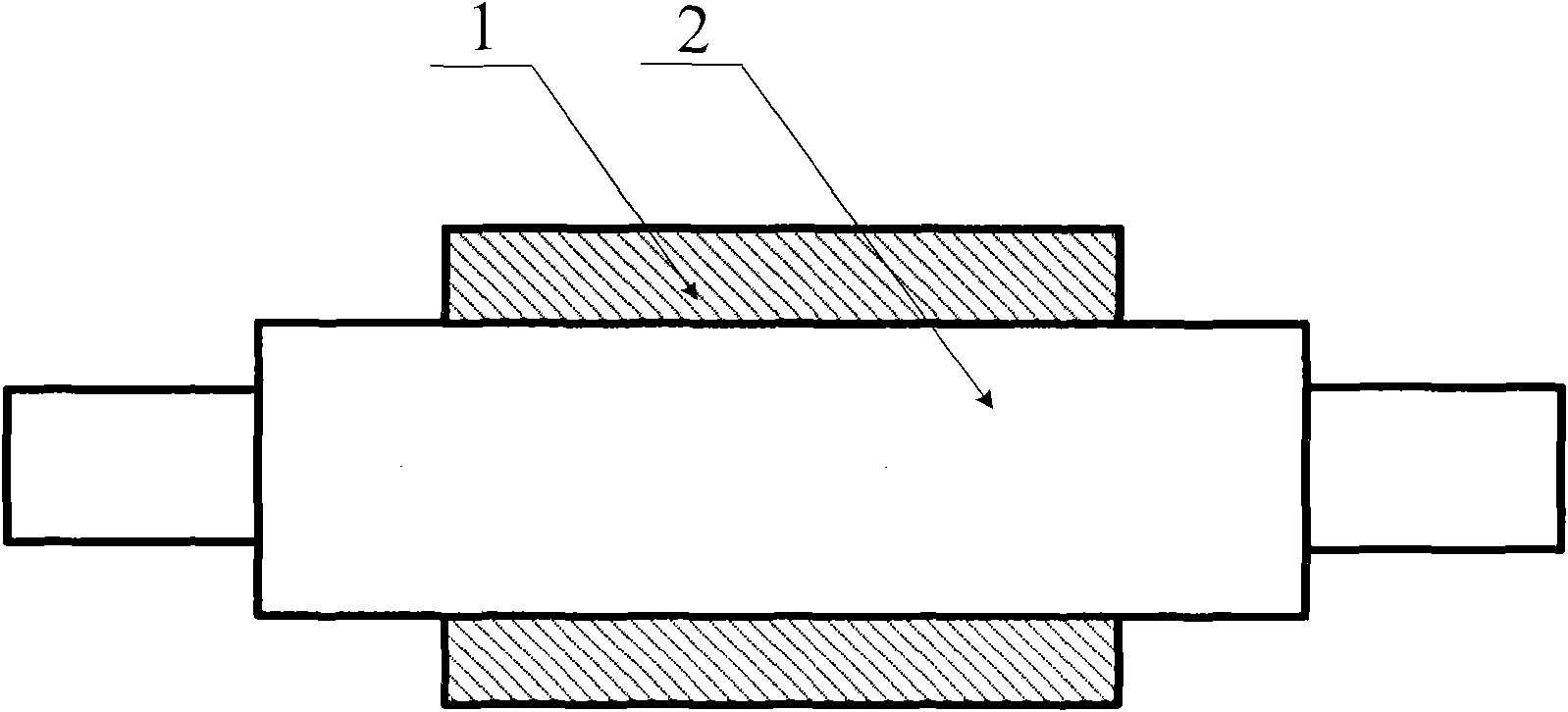
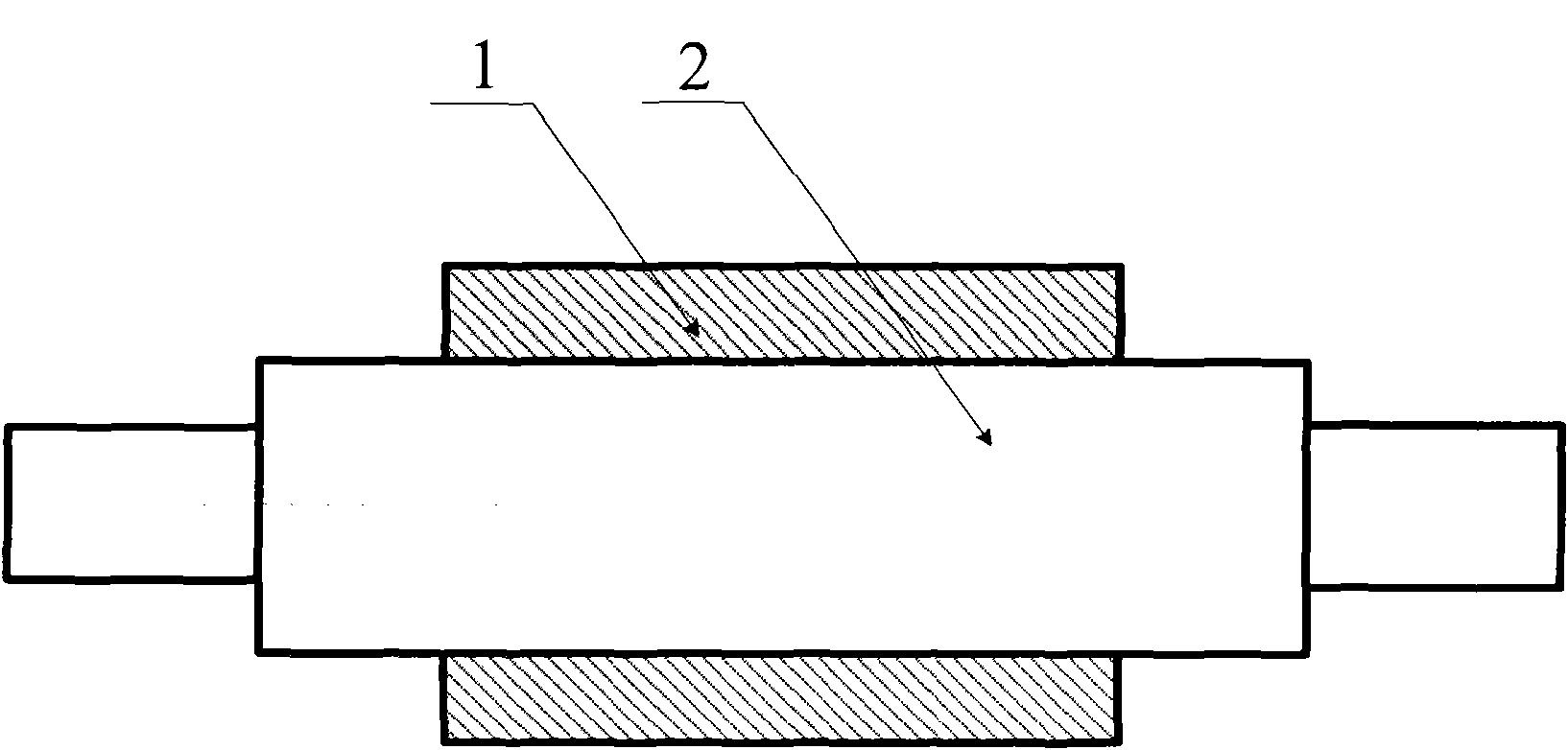
High-boron low-alloy high-speed steel roll and preparation method thereof
A low-alloy, high-speed steel technology, applied in the direction of metal rolling, metal rolling, rolls, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A 500 kg medium frequency induction furnace is used to melt the roll body 1, and a 1500 medium frequency induction furnace is used to melt the roll core 2. Its manufacturing process steps are:
[0049] ① First, common steel scrap, ferrochrome and ferrotungsten are mixed and heated and melted, and ferrosilicon and ferromanganese are added after molten steel is melted.
[0050] ② After adjusting the composition before the furnace, the temperature is raised to 1510°C, aluminum is added for deoxidation, and then ferroniobium, ferro-vanadium, ferro-boron and ferro-titanium are added in sequence, and the molten steel is released when the temperature rises to 1570°C.
[0051] ③Crush nitrogen-containing ferrochromium and yttrium-based rare earth magnesium alloys into small pieces with a particle size of 8-12mm, dry them at 150°C, place them at the bottom of the ladle, and perform compound modification treatment on molten steel by pouring into the ladle.
[0052] ④Centrifugal c...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The roll body 1 is smelted in a 500 kg intermediate frequency induction furnace, and the roll core 2 is processed from forged steel blanks. Its manufacturing process steps are:
[0061] ① First, common steel scrap, ferrochrome and ferrotungsten are mixed and heated and melted, and ferrosilicon and ferromanganese are added after molten steel is melted.
