Method for producing industry molybdenum oxide from molybdenum concentrate
A technology for industrial molybdenum oxide and molybdenum concentrate is applied in the field of producing industrial molybdenum oxide from molybdenum concentrate, which can solve the problems of difficulty in producing acid with sulfur dioxide, pollution of flue gas and soot, and low recovery rate of molybdenum, and achieves high recovery rate of molybdenum, The effect of high practical value and low input cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
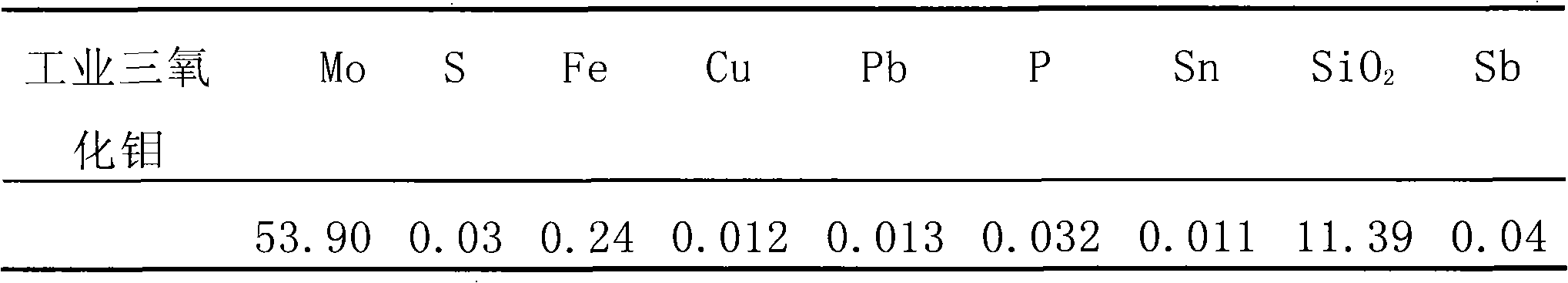
[0049] In this embodiment, the selected molybdenum concentrate is a high-lead molybdenum concentrate containing the following elements by weight: Mo: 42.37%, Cu: 0.15%, Pb: 0.25%, Ca: 0.08%, phosphorus: 0.11%, S : 30.15% and Fe: 2.73%. And when the selected molybdenum concentrate is used to produce industrial molybdenum oxide, the production process is as follows:
[0050] Step 1, crushing and grinding the molybdenum concentrate: crushing and grinding the selected molybdenum concentrate to obtain molybdenum concentrate powder with an average particle size below 200 mesh.
[0051] Step 2. Use acid solution to heat up and leach the impurities contained in the molybdenum concentrate powder: mix industrial hydrochloric acid with 200g of the molybdenum concentrate powder at a liquid-solid weight ratio of 5:1, and heat the molybdenum concentrate powder at a temperature of 92°C The industrial hydrochloric acid is used under conditions to leach impurities contained in the molybdenum ...
Embodiment 2
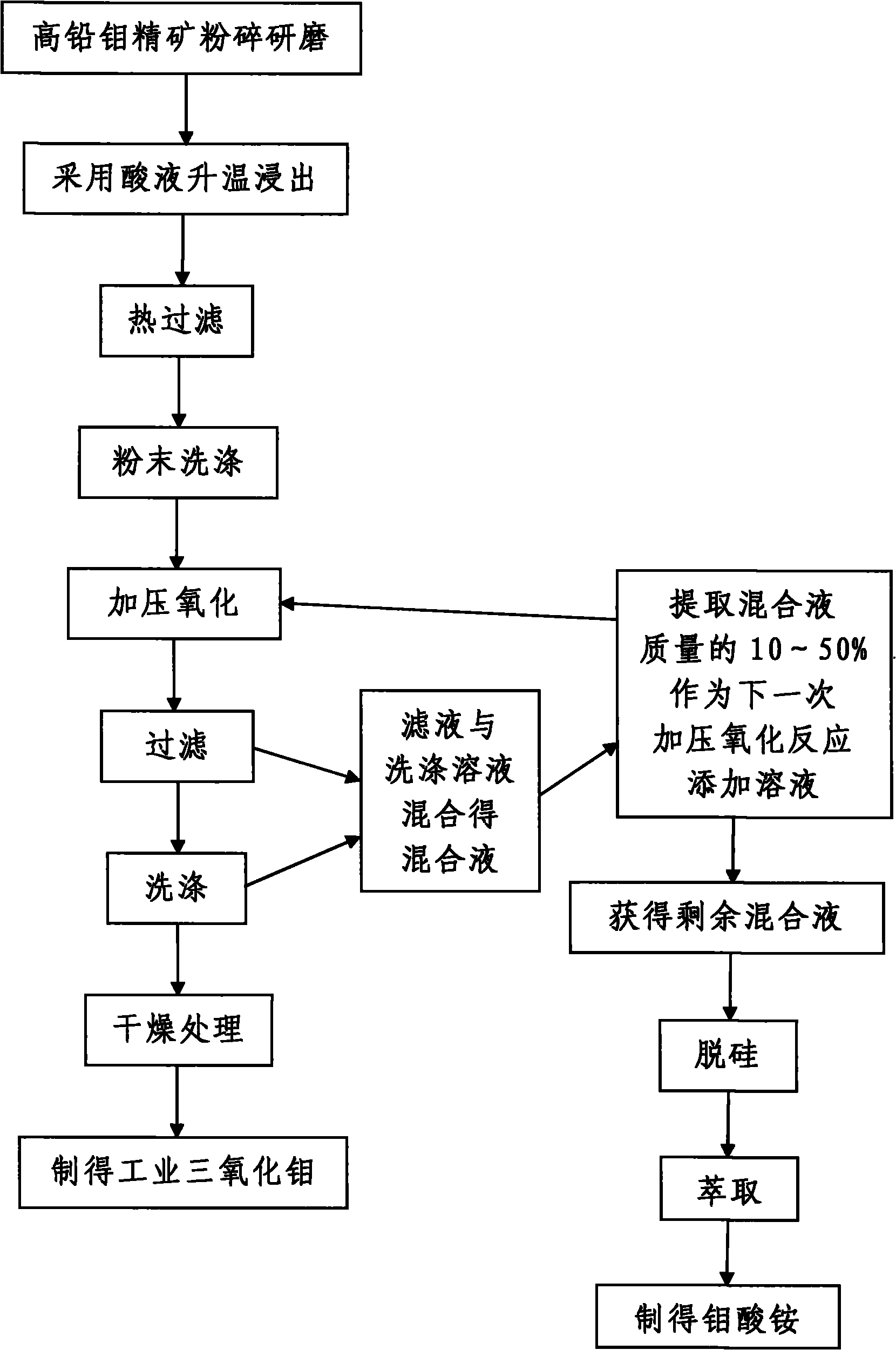
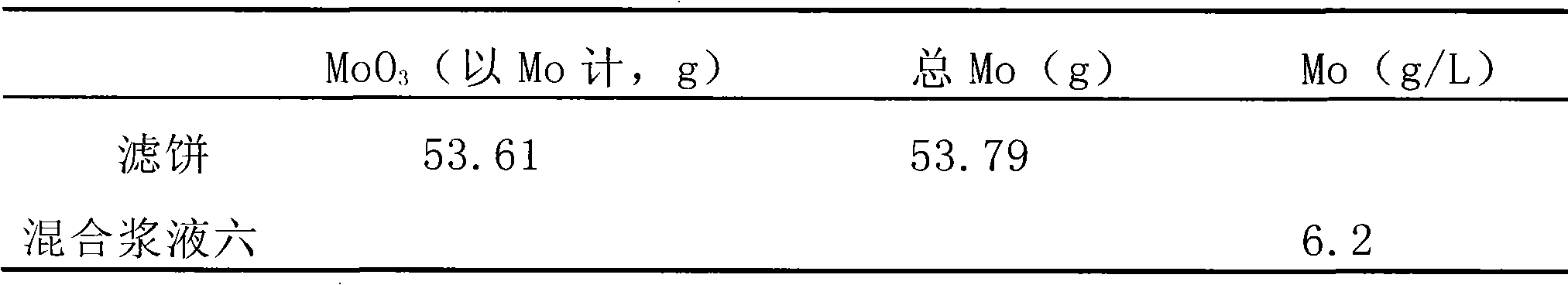
