Nondestructive testing method of heterogeneous property of solid material
A solid material, non-destructive testing technology, applied in the use of sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves to analyze solids, ultrasonic waves/sonic waves/infrasonic waves, etc., can solve problems such as large analysis errors, inability to guarantee measurement reliability, and high equipment costs, and achieve improvement Effects of measurement accuracy, avoidance of overheating phenomenon, and improvement of spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
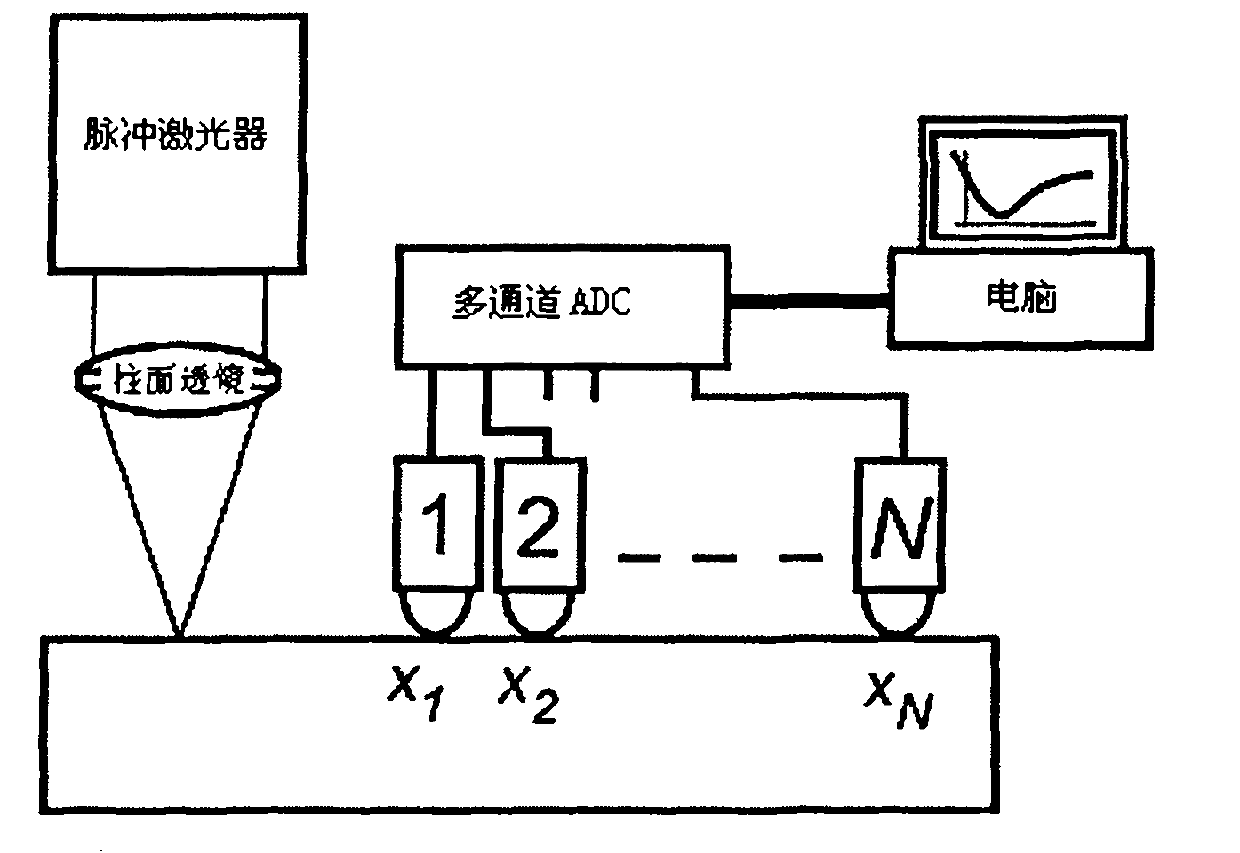
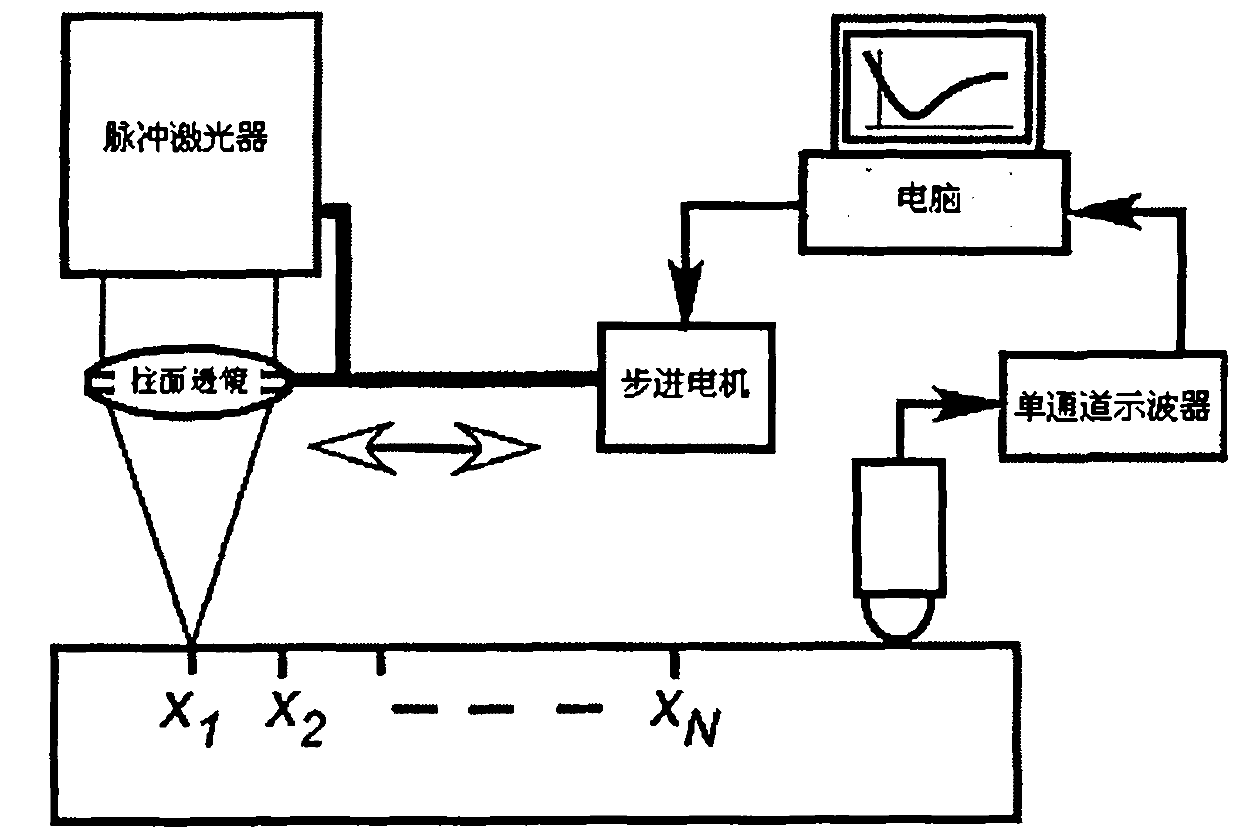
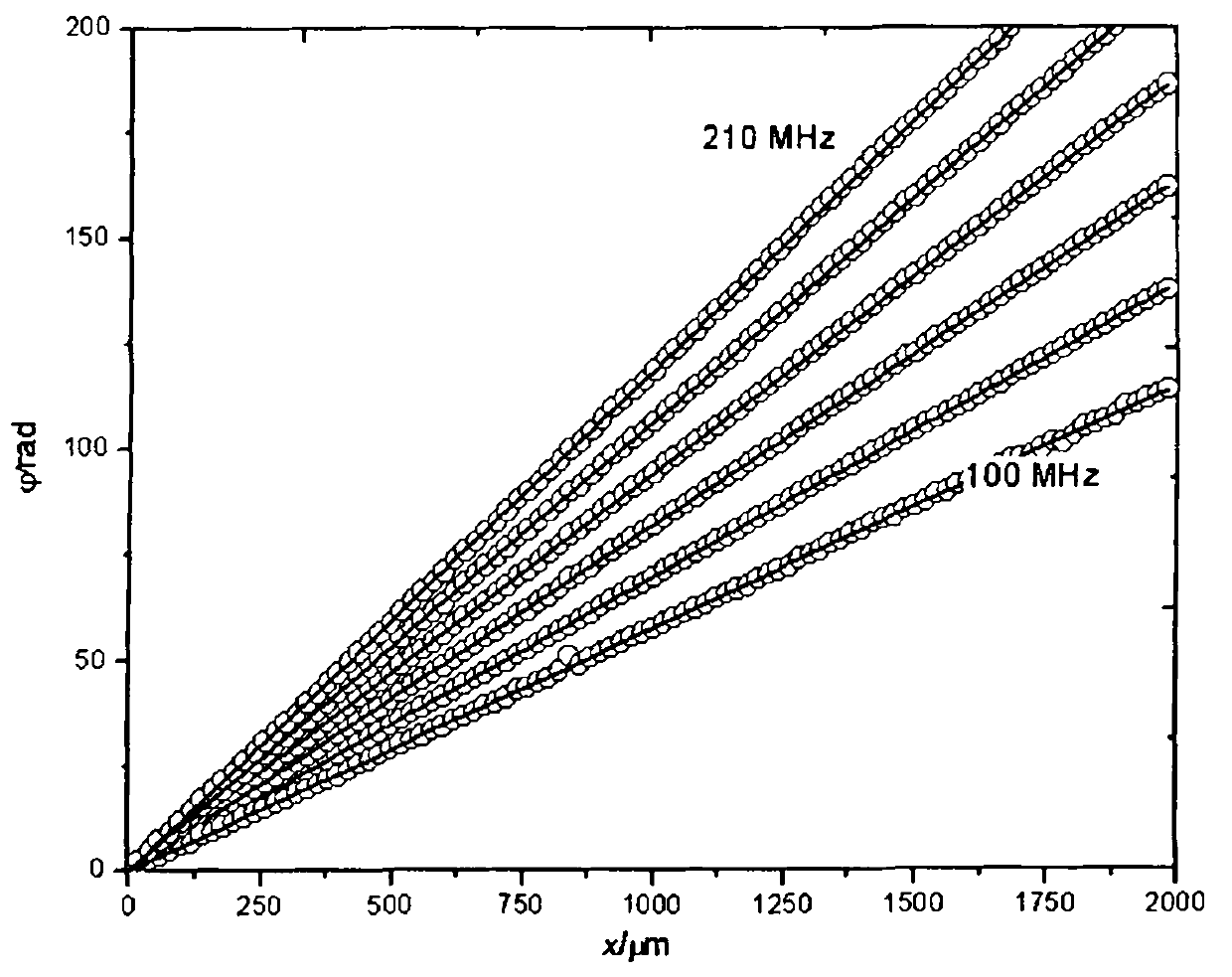
[0032] Taking the second method of detecting N surface acoustic wave signals excited by laser and propagating at different distances as an example, a pulsed laser with a pulse width of 1 nanosecond and a wavelength of 532 nm is used to excite the surface acoustic wave. As an example of a sample with non-uniform properties, a layer of 800nm diamond film attached to a silicon wafer is used. This layer of film with different properties from the base silicon can cause surface acoustic wave dispersion. The bandwidth of the measured surface acoustic wave signal can reach 300MHz, which is much higher than the 2.25MHz bandwidth of the acoustic wave excited by the piezoelectric transducer in Literature 1, so the spatial resolution of the non-uniformity that can be measured is much higher. many. Let's compare this scheme using N equidistant points with the phase velocity error obtained by using only two-point surface acoustic wave signals in the literature [1]. Assuming that the propa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com