1 f 2 / f 1 . Polarizer P 1 To adjust the light intensity of the polarized component of the reduced beam along the horizontal and vertical directions, set P 1 The polarizing angle is θ, then the light intensity ratio η of the polarization component along the horizontal direction and the vertical direction 1 like
[0048] (16) formula shows:
[0049] n 1 =1 / tanθ (16)
[0050] After the modulated beam enters the circular shearing system (CRS), it first passes through the polarizing beam splitter PBS 1 Divided into reflected linearly polarized light B vibrating in the horizontal direction ||...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com