Method for quickly screening oxygenase microbes or oxygenase genes
A technology of oxygenase and microorganisms, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of screening natural source microorganisms from environmental samples that have not been reported yet, and achieve the effect of improving screening sensitivity and high molar absorptivity coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1 takes 4-chloroindole as substrate screening producing cyclooxygenase strain
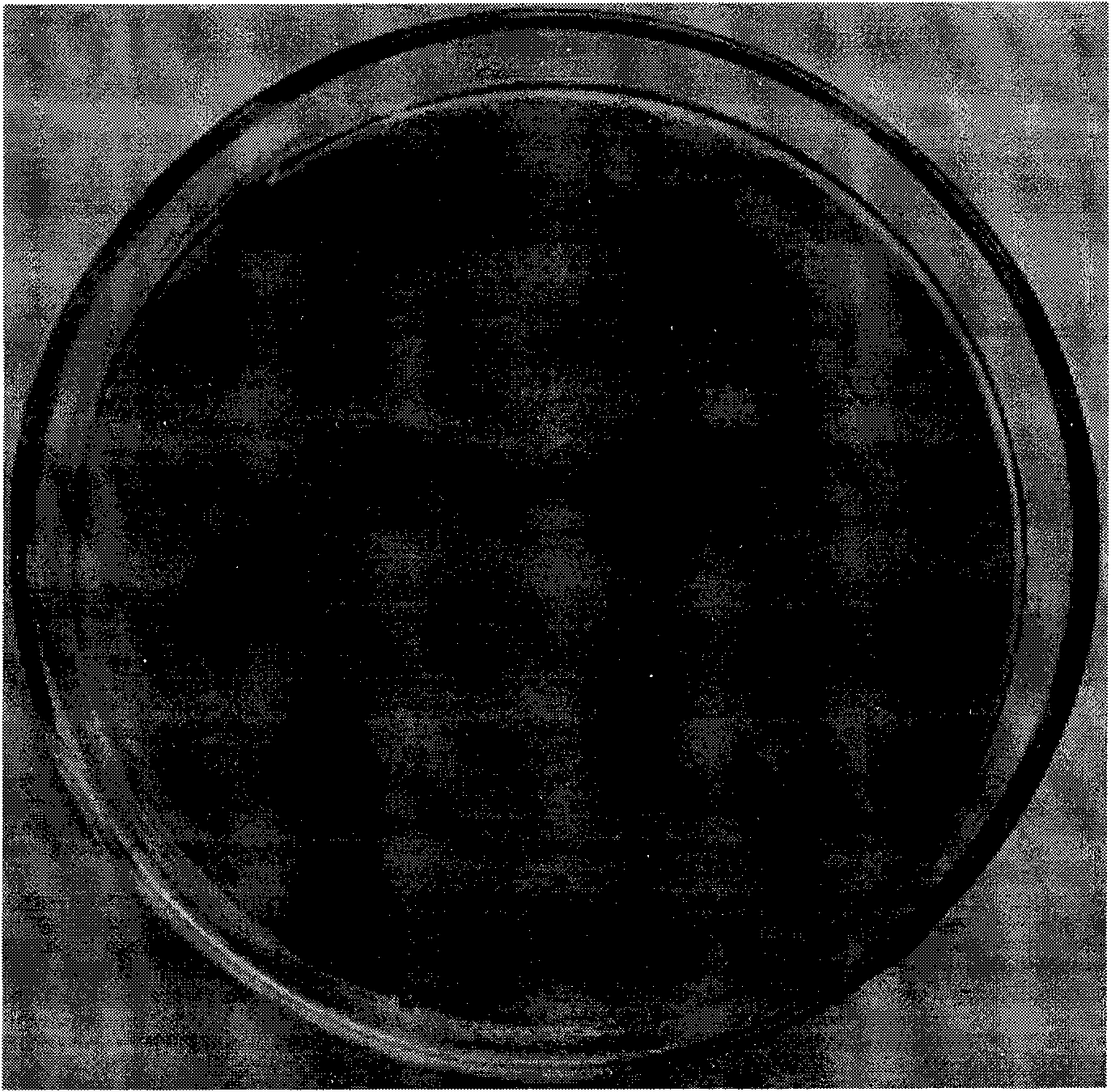
[0026] Activated sludge samples were taken from a sewage treatment plant, enriched in a medium containing M12 inorganic salts and styrene (concentration: 2mM), and cultured at 30°C and 225rpm for 10 days. Dilute the enriched culture solution onto a screening plate (M12+styrene 2mM+4-chloroindole 0.1mM+0.01% yeast powder+1.5% agar powder) and culture at 30°C for 3 days, multiple flakes can be seen on each plate blue plaque ( figure 1 ), pick out and continue to purify ( figure 2 ), and 11 pure strains were obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2 Using 4-methylindole as a substrate to screen cyclooxygenase-producing strains
[0028] The sample and enrichment method are the same as in Example 1, and the enriched culture solution is diluted onto a screening plate (M9+styrene 2mM+4-methylindole 0.2mM+0.05% yeast powder+1.5% agar powder) and cultured at 30°C for 3 One day, blue plaques appeared, and the purification was continued to obtain 15 pure strains.
[0029] Example 3 Using 4-indolecarboxylate as a substrate to screen cyclooxygenase-producing strains
[0030] The sample and enrichment method are the same as in Example 1. Dilute the enriched culture solution onto a screening plate (M9+styrene 3mM+4-indolecarboxylate methyl ester 0.3mM+0.06% yeast powder+1.5% agar powder) and culture at 30°C After 4 days, blue plaques appeared, and the purification was continued to obtain 12 pure bacterial strains.
Embodiment 4
[0031] Embodiment 4 uses 4-bromoindole as substrate screening to produce cyclooxygenase strain
[0032] Take from another sewage treatment plant sample, the enrichment method is the same as in Example 1, and the enrichment culture solution is diluted onto the screening plate (M9+styrene 3mM+4-bromoindole 0.2mM+0.05% yeast powder+1.5% agar powder ) was cultured at 30°C for 4 days, dark blue plaques appeared, and the purification was continued to obtain 10 pure strains.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com