[0068] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Example 1 is that the collected washing solution described in step 7 is mixed with the mixed slurry 3 described in step 6 to obtain the mixed slurry 4, and then the collected washing solution is extracted. 50% of the above-mentioned mixed slurry quality is used as the pressurized oxidation reaction adding solution when producing industrial molybdenum oxide next time; When the solution is added to the pressurized oxidation reaction, in this embodiment, the quality of ammonium molybdate prepared by using the mixed slurry 4 is 5.6g. And the next production process of producing industrial molybdenum oxide from molybdenum concentrate is as follows:
[0069] 101. Pretreatment process of pressurized oxidation: according to step 1 to step 4, the selected molybdenum concentrate is crushed and ground, heated and leached, hot filtered and powder washed to obtain preliminary purified molybdenum concentrate powder. ...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Such as figure 1 As shown, in the present embodiment, different from Example 2 is: the volume concentration of the industrial hydrochloric acid adopted in the step 2 is 10%, and when carrying out heating up leaching, industrial hydrochloric acid and 200g molybdenum concentrate powder are mixed with liquid-solid weight ratio Mix at a ratio of 4.5:1, and use the industrial hydrochloric acid to leach the molybdenum concentrate powder at a temperature of 90°C to obtain a solid-liquid mixture after acid leaching, and the leaching time is 2.5h; During powder washing, the leached molybdenum concentrate powder described in step 3 is washed multiple times with hot water at 70°C; The solid-liquid weight percentage of the mixed slurry one obtained by adding water to the powder is 15%, and the weight percent of the molybdenum concentrate powder after the initial purification in the mixed slurry one is that the sodium nitrate added in the mixed slurry one is 3%, the pressurized oxi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com