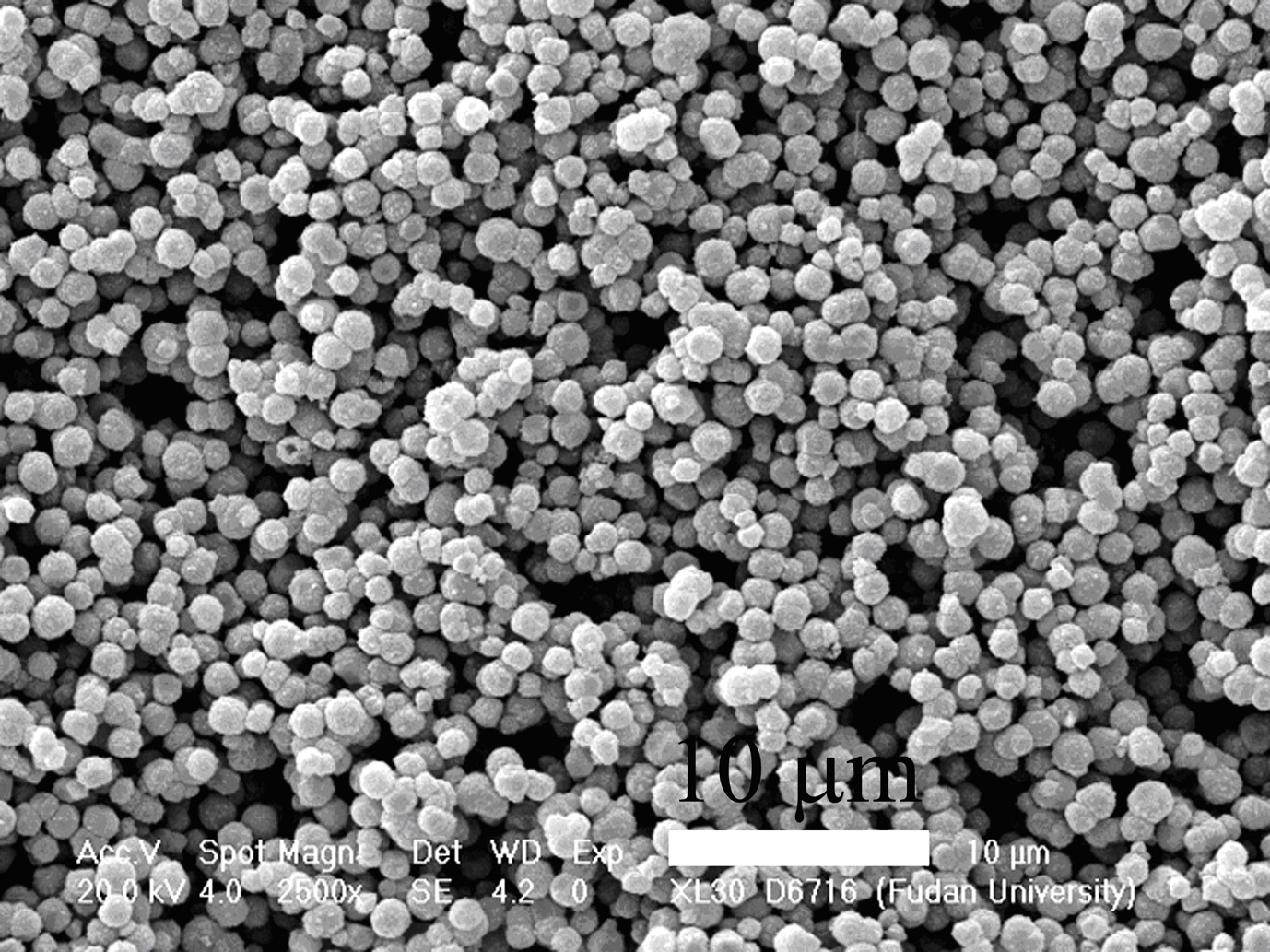
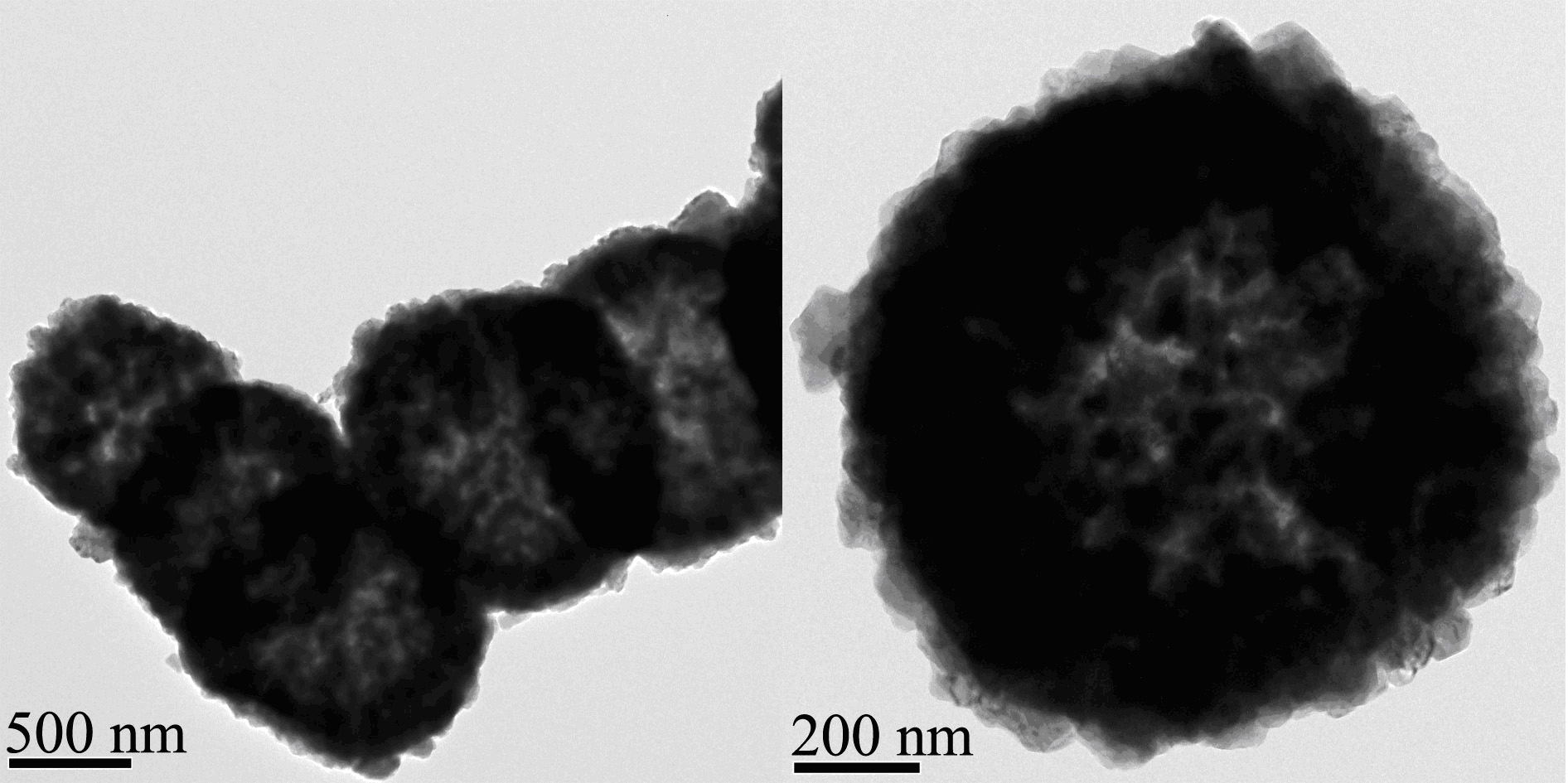
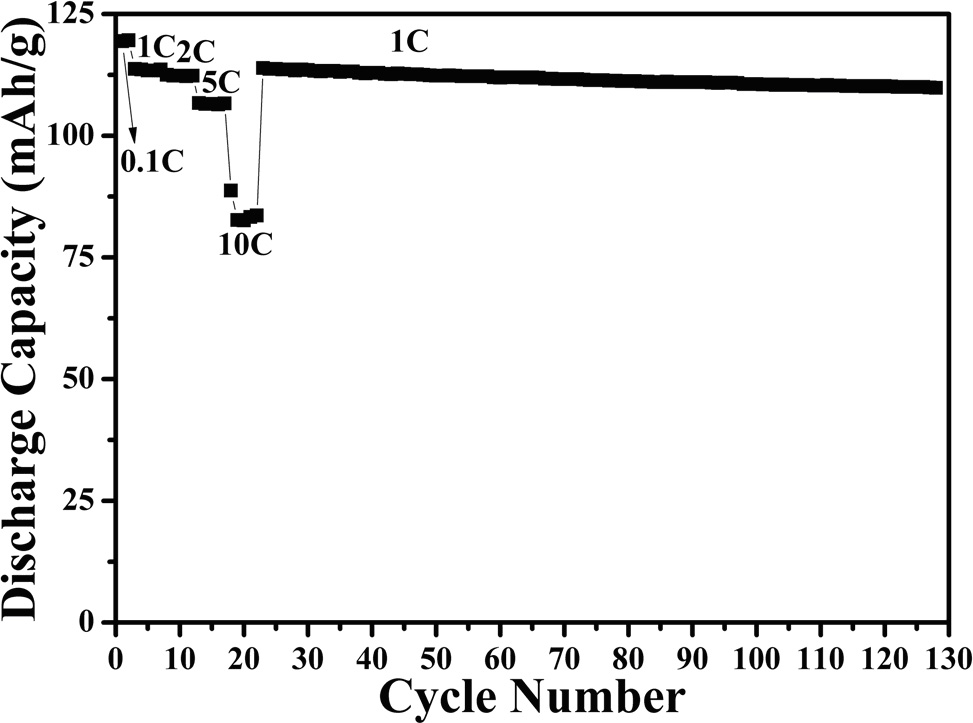
Method for preparing lithium manganate hollow ball material
A hollow ball, lithium manganate technology, applied in the direction of manganate/permanganate, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in ensuring uniform mixing of raw materials, difficulty in obtaining lithium manganate materials, affecting product performance, etc., to achieve superior rate performance, Good cycle performance and rate capability, easy processing results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 31.7 g of manganese chloride tetrahydrate was dissolved in 800 g of water and 63.2 g of ethanol to obtain solution A, and 16.8 g of sodium bicarbonate was dissolved in 800 g of water to obtain solution B. Pour solution B into solution A under vigorous stirring, continue stirring for 2 hours, filter with suction and dry to obtain microspheres of manganese carbonate. The