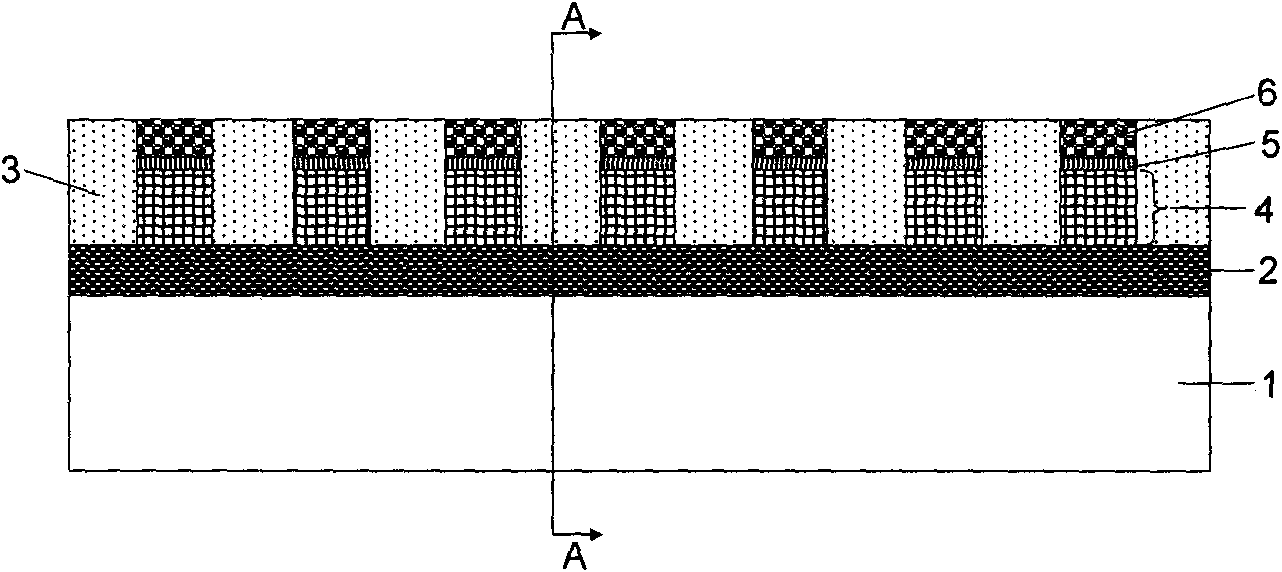Method for manufacturing three-dimensionally stacked resistance conversion memory
A resistance conversion, three-dimensional technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of resistance conversion memory without a good technical route, and achieve the effect of less defects and good reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Please refer to FIG. 1, the present invention discloses a method for manufacturing a three-dimensional stacked resistance switching memory, including the following steps:
[0053] (1) Figure 1A Shown is the substrate manufactured with peripheral circuits and resistance switching memory storage arrays. The peripheral circuit part is not drawn in the substrate 1 in the figure, and the size of the illustration is not drawn to scale. The substrate has a layer of storage arrays. In this case, the used The gating transistor is a PN diode, and of course other gating units can also be used, such as Schottky diodes, bipolar transistors, and field effect transistors. Here, the PN diode is used as an example, but it should be noted that the The selected gate transistor is not limited to PN diodes. The memory resistive storage unit used may also be one of phase change memory, resistive random access memory, and Sb-based resistive switching memory. Here, for the convenience of expr...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment is a method for manufacturing a bipolar transistor-gated three-dimensional stacked resistive switching memory.
