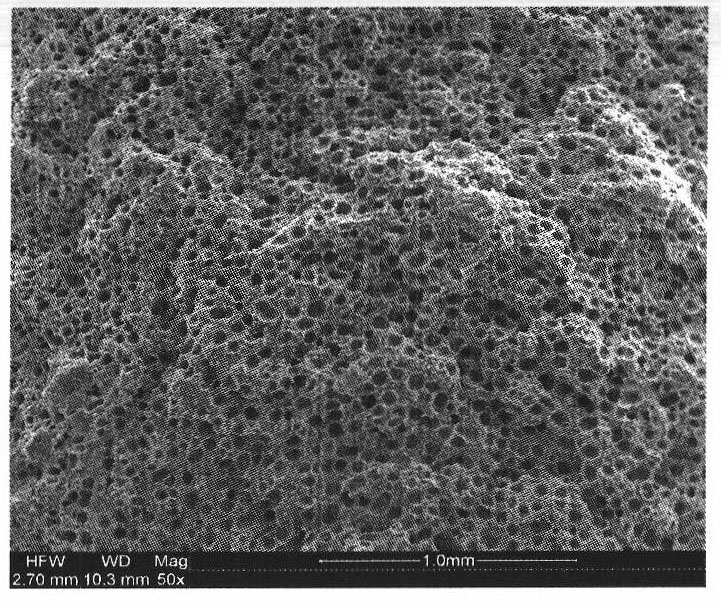
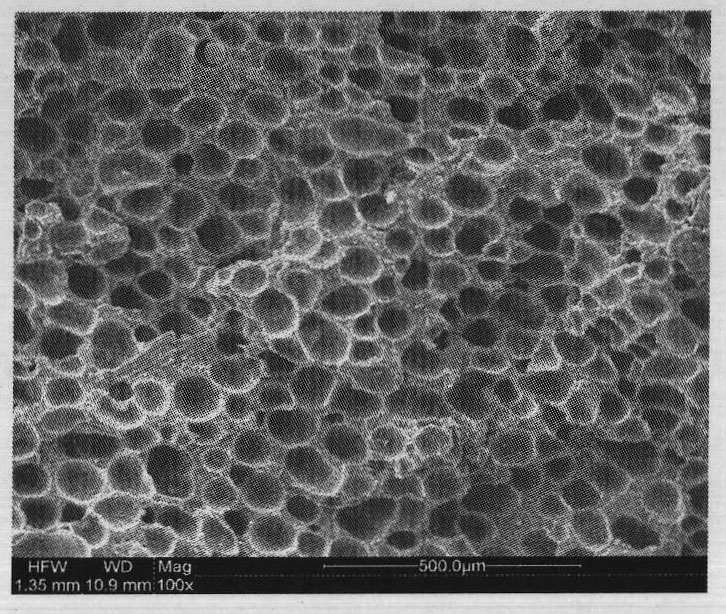
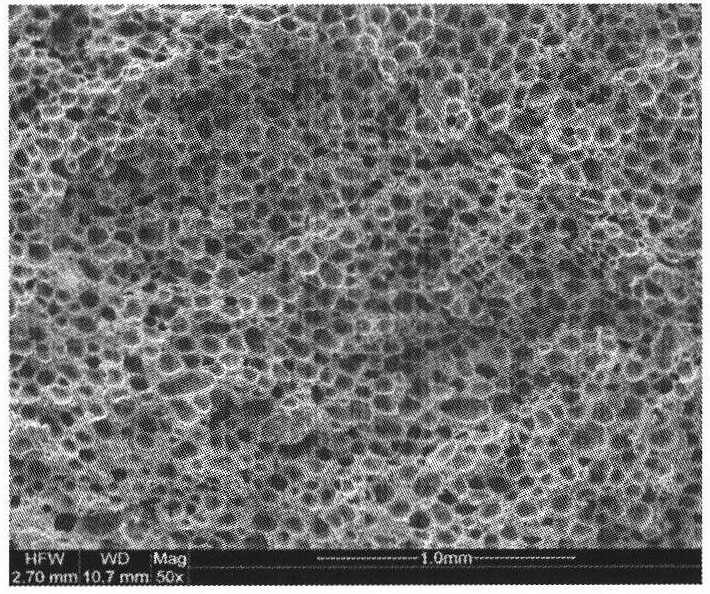
Injection microcellular foamed wood-plastic composite material and preparation method thereof
A wood-plastic composite material, injection foaming technology, applied in the direction of coating, can solve the problems of poor dispersion and uneven distribution of cells, and achieve the effect of high strength and toughness, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] (1) Process
[0065] Process recipe
[0066] 1. Wood plastic pellets
[0067] ① 30.0 parts by mass of wood flour with a particle size of 120-180 mesh;
[0068] ② Regenerated PP 70.0 parts by mass;
[0069] ② 4.0 parts by mass of zinc stearate;
[0070] ③ 6.0 parts by mass of PP grafted with maleic anhydride with a molecular weight of 1.0 to 15,000;
[0071] ⑤ 1.5 parts by mass of titanate coupling agent;
[0072] ⑥ 10.0 parts by mass of nano-calcium oxide;
[0073] 7. 1.5 parts by mass of nano zinc oxide;
[0074] ⑧ 1.0 parts by mass of superfine talcum powder;
[0075] 2. Foam masterbatch
[0076] ①LDPE 75.0 parts by mass;
[0077] ② 10.0 parts by mass of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer;
[0078] ③ 5.0 parts by mass of azodicarbonamide;
[0079] ④ 1.0 parts by mass of stearic acid;
[0080] Mix the wood powder, nano-adsorbent and ultra-fine talcum powder at high speed (1800-2000 rpm) for 10-15 minutes, add titanate coupling agent and then mix at high speed...
Embodiment 2
[0097] (1) Process
[0098] Process recipe
[0099] 1. Wood plastic pellets
[0100] ① 40.0 parts by mass of wood flour with a particle size of 120-160 mesh;
[0101] ② Regenerated PP 60.0 parts by mass;
[0102] ③ 3.0 parts by mass of stearic acid;
