Macrolattice mismatch epitaxial material buffer layer structure containing superlattice isolated layer and preparation thereof
A lattice mismatch and epitaxial material technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem that the buffer layer has no special function, and achieve improved material properties, reduced thickness, and easy operation control. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
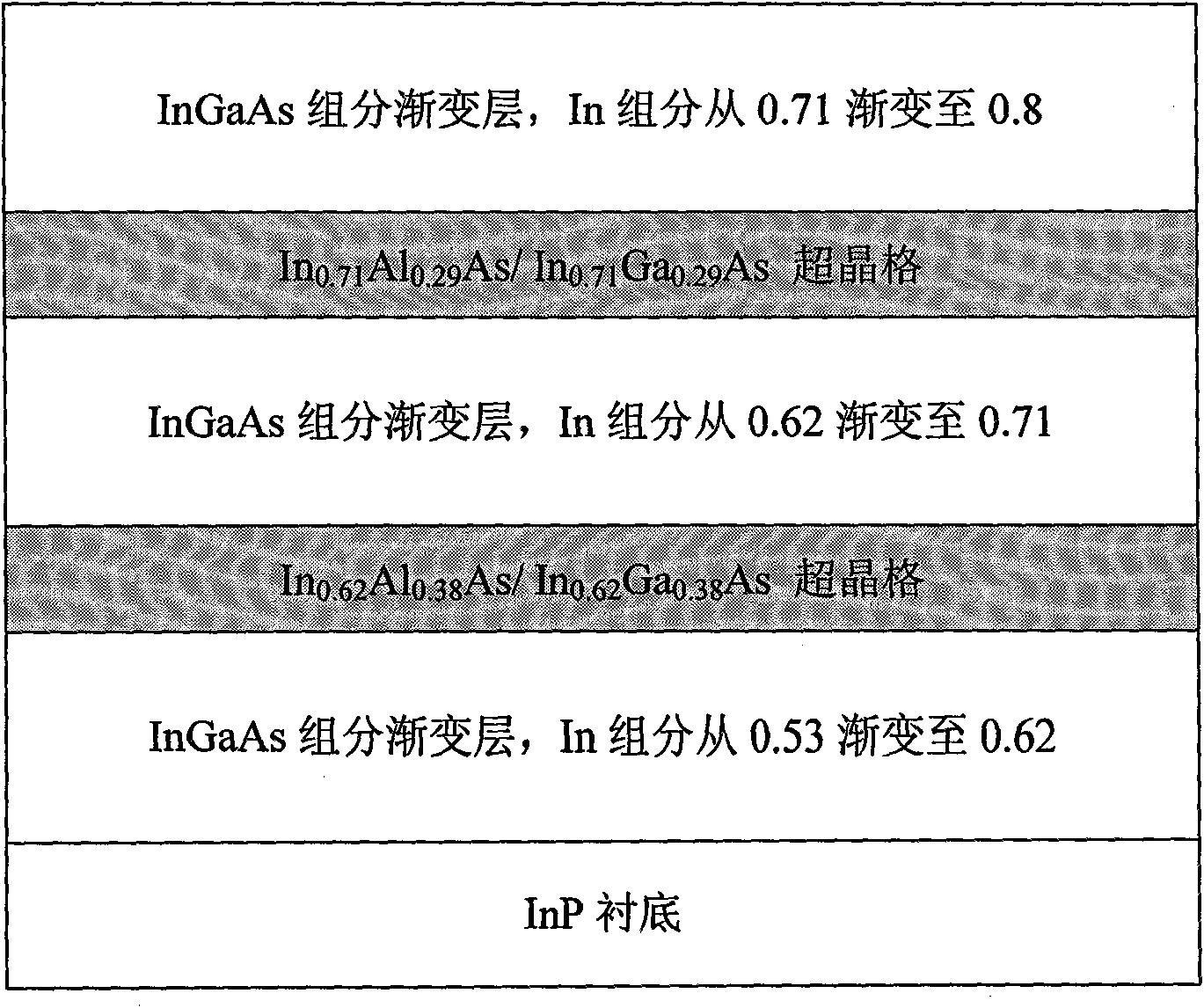
[0045] For epitaxy of In on InP substrates 0.8 Ga 0.2 Buffer Layer Structure of InAlAs / InGaAs Superlattice Isolation Layer Inserted in Continuous Gradient Buffer Layer of As Large Lattice Mismatched Material
[0046] (1) It is necessary to epitaxially high-quality In on the InP substrate .8 Ga 0.2 As large lattice mismatch material, the required growth thickness is thicker than the critical thickness, and it needs to be grown in the epitaxial In .8 Ga 0.2 The buffer layer was grown before the As material;
