Method for sintering anhydrous calcium sulfate biomedical material
A biomedical material, anhydrous calcium sulfate technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of lack of commercial application value, no sintering behavior, no formability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
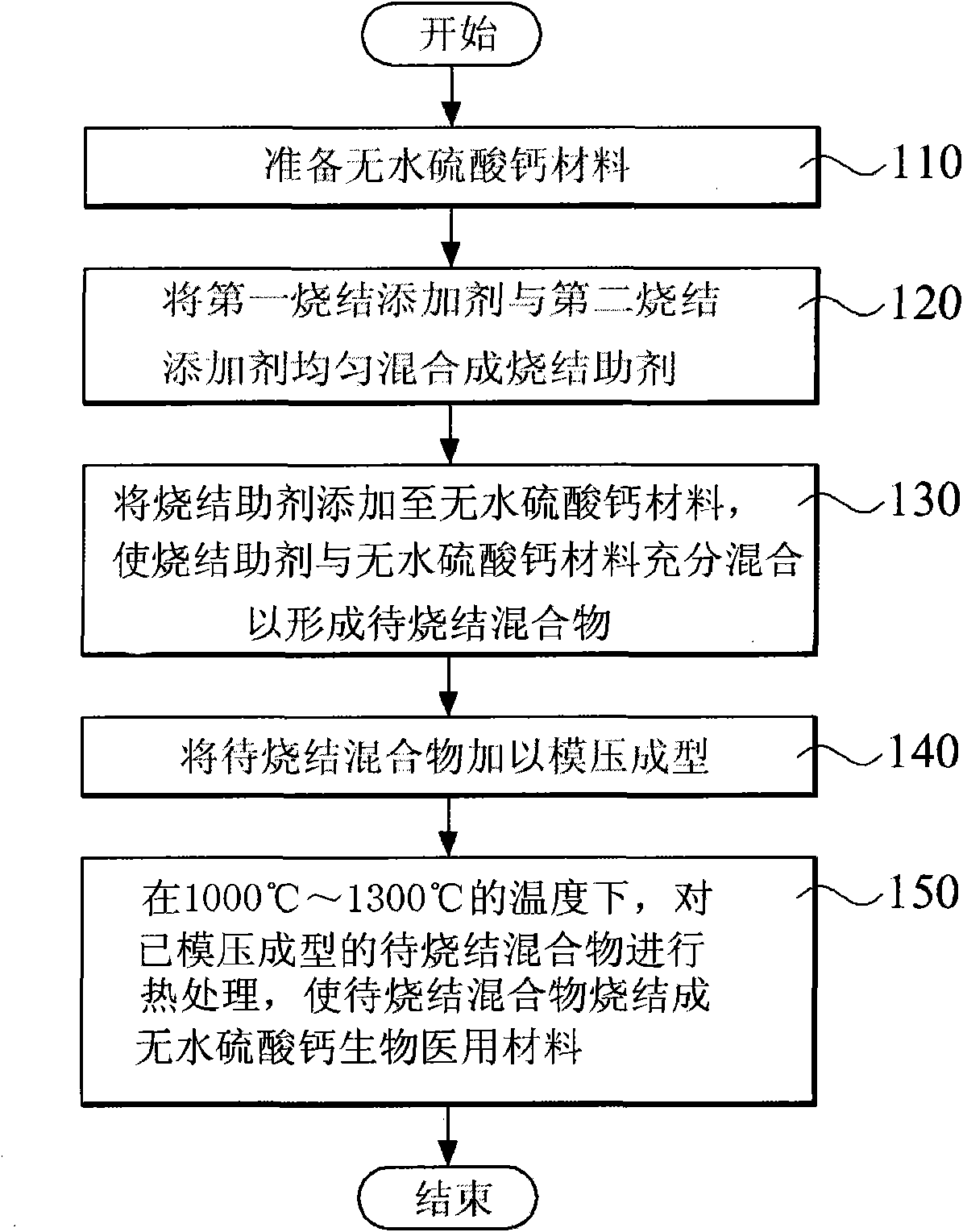
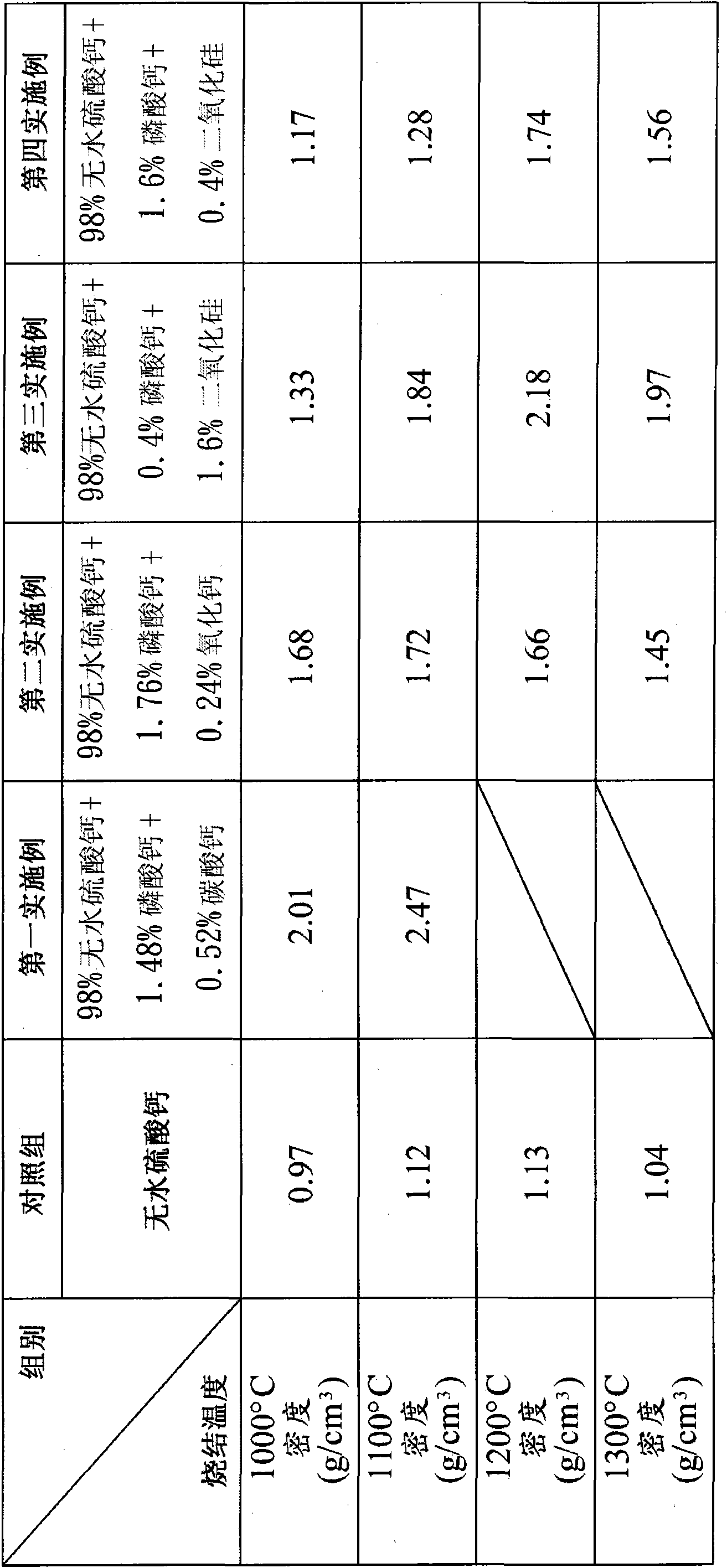
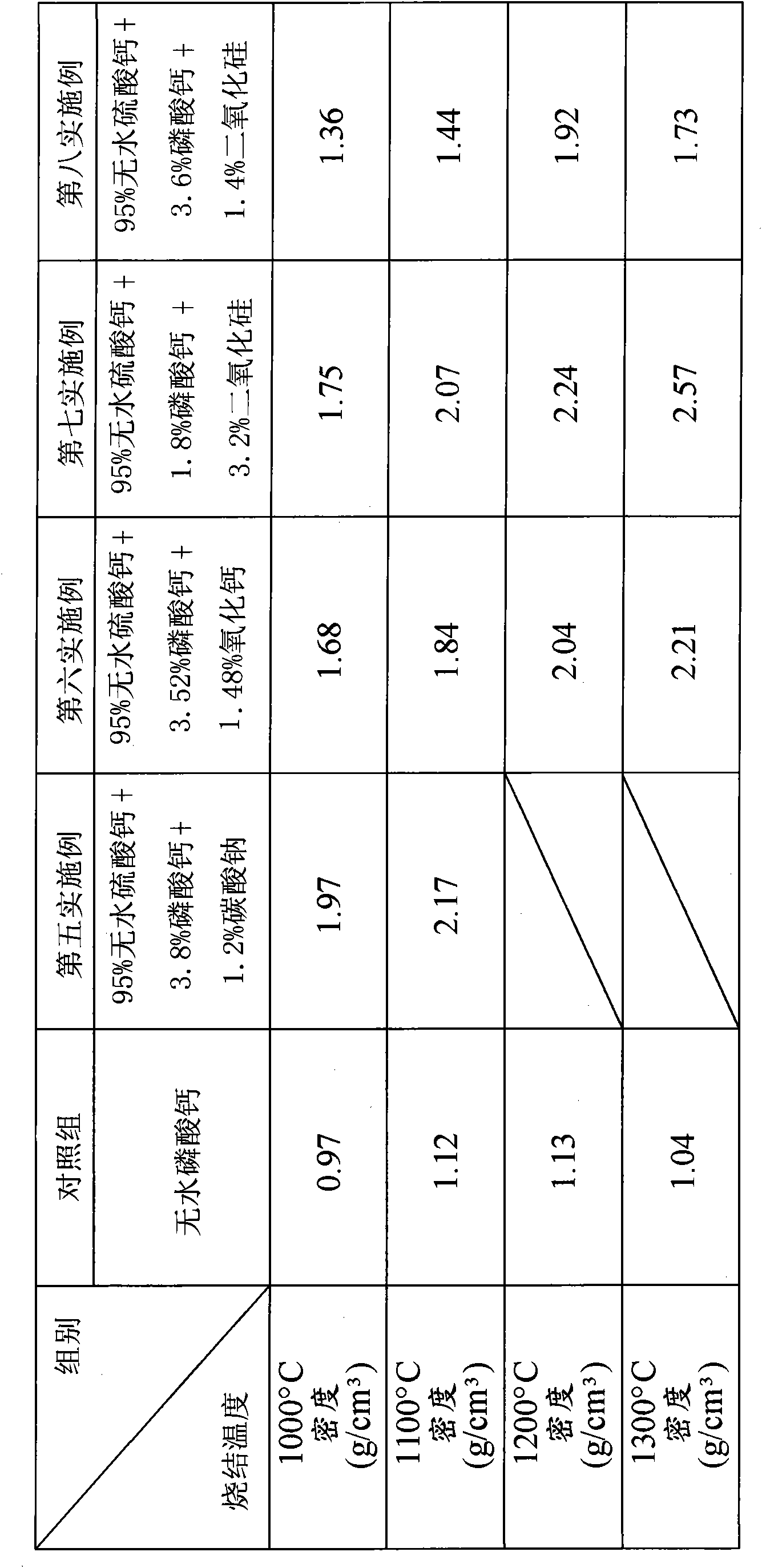
[0031]Due to the sintering method of anhydrous calcium sulfate biomedical materials provided by the present invention, it can be widely used in the production of biomedical materials for various biomedical purposes, especially as a bone substitute to induce rapid growth and repair of bones. Protection, and its combined implementations are too numerous to enumerate, so I will not repeat them one by one here, but only list twelve preferred embodiments for specific illustration, and cite relevant experimental results to verify the aforementioned effects.
[0032] figure 1 It is a flow chart showing the simple sintering method of the first embodiment to the twelfth embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 Shown, when realizing the present invention, must prepare anhydrous calcium sulfate (anhydrous calciumsulfate) material (step 110) earlier, and a first sintering additive and a second sintering additive are uniformly mixed into a sintering aid (step 120) , wherein ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com