Production method of fermented vine tea, vine tea extract and vine tea drink
A technology of a rattan tea extract and a production method, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as precipitation, and achieve the effects of high availability and increased flavonoid and polyphenol content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
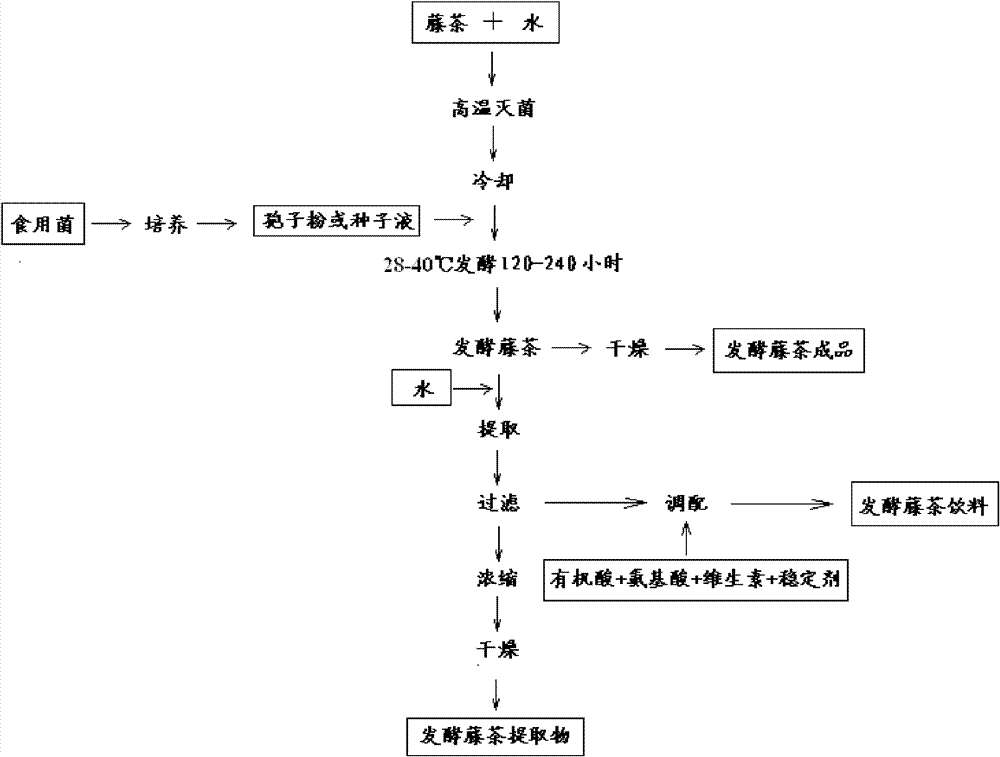
[0032] Example 1: Weigh 50kg of rattan tea, add 55kg of water, soak for 1-2 hours, and steam at 100-120°C for 20 minutes. Insert Aspergillus oryzae spore powder by 3% of the weight of vine tea, and ferment for 150 hours at 30-32°C. The mature fermented material was dried at 80-100° C. to obtain 49.4 kg of fermented vine tea.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Weigh 80 kg of rattan tea, add 80 kg of water, soak for 2-3 hours, and steam at 100-120° C. for 30 minutes. Insert Aspergillus niger seed solution by 5% of the weight of rattan tea, and ferment for 168 hours at 28-30°C. Add 1500kg of water to the mature fermentation material, extract at 40-50°C for 1 hour, filter, add 800kg of water to the filter residue, extract at 40-50°C for 1 hour, filter, combine the two filtrates, concentrate under reduced pressure, and dry to obtain fermented vine tea extract 35.2 kg.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Weigh 100kg of rattan tea, add 120kg of water, and steam at 100-120°C for 20-30 minutes. Insert Monascus spore powder according to 8% of the weight of vine tea, and ferment for 240 hours at 30-32°C. Add 3000kg of water to the mature fermentation material, extract at 40-50°C for 2 hours, and filter. Add citric acid, malic acid, amino acids, vitamins, stabilizers, etc. to make a fermented vine tea drink, fill it, and sterilize it to become the finished product.
[0035] In summary, the present invention provides a production method about edible fungus fermented vine tea and its products, specifically including the following:
[0036] 1. Provide food grade Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, Monascus, yeast and lactic acid bacteria;
[0037] 2. A vine tea fermentation material is provided, which is a mixture of vine tea and water;
[0038] 3. The vine tea fermentation material is sterilized at high temperature, and after cooling, add edible fungi, and ferm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com