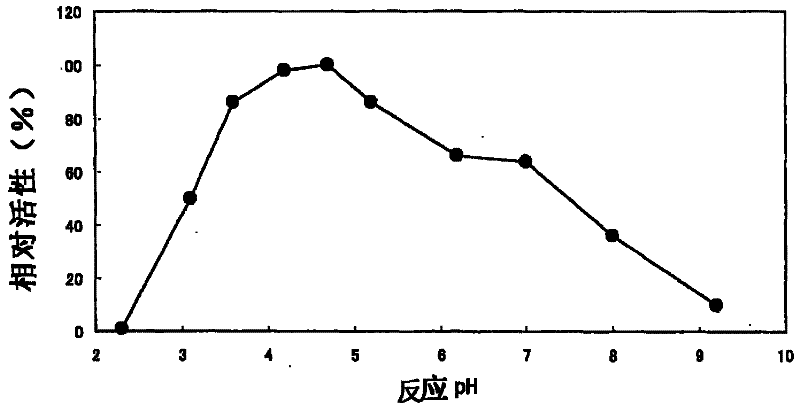
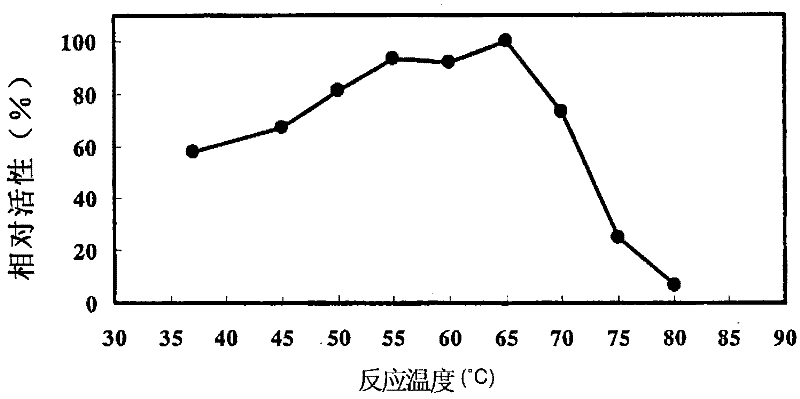
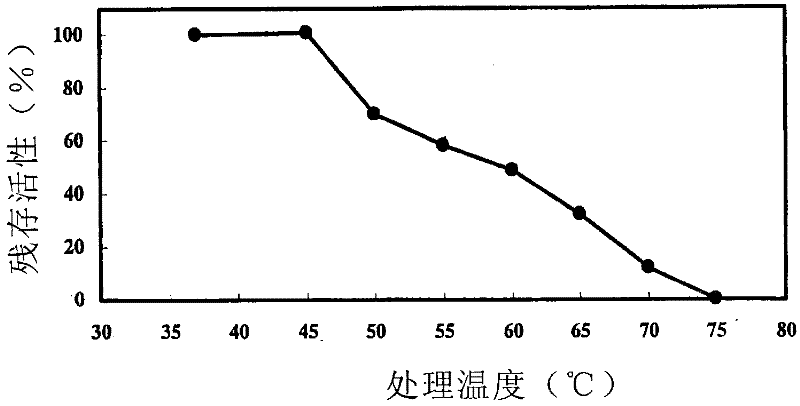
Phospholipase C, food enzyme agent comprising same and processing method for food raw materials
A phospholipase and food technology, applied in the field of phospholipase C, can solve problems such as insufficient efficacy and safety problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0183] Example 1: Phospholipase C was purified from the FERM ABP-10200 strain of Aspergillus oryzae
[0184] 1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0185] In the 500ml Erlenmeyer flask (seed flask) that added 100ml of sterilized culture medium with the composition shown in Table 2, inoculate 1ml of 5% sodium deoxycholate solution through filter sterilization, and aspergillus oryzae (Aspergillus oryzae) The bacterial body of FERM ABP-10200 strain was shaken at 170rpm at 26°C for 7 days.
[0186] Table 2
[0187] culture medium
[0188]
[0189] Polypeptone 40g
[0190] Yeast Extract 5g
[0191] Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g
[0193] 1000ml after adding pure water
[0194]
[0195] After the cultivation, centrifugation was performed at 10000G for ten minutes at 4°C, and the obtained supernatant was used as a crude enz...
Embodiment 2
[0212] Example 2: Purification of Phospholipase C from IAM 13907 Strain of Aspergillus tamarii
[0213] 1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0214] In the 500ml capacity Erlenmeyer flask (seed flask) that has the substratum of composition shown in 100ml Table 2, inoculate 1ml of the IAM 13907 strain of 5% sodium deoxycholate solution and Aspergillus tamarii through filter sterilization Bacteria were cultured with shaking at 170 rpm for 5 days at 26°C. After the incubation, centrifugation was performed at 10000G for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the obtained supernatant was used as a crude enzyme solution.
[0215] 2) Preparation of purified enzyme solution
[0216]In this example, purification was carried out in the same manner as described in 3) of Example 1 to obtain a purified enzyme solution.
[0217] 3) Molecular weight determination of purified enzyme
[0218] This example is to measure with the same method described in 4) in the embodiment 1. The purified enzyme show...
Embodiment 3
[0219] Example 3: Phospholipase C was purified from NBRC 4190 strain of Aspergillus oryzae
[0220] 1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0221] Add 100ml of sterilized 500ml Erlenmeyer flask (seed flask) with the medium shown in Table 3, inoculate the bacterium of NBRC 4190 strain of Aspergillus oryzae, and shake at 170rpm at 26°C Cultured for 7 days.
[0222] table 3
[0223] culture medium
[0224]
[0225] Fish meal 50g
[0226] 1000ml after adding pure water
[0227]
[0228] After the incubation, centrifugation was performed at 10000G for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the obtained supernatant was used as a crude enzyme solution.
[0229] 2) Preparation of purified enzyme solution
[0230] First, 600 ml of the crude enzyme solution obtained in 1) was dialyzed 5 times every 12 hours using 8000 ml of 10 mM tris-hydrochloric acid buffer solution (pH 7.5). T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com