Room temperature hydrogen sensor based on palladium-nanometer-scale stannic oxide film type electrode
A nano-tin dioxide and sensor technology, applied in the direction of material resistance, etc., can solve the problems of lack of gas selectivity, hydrogen embrittlement film shedding, loss of hydrogen sensing performance, etc., to achieve improved detection sensitivity, enhanced absolute strength, and tiny size Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
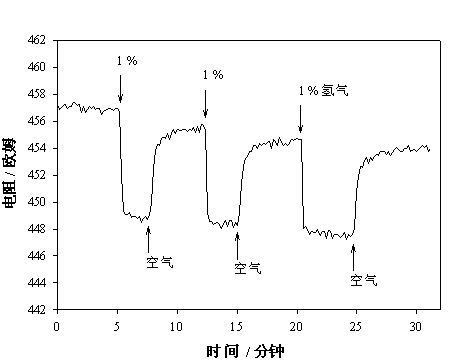
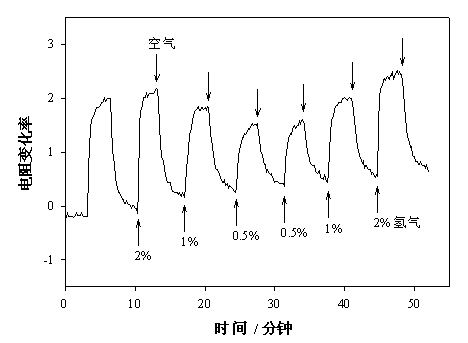
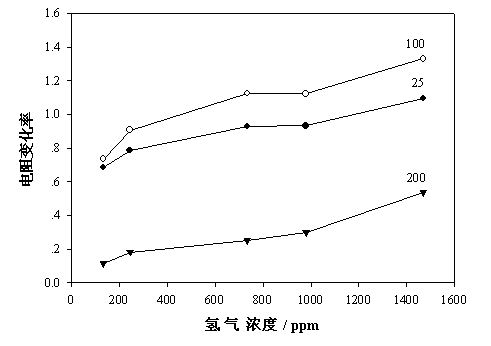
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The preparation method of the palladium-nano-tin dioxide thin-film electrode in the hydrogen sensor is to use aluminum oxide as the negative film, and adopt the method of electroless electrolysis to deposit palladium and nano-tin dioxide on the negative film as the hydrogen-sensitive material. The palladium-tin dioxide in the hydrogen sensor is The process steps of nano-tin dioxide film electrode preparation include: preparation of nano-tin dioxide, pretreatment of alumina ceramic sheet, composite coating, post-treatment and other steps. The specific process is as follows:
[0024] ● Preparation of nano-tin dioxide: Add tin protochloride dihydrate into ethanol solution, adjust the pH to 11, and make the Sn (divalent) concentration reach 15.8 mM. After the obtained white suspension was magnetically stirred for 1 hour, it was transferred to a stainless steel pot with Telflon coating, heated in a muffle furnace at 120°C for 6 hours, centrifuged and dried overnight at 50°C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com