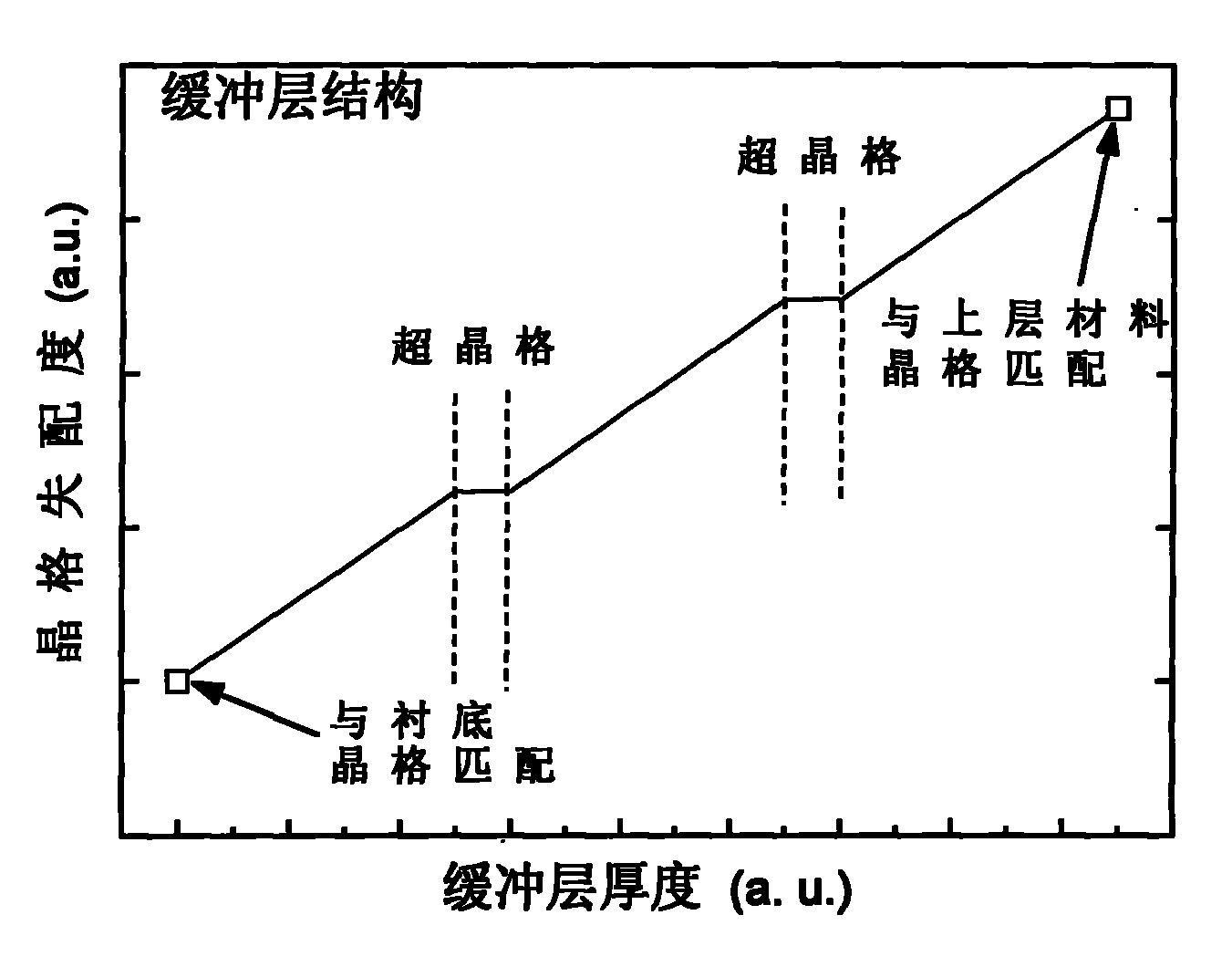
[0047] (2) The material is grown by the conventional molecular beam epitaxy method. The schematic diagram of the In composition change in the buffer layer structure is shown in Figure 2, and the schematic diagram of the buffer layer structure is shown in Figure 3. x Ga 1-x Two layers of InAlAs / InGaAs superlattice are inserted into the buffer layer with graded As composition, and the buffer layer is divided into 3 parts on average;
[0048] (3) Before the formal growt...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Buffer layer structure with InGaSb / InAlSb superlattice isolation layer inserted in InGaSb composition continuously graded buffer layer for epitaxial InSb large lattice mismatch material on GaSb substrate
