Programmable TVS apparatus with low capacitance and low voltage
A low-capacitance, device technology, applied in the field of low-capacitance voltage programmable TVS devices, can solve the problems that TVS has not yet been launched, and achieve the effect of low clamping, low device capacitance, and lower clamping voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
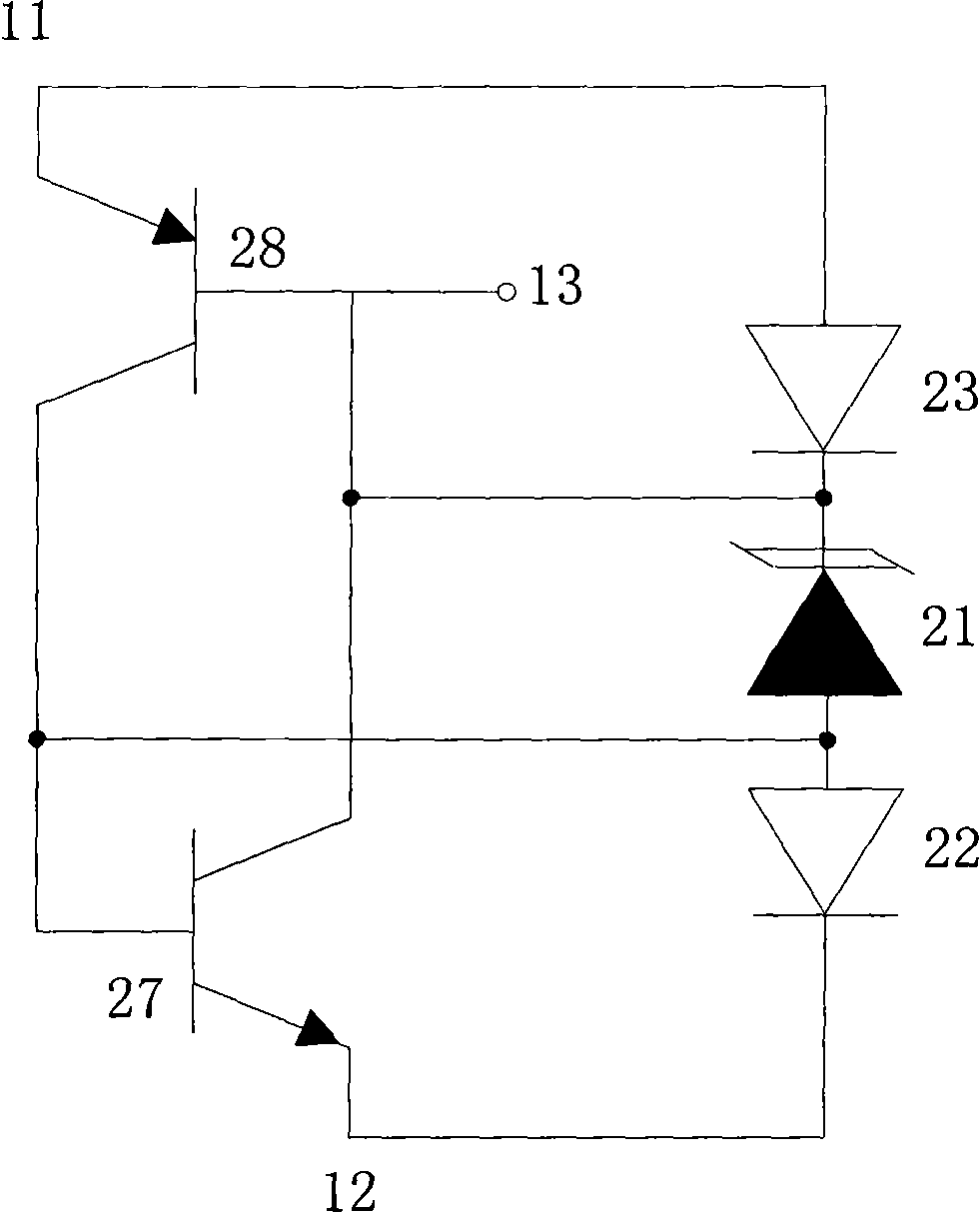
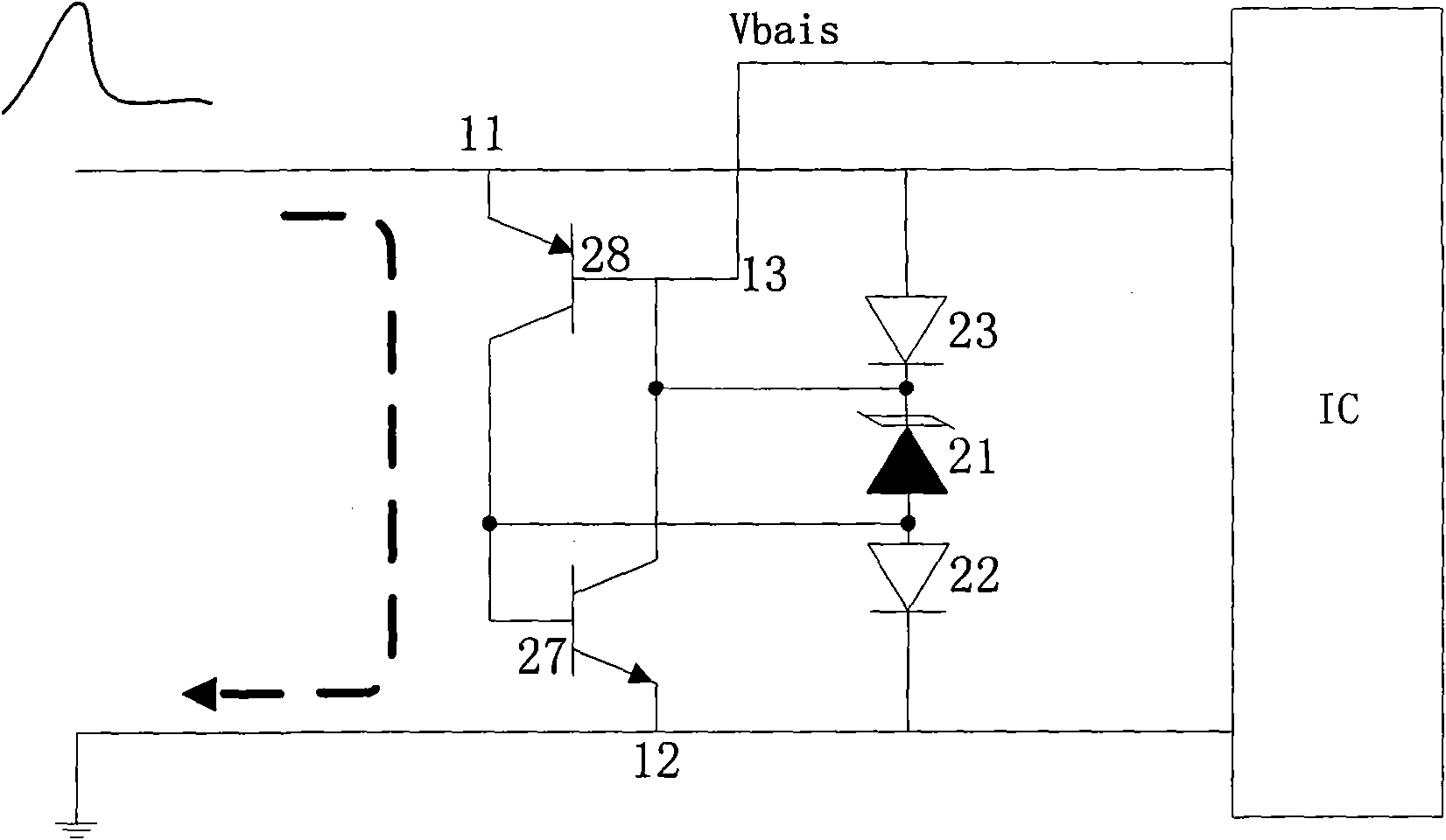
[0095] see figure 1 As shown in the circuit schematic diagram of the TVS device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, a low-capacitance voltage programmable TVS device is composed of a latch path and a voltage-limiting protection path of a low-capacitance diode. The TVS device is composed of a PNP transistor and an NPN transistor. Composed of TVS tubes, used for programmable protection, low capacitance and limited protection voltage upper limit, among which:
[0096] On the latch path, the PNP transistor 28 and the NPN transistor 27 form a latch structure, the input terminal 11 is connected to the emitter of the PNP transistor 28, the collector of the PNP transistor 28 is connected to the base of the NPN transistor 27, and the base of the PNP transistor 28 is connected to The collector of the NPN transistor 27, the emitter of the NPN transistor 27 is connected to the output terminal 12, and the collector of the PNP transistor 28 is connected to the anode of the TVS tube 21, ...