[0103] ④ 8.0 parts by mass of maleic anhydride grafted PP with a molecular weight between 2.5 and 3.0;
[0104] ⑤ 2.0 parts by mass of titanate coupling agent;
[0105] ⑥ 5.0 parts by mass of nano-calcium oxide;
[0106] ⑦Nano zinc oxide 1.0 parts by mass;
[0107] ⑧ 1.5 parts by mass of superfine talcum powder.
[0108] 2. Foam masterbatch
[0109] ①LDPE 82.5 parts by mass;
[0110] ② 5.0 parts by mass of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer;
[0111]③ 15.0 parts by mass of azodicarbonamide;
[0112] ④ 1.5 parts by mass of stearic acid;
[0113] Mix wood powder, nano-adsorbent and ultra-fine talcum powder at high speed (1500-1700 rpm) for 10-15 minutes, add titanate coupling agent and then mix at high speed (1500-1700 rp...
Embodiment 3
[0130] (1) Process
[0131] Process recipe
[0132] 1. Wood plastic pellets
[0133] ① 50.0 parts by mass of wood flour with a particle size of 160-200 mesh;
[0134] ② Regenerated PP 50.0 parts by mass;
[0135] ③ 5.0 parts by mass of stearic acid;
[0136] ④ 10.0 parts by mass of PP grafted with maleic anhydride with a molecular weight between 25,000 and 30,000;
[0137] ⑤ 1.0 parts by mass of titanate coupling agent;
[0138] ⑥ 7.5 parts by mass of nano calcium oxide;
[0139] ⑦Nano zinc oxide 1.0 parts by mass;
[0140] ⑧ 1.0 parts by mass of superfine talcum powder.
[0141] 2. Foam masterbatch
[0142] ①LDPE 90.0 parts by mass;
[0143] ② 7.5 parts by mass of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer;
[0144] ③ 10.0 parts by mass of azodicarbonamide;
[0145] ④ 0.5 parts by mass of stearic acid;
[0146] After mixing the wood powder, nano-adsorbent and ultrafine talc powder at high speed (2200-2400 rpm) for 15 minutes, add titanate coupling agent and then mix at high...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com