Samarium-cobalt sintered magnet material and preparation method thereof
A sintered magnet, samarium cobalt technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, high industrialization cost, and the decline of permanent magnet magnetic performance, so as to improve the magnetic energy product, promote industrialization, The effect of reducing the temperature coefficient of remanence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Raw materials: Samarium, Cobalt, Iron, Copper, Zirconium, Gadolinium, Dysprosium.
[0036] The above raw materials are compounded by mass percentage, wherein samarium accounts for 18.14%, cobalt accounts for 51.71%, iron accounts for 13.90%, copper accounts for 6.33%, zirconium accounts for 1.70%, gadolinium accounts for 5.42%, and dysprosium accounts for 2.80%.
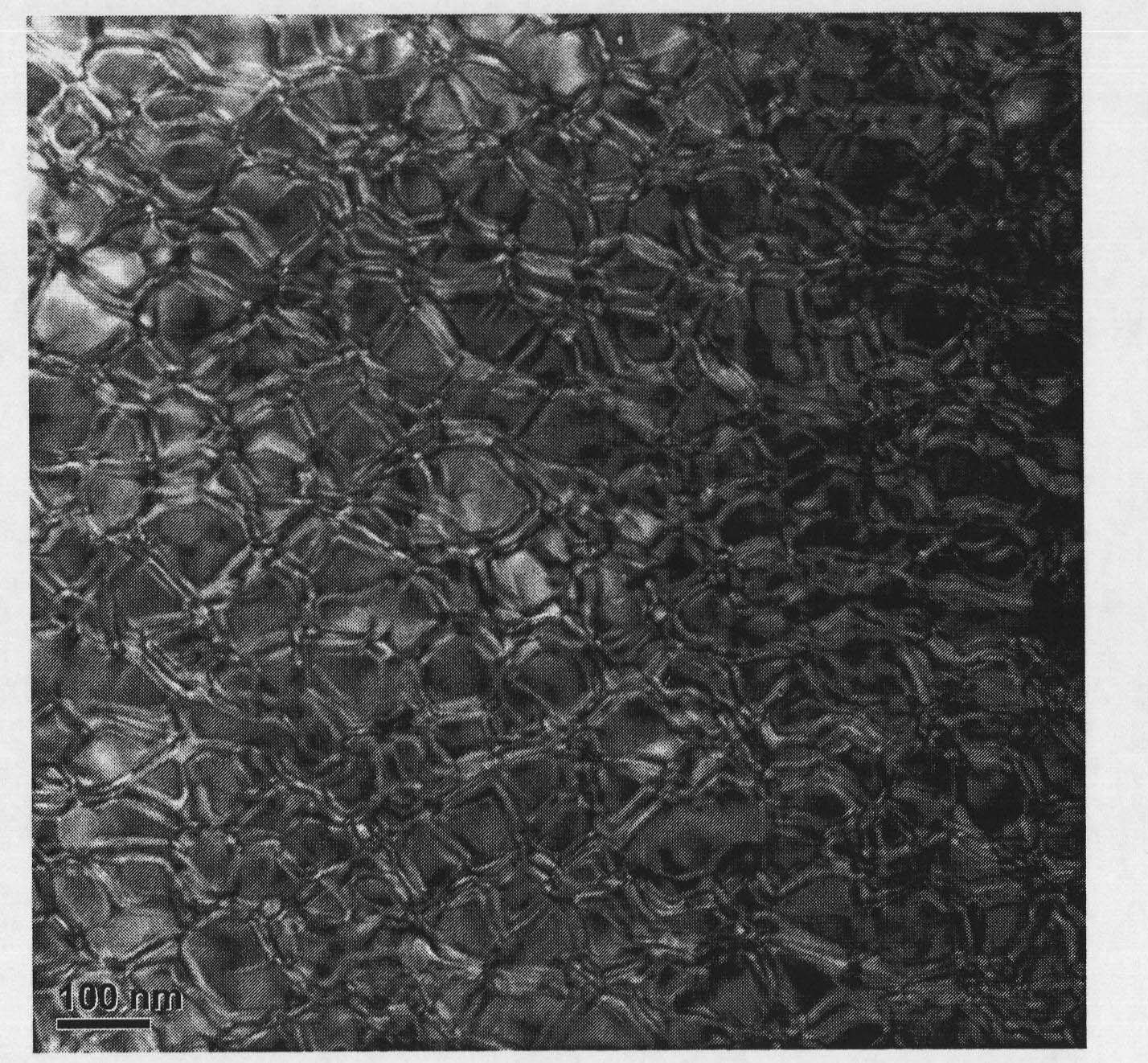
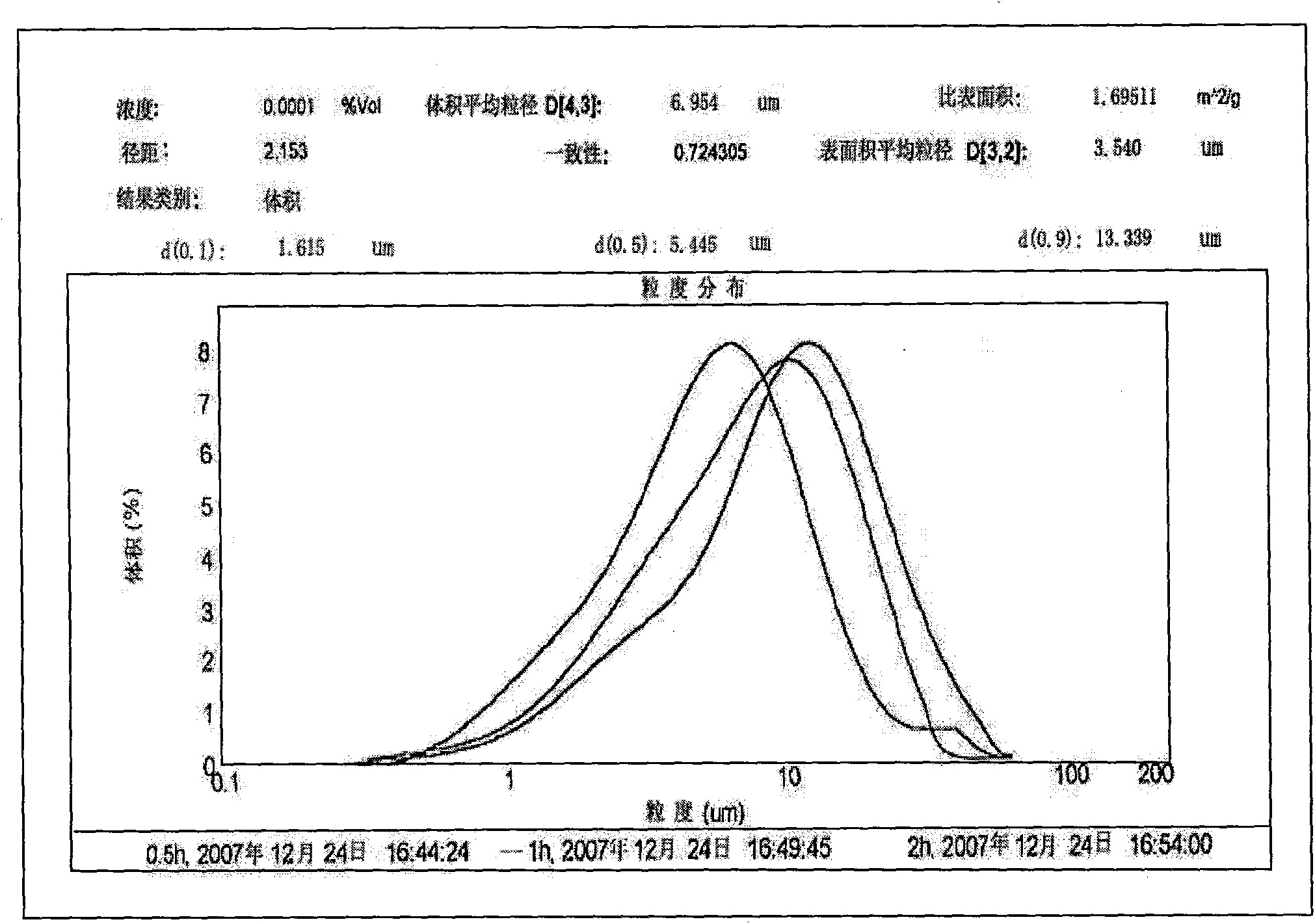