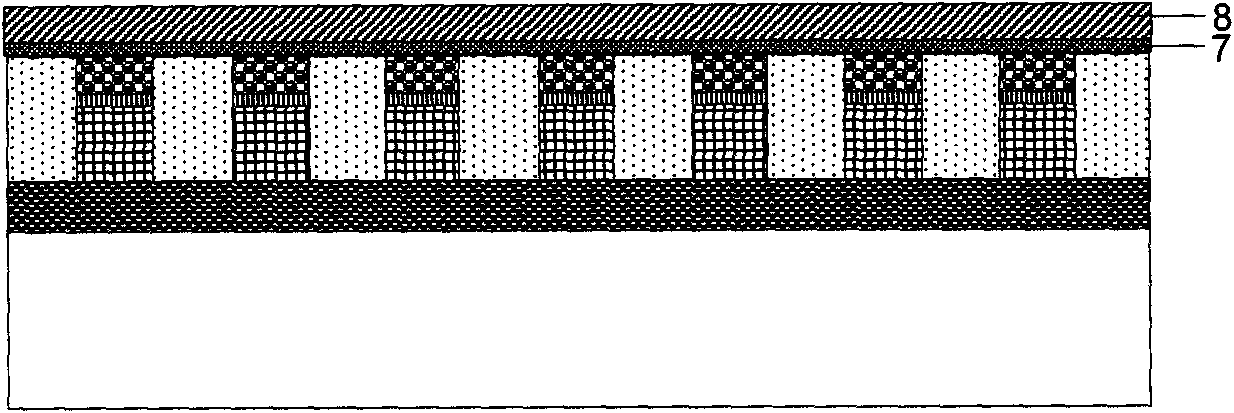
[0065] It has also been described in the above-mentioned embodiments, and in Figure 1A and Figure 1B In the structure, a bipolar transistor can be used instead of the PN diode 4 as the gating transistor. If a bipolar transistor is used as the gating tube, Figure 1D The PN layer 10 formed in the above method should be correspondingly changed into an NPN layer or a PNP layer, and the subsequent corresponding process is similar to that of the first embodiment. In the finally obtained multi-layer stacked resistive memory structure shown in FIG. 10 , the difference is that the gating units used in the layers 22-25 are bipolar transistors.
Embodiment 3
[0067] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment is a method for manufacturing a Schottky diode-gated three-dimensional stacked resistive switching memory.
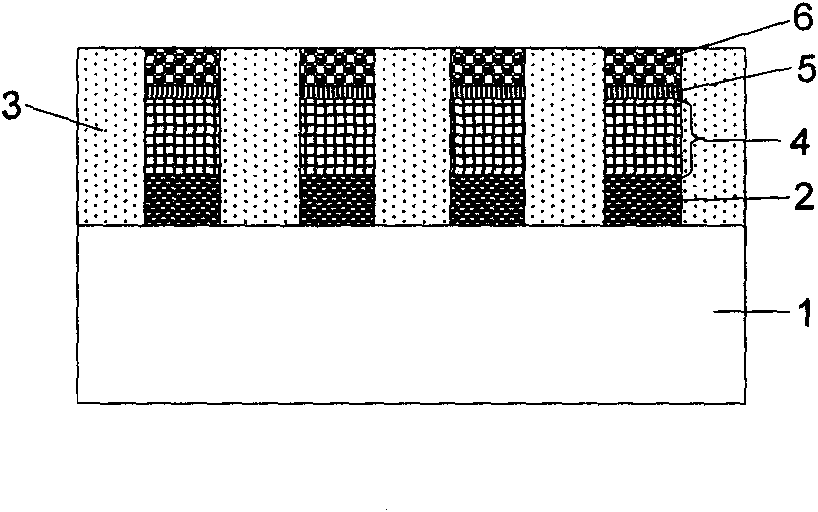
[0068] (1) Figure 2A What is shown is a substrate fabricated with peripheral circuits and a layer of resistive switch memory storage array, and the peripheral circuits are also not shown, but it does not mean that the substrate 31 does not have peripheral circuits. The gating tube used in this case is a Schottky diode. Of course, other gating units can also be used, such as PN diodes and bipolar transistors. Here, the Schottky diode is used as an example, but it is not necessary to explain limited to Schottky diodes. Multiple Schottky diodes 34 share one word line 32 , and the interface of the Schottky barrier formed by the Schottky diodes can be at the interface with the word line 32 or with the electrode 35 . The electrode 35 is also the heating electrode of the phase change memo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com