[0057] (1) In order to epitaxially thicker high-quality InSb large lattice mismatch materials on GaSb substrates, it is necessary to grow In before epitaxial InSb materials. x Ga 1-x Sb buffer layer structure (0
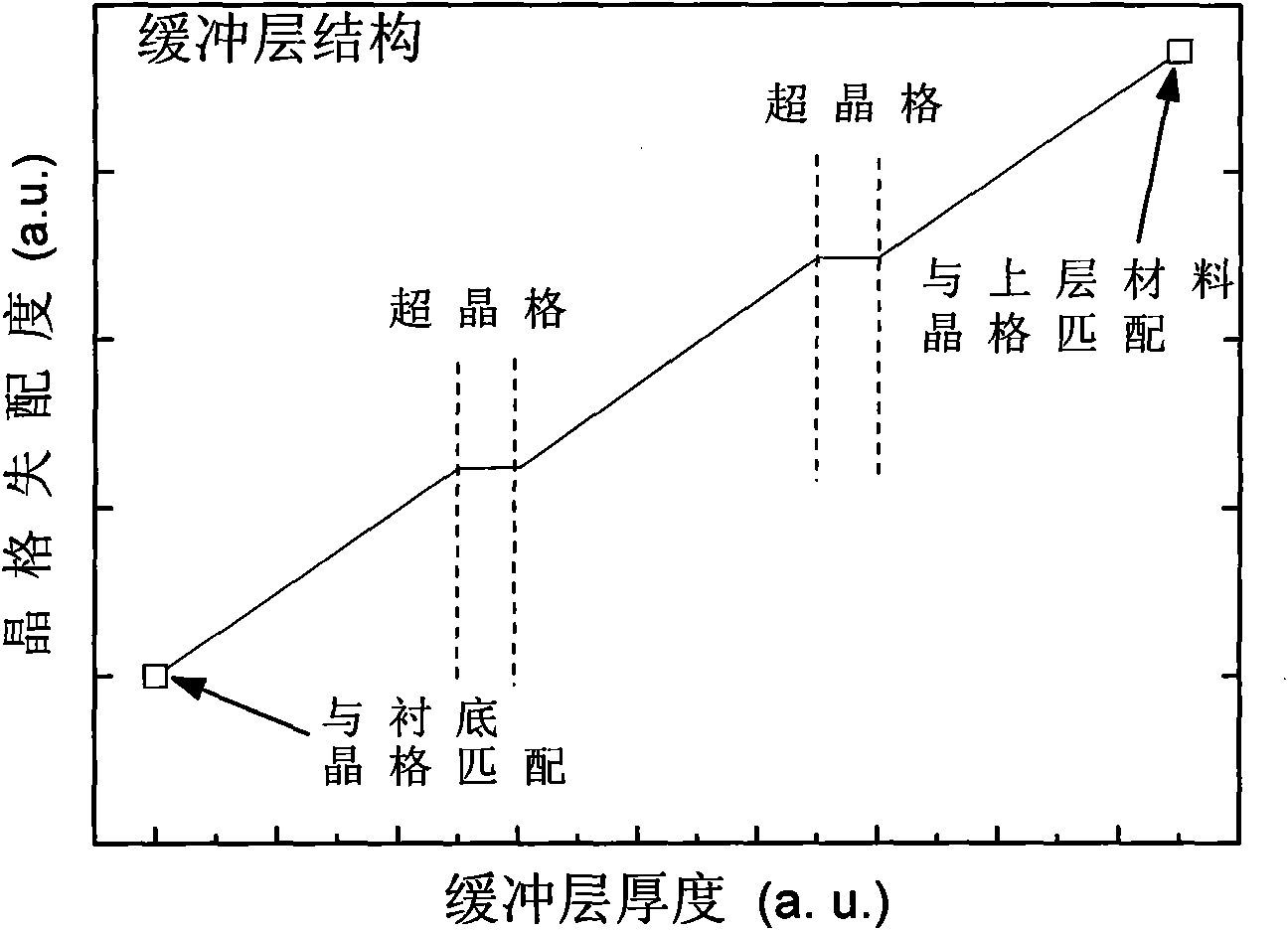
[0058] (2) The conventional molecular beam epitaxy method is used to grow the material. The schematic diagram of the composition change of In in the buffer layer structure is shown in Fig. 4, and the schematic diagram of the buffer layer structure is shown in Fig. 5. In the In x Ga 1-x 2 layers of InGaSbAs / InAlSb superlattice are inserted into the buffer layer with graded Sb composition, and the buffer layer is divided into 3 parts on average;
[0059] (3) Determine the beam source furnace temperature when growing GaSb and InSb on the GaSb substrate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com