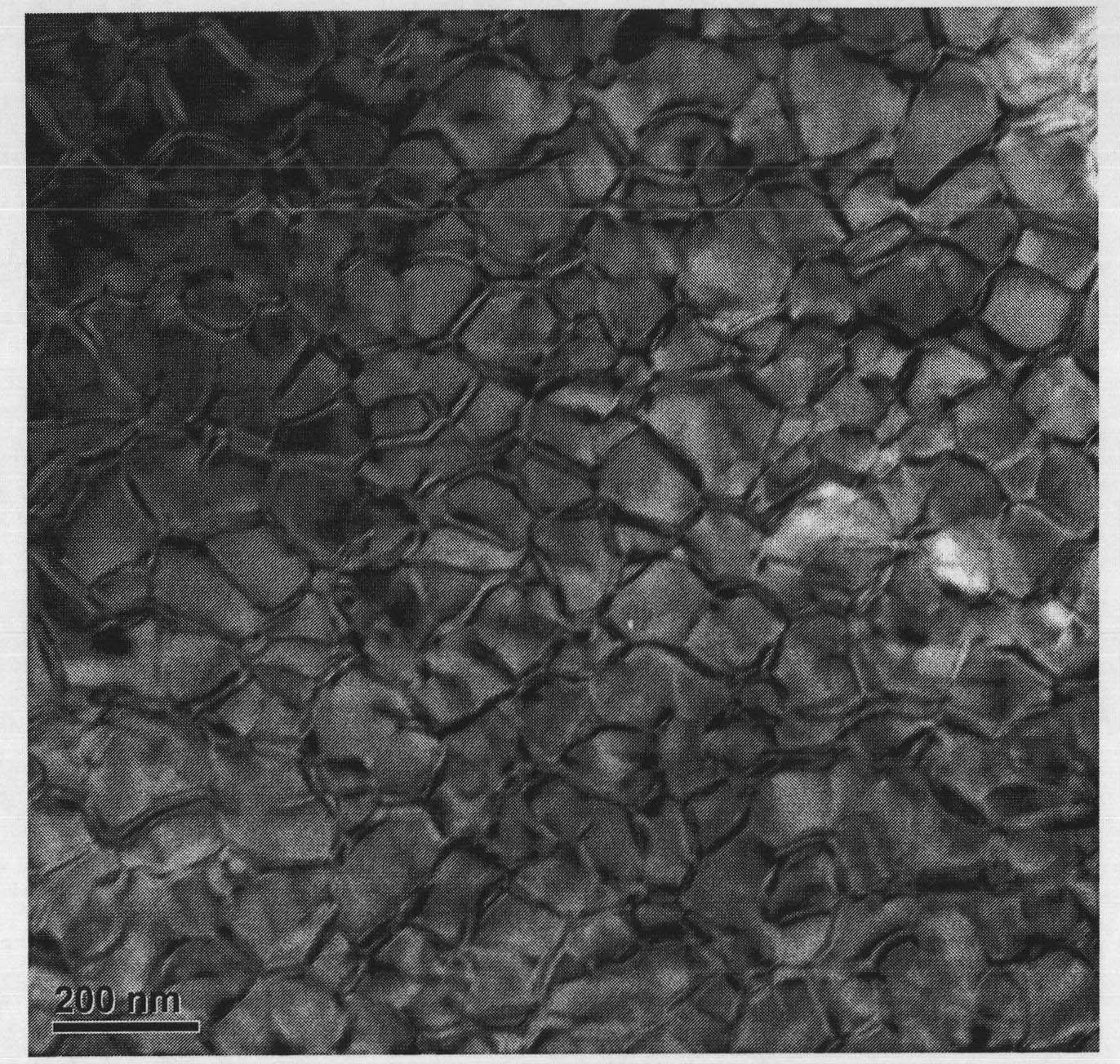
[0037] In the quick-setting furnace, the above ingredients are smelted into alloys, and then cast into thin strip-shaped quick-setting sheets on water-cooled copper rollers; the quick-setting sheets are ground by a two-stage grinding process, and the quick-setting sheets are first coarsely crushed for disc grinding. The medium is gasoline, and the quick-setting sheet is ground into magnetic powder with a particle size of about 100 μm, and then the magnetic powder is calcined under vacuum conditions to obtain dry magnetic powder at a calcination temperature of 100 degrees; the obtained dry magnetic powder is subje...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Raw materials: Samarium, Cobalt, Iron, Copper, Zirconium, Dysprosium.
[0055] The above raw materials are compounded in mass percentage, wherein samarium accounts for 20.78%, cobalt accounts for 51.81%, iron accounts for 13.93%, copper accounts for 6.34%, zirconium accounts for 1.71%, and dysprosium accounts for 5.43%.
[0056] In the quick-setting furnace, the above ingredients are smelted into alloys, and then cast into thin strip-shaped quick-setting sheets on water-cooled copper rollers; the quick-setting sheets are ground by a two-stage grinding process, and the quick-setting sheets are first coarsely crushed for disc grinding. The medium is gasoline, and the quick-setting sheet is ground into magnetic powder with a particle size of about 100 μm, and then the magnetic powder is calcined under vacuum conditions to obtain dry magnetic powder at a calcination temperature of 100 degrees; the obtained dry magnetic powder is subjected to jet milling, and the powder parti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com