Artificial feed for armyworm, preparation method thereof, and feeding method
A technology of artificial feed and armyworm, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve the problems of low pupation rate, high feed cost, time-consuming, etc., to overcome seasonal changes, simple production process, safe storage and convenient Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1 (preparation 1000g artificial feed)
[0027] 24g of soybean powder; 48g of yeast powder; 10g of casein; 85g of dry corn leaf powder; 0.7g of cholesterol; 20g of sucrose; 3.5g of ascorbic acid; 1g of sorbic acid; 18g of agar; ml.
[0028] Formula with vitamin B solution:
[0029] Niacin: 0.031g; Calcium Pantothenate: 0.031g; Riboflavin: 0.0153g; Vitamin B1: 0.00764g; Vitamin B6: 0.00764g; Folic Acid: 0.00764g; D-Biotin 0.0061g; Water 10g
[0030] Feed preparation method:
[0031] 1. Weigh each component in proportion for later use, put the weighed sterilized soybean powder, dry corn leaf powder, yeast powder, casein, and cholesterol into the pot, and stir evenly, as component A;
[0032] 2. Make two parts of distilled water, dissolve about 1 / 4 of the sucrose and ascorbic acid that have been weighed in proportion, as component B; pour B into A, stir evenly, and use it as component C;
[0033] 3. Pour the remaining distilled water into the pot and boil, add ...
Embodiment 2
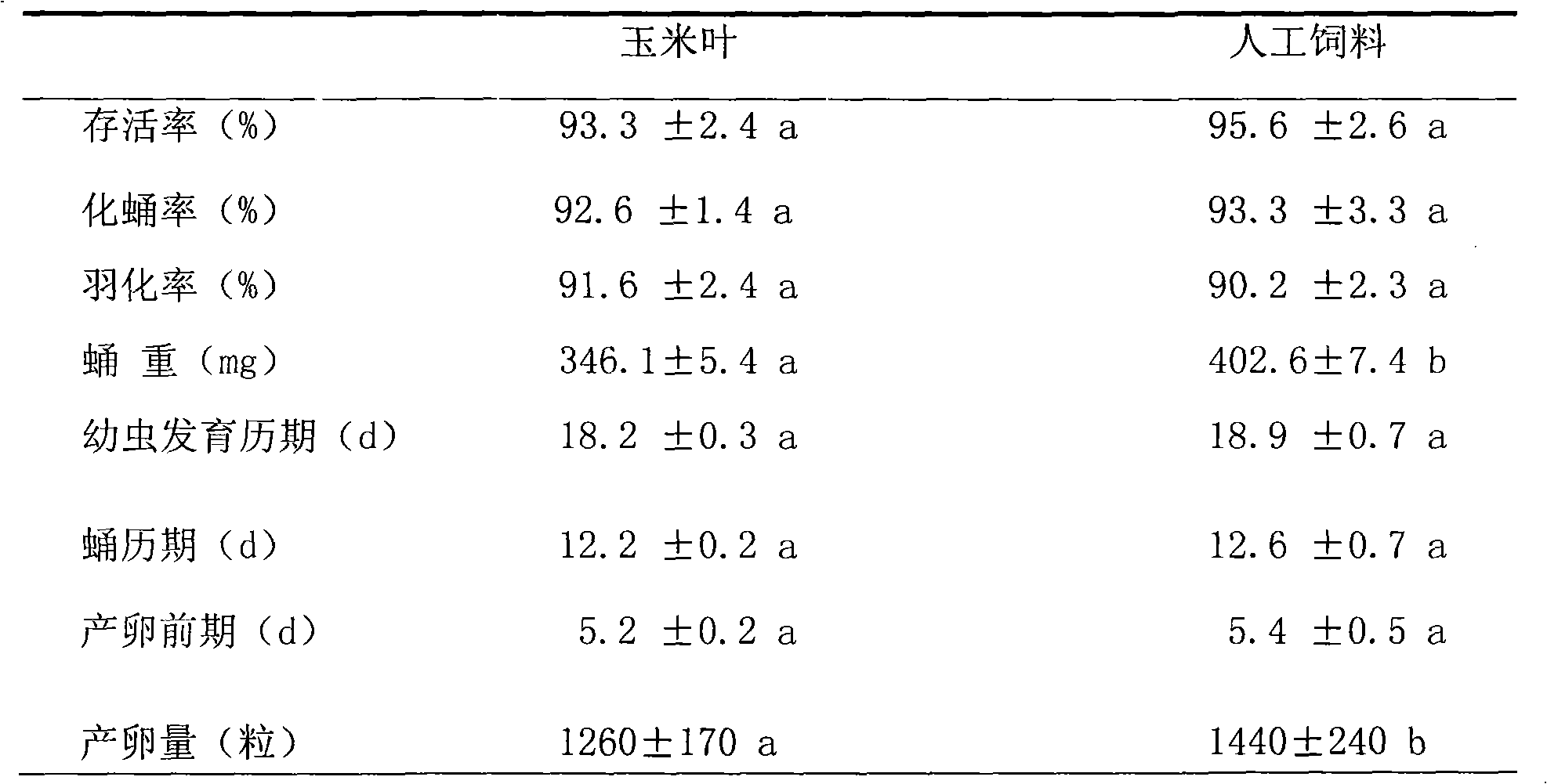
[0043] Embodiment 2: The comparative test of the effect of artificial feed and natural feed corn leaf
[0044] Test materials and methods:
[0045] Insect source for testing: Insect source comes from overwintering adults collected in the field in Kangbao, Hebei (41.87°N, 114.6°E), and 6 generations of armyworm eggs raised with artificial feed indoors.
[0046] Test feed:
[0047] Natural feed corn leaves: take corn leaves grown in the greenhouse of the Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
[0048] Artificial feed: adopt the feed described in embodiment 1
[0049] Test method: the test worm breeding method is with reference to the method described in Example 1, and every treatment is repeated 3 times, and 36 larvae are tested for every repetition. During the raising process, the developmental period, survival rate, pupae weight, pupation rate, Pupal duration, eclosion rate, egg production, and pre-oviposition period. This experiment was co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com