[0062] ② After adjusting the composition before the furnace, the temperature is raised to 1538°C, aluminum is added for deoxidation, and then ferroniobium, ferro-vanadium, ferro-boron and ferro-titanium are added in sequence, and the molten steel is released when the temperature rises to 1594°C.
[0063] ③Crush nitrogen-containing ferromanganese and yttrium-based rare earth-magnesium alloys into small pieces with a particle size of 8-12mm. After drying at 180°C, place them at the bottom of the ladle, and perform compound modification treatment on molten steel by pouring into the ladle.
Embodiment 3
[0072] A 1000 kg medium frequency induction furnace is used to melt the roll body 1, and a 3000 medium frequency induction furnace is used to melt the roll core 2. Its manufacturing process steps are:
[0073] ① First, common steel scrap, ferrochrome and ferrotungsten are mixed and heated and melted, and ferrosilicon and ferromanganese are added after molten steel is melted.
[0074] ② After adjusting the composition before the furnace, the temperature is raised to 1525°C, aluminum is added for deoxidation, and then ferroniobium, ferro-vanadium, ferro-boron and ferro-titanium are added in sequence, and the molten steel is released when the temperature rises to 1571°C.
[0075] ③Crush nitrogen-containing ferrochromium and yttrium-based rare earth magnesium alloys into small pieces with a particle size of 8-12mm, dry them at 170°C, place them at the bottom of the ladle, and use the method of pouring into the ladle to perform composite modification of molten steel.
[0076] ④The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com