Pseudomonas fluorescens of endophytic fungi of achnatherum inebrians and application thereof to biological control
A technology of Pseudomonas fluorescens and endophytic bacteria, applied in the field of endophytic bacteria, to achieve the effect of safe and reliable prevention and control, no pollution to the environment, and no harm to human health
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
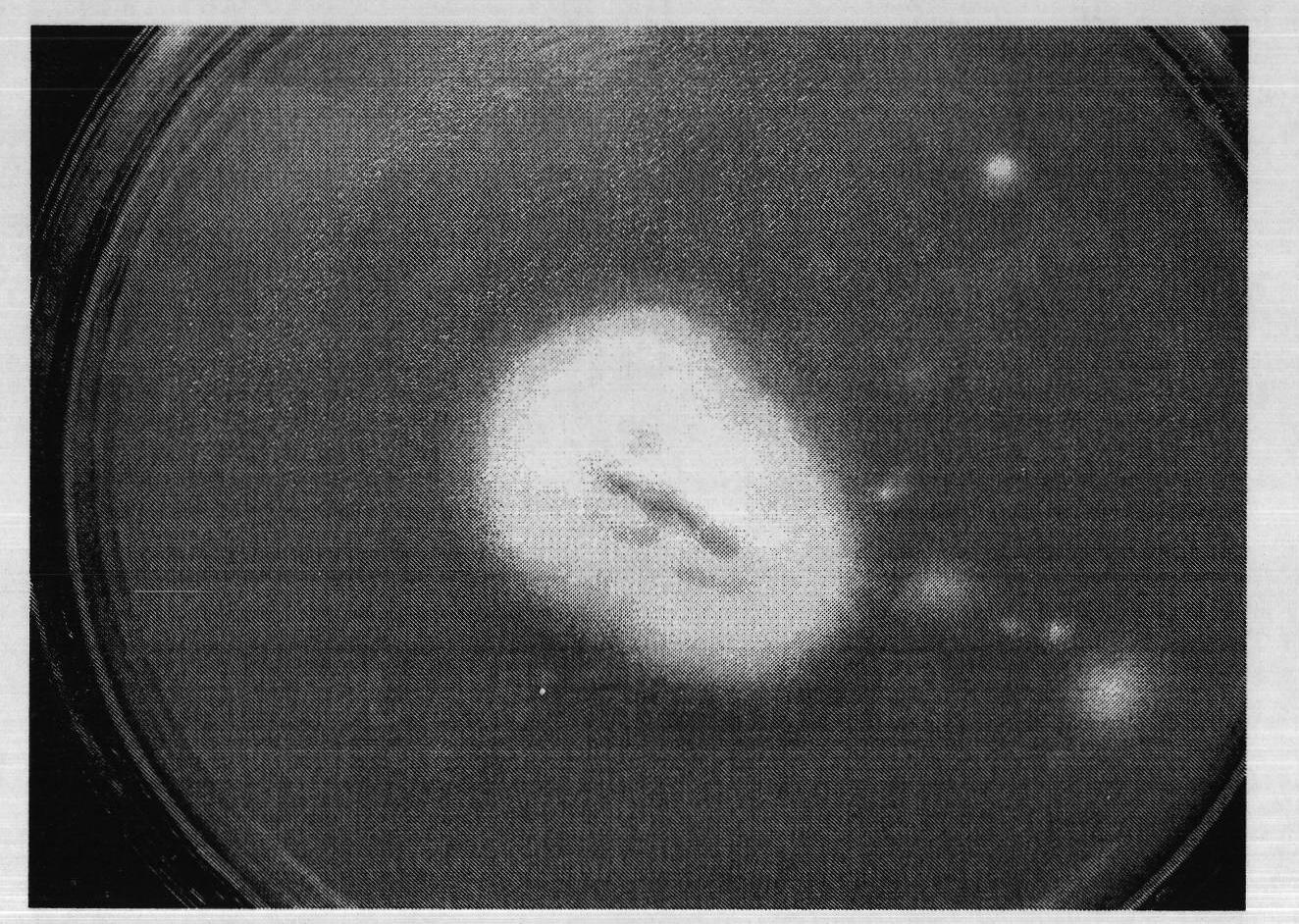
[0029] Example 1: Isolation, screening and identification of endophyte Claviceps purpurea CGMCC.No3073
[0030] Through the sampling of Drunken Horse Grass in Nanshan Mountain in Urumqi, the samples were divided into root, leaf and seed parts. Sampling adopts 5-point sampling method (east, south, west, north, middle) at every distance of 10 meters, and each point selects 1 strain of test grass, and each strain of grass gets root, leaf, seed (maturity stage), each 2 organ samples were taken. Put the sampled organs of this subspecies into food storage bags and bring them back to the laboratory for isolation.
[0031] Rinse the sample with sterile water first, then soak it in 75% alcohol for 30s, rinse it with sterile water, then soak it with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 1min, rinse it three times with sterile water, add sterile water to grind, absorb the grinding solution Spread on beef extract peptone medium, Gao's No. 1 medium, and PDA medium respectively. Beef extract peptone...
