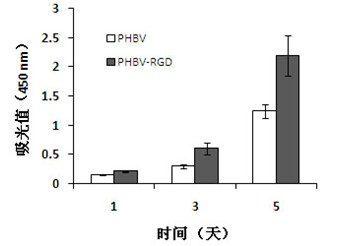
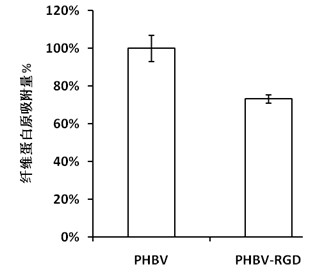
Surface biological functionalization method for hydrophobic medical high polymer materials
A polymer material and biological functionalization technology, applied in the field of biofunctional modification of the surface of hydrophobic medical polymer materials, can solve the problem of lack of cell recognition sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
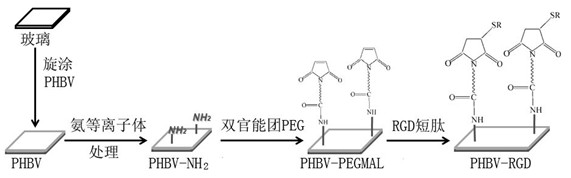
[0015] 1) The PHBV film was prepared by spin coating method; PHBV was dissolved in chloroform at a concentration of 10 (w / v)%, and stirred evenly by a magnetic stirrer. The PHBV film was prepared on the surface of the glass slide by spin coating: put the clean slide (Φ: 10 mm) in a homogenizer, drop 60 μL of PHBV solution onto the surface of the slide, and spin coat at 4000 rpm for 30 sec. Then put the spin-coated slides with PHBV membrane into a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for overnight drying in vacuum to remove residual chloroform.
[0016] 2) Amino groups were modified on the surface of the PHBV membrane: (a) Amino groups were introduced into the surface by ammonia plasma treatment: the prepared PHBV membrane was placed in a plasma cleaning machine, vacuumed to 7 Pa, and ammonia gas was introduced to 50 Pa, 60 W process 120 sec. Or (b) introduce amino groups on the surface through dopamine: Dissolve 40 mg of dopamine in 20 mL of 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5) to make a rea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com