prepared manganese carbonate microspheres were calcined at 400° C. for 2 hours to obtain porous manganese dioxide microspheres. Dissolve 0.6 g of lithium hydroxide monohydrate in 20 g of ethanol, add 2.44 g of porous manganese dioxide microspheres, stir evenly, evaporate the solvent at room temperature, and roast at 700 °C for 10 hours to obtain lithium manganate hollow sphere materials.
Embodiment 2
[0031] 128 g of 50 wt% manganese nitrate was dissolved in 800 g of water and 63.2 g of ethanol to obtain solution A, and 33.6 g of sodium bicarbonate was dissolved in 800 g of water to obtain solution B. Pour solution B into solution A under vigorous stirring, continue stirring for 2 hours, filter with suction and dry to obtain microspheres of manganese carbonate. The prepared manganese carbonate microspheres were calcined at 400° C. for 2 hours to obtain porous manganese dioxide microspheres. Dissolve 0.6 g of lithium hydroxide monohydrate in 20 g of ethanol, add 2.44 g of porous manganese dioxide microspheres, stir evenly, evaporate the solvent at room temperature, and roast at 700 °C for 10 hours to obtain lithium manganate hollow sphere materials.
Embodiment 3
[0033] 31.7 g of manganese chloride tetrahydrate was dissolved in 800 g of water and 63.2 g of ethanol to obtain solution A, and 21.2 g of sodium carbonate was dissolved in 800 g of water to obtain solution B. Pour solution B into solution A under vigorous stirring, continue stirring for 2 hours, filter with suction and dry to obtain microspheres of manganese carbonate. The prepared manganese carbonate microspheres were calcined at 400° C. for 10 hours to obtain porous manganese dioxide microspheres. Dissolve 0.99 g of lithium hydroxide monohydrate in 20 g of water, add 2.44 g of porous manganese dioxide microspheres, stir well, evaporate the solvent at room temperature, and roast at 700 °C for 10 hours to obtain lithium manganate hollow sphere materials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com