Embodiment 2
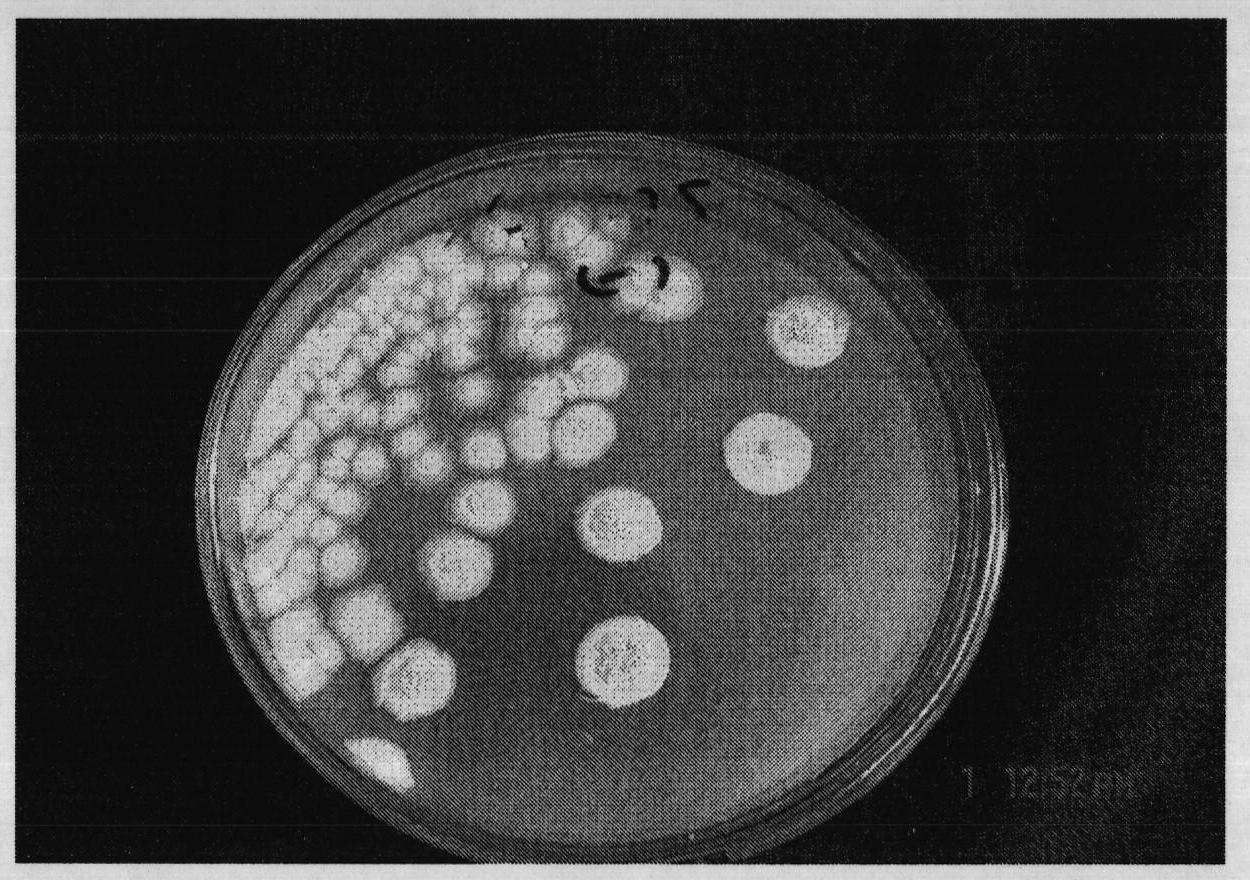
[0041] Example 2: Isolation, screening and identification of endophyte Pseudomona fluorescens CGMCC.No3026
[0042] Through the sampling, screening, and separation of Urumqi Nanshan Drunken Horse Grass, the specific method can be as described in Example 1. See attached image 3 , 5
[0043] The obtained GA colony was round with white hyphae. Microscopic observation shows long rod-shaped, medium-growing spores. According to the ninth edition of "Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacterio-logy" ("Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacterio-logy") and "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual", the shape, size, physiological and biochemical reactions of strain GA were detected. The biological characteristics of the invented GA strains are shown in Table 2.
[0044] Table 2: Physiological and biochemical characteristics of insecticidally active strain GA
[0045]
[0046] GA utilizes bacterial universal primers 27F and 1492R:
[0047] 27F: (5'AGAGTTTTTATCNTGGCTCAG3')
[004...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment three: the growth factor of ergot fungus (Claviceps purpurea) CGMCC.No 3073
[0052] The strain PF-2 was inoculated on PDA medium containing different concentrations of salt (NaCl), antibiotic (ampicillin) and pH, and cultured in a 28°C incubator for 7 days. Then the strain PF-2 was connected to the PDA medium, and placed in 4°C, 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 55°C, 60°C, respectively. Cultivate in an incubator. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0053] Table 3: Effects of temperature, pH, salt, and antibiotics on the growth of strain PF-2
[0054] temperature(℃)
[0055] It can be concluded from Table 3 that the bacterial strain PF-2 can grow in the environment of temperature 20°C-45°C, pH7-8, NaCl concentration 0.5%-8%, ampicillin concentration 50μg / ml-400μg / ml, especially respectively It is most suitable for growth when the temperature is 35°C-40°C, pH7, NaCl concentration 7%-8%, ampicillin concentration 50μg / ml-100μg / m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com