Embodiment 2
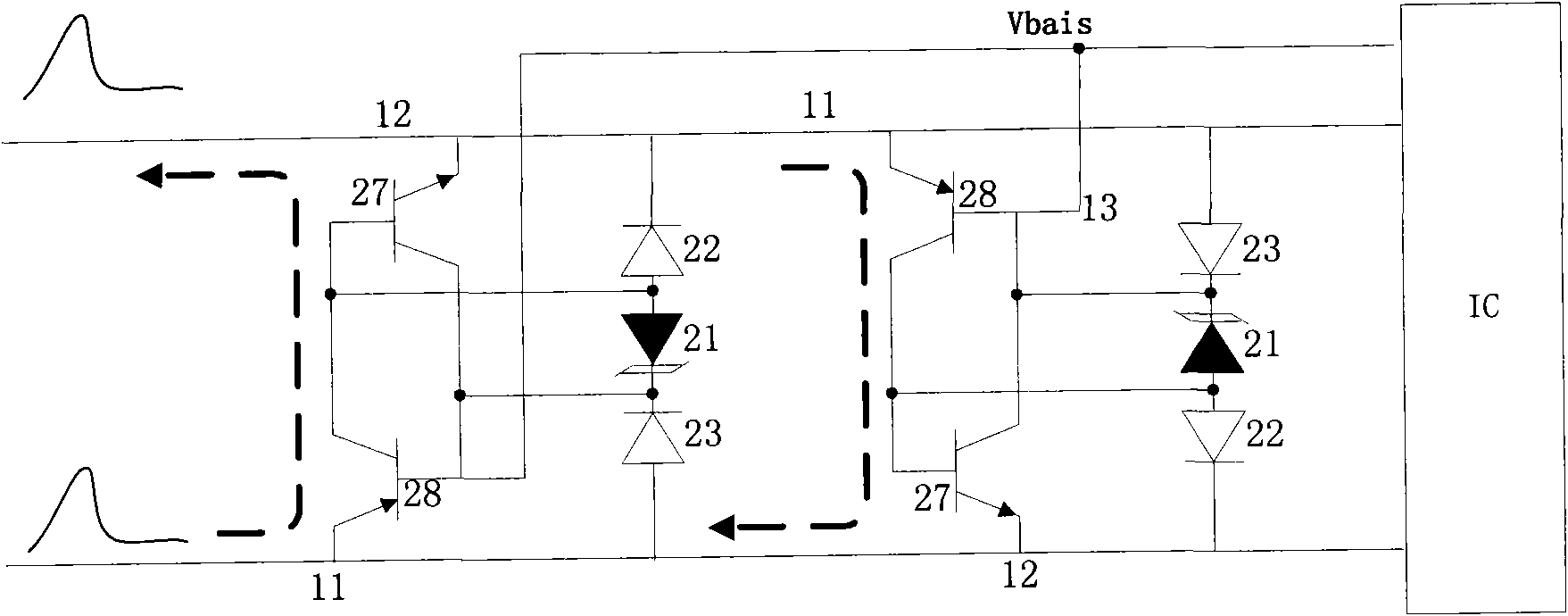
[0121] see Figure 10 It is the circuit schematic diagram and the Figure 11 It is a schematic diagram of the side sectional structure of the TVS device in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and other structures and manufacturing methods from the first step to the fourth step are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0122] Step 5: Doping boron elements on the left side of the epitaxial layer 32a to make a P+ expansion region 24 to form the anode of the forward-directed diode 29 to form the ohmic contact of the gate electrode 13, and doping a phosphorus element on the right side to make an N+ contact region 44, forming an ohmic contact leading to the cathode of the diode 22;
[0123] Step 6: Deposit a metal layer on the surface of the device, and divide the metal layer into three parts by photolithography. The metal layer 33 on the left leads out the P+ expansion area 24 to form the gate 13 electrode, and the middle metal layer 34 separates the P+ expansion area 43 lead out to ...
Embodiment 3
[0125] see Figure 12 It is the circuit schematic diagram and the Figure 13 It is a schematic diagram of the side sectional structure of the TVS device in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and other structures and manufacturing methods from the first step to the fifth step are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0126] Step 6: Connect the polysilicon resistor 20 to the N+ contact area 46 on the left;
[0127] Step 7: Deposit a metal layer on the surface of the device, and divide the metal layer into three parts by photolithography. The metal layer 33 on the left leads out one end of the polycrystalline resistor 20 to form the gate 13 electrode, and the other end passes through the N+ contact area 46 In contact with the N- epitaxial layer 32, the middle metal layer 34 leads out the P+ expansion region 43 to form the electrode of the input terminal 11, and the right metal layer 35 leads out the right N+ contact region 44 to form the electrode of the output terminal 12.
[012...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com