Semiconductor structure and manufacturing method thereof
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as hindering device performance and low dielectric constant, and achieve the effect of improving performance and reducing EOT
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
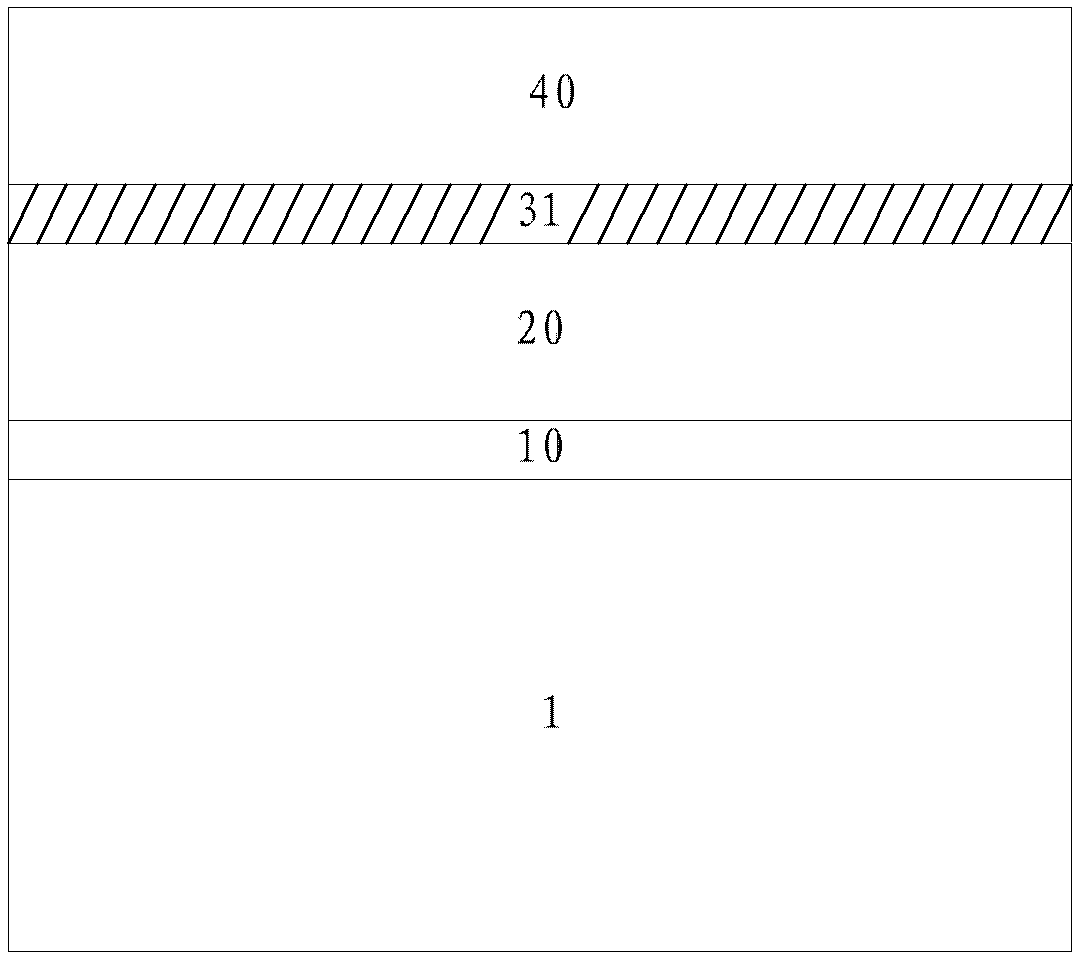
[0031] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a semiconductor structure according to an embodiment of the present invention. The semiconductor structure includes an interface layer 10 , a gate dielectric layer 20 , an oxygen absorbing layer 31 and a metal gate electrode layer 40 in sequence from the substrate 1 upward. Wherein, the metal atom in the oxygen absorbing layer 31 has a higher ability to bind oxygen than the atoms in the gate dielectric layer 20 and the interface layer 10 below the oxygen absorbing layer 31 .
[0032] In this embodiment, the thickness of the oxygen absorbing layer 31 is set so that the oxygen in the interface layer 10 can be partially adsorbed, or the oxygen in the interface layer 10 can be completely adsorbed, and the specific amount of adsorption needs to be set according to the process conditions. Set and adjust.
[0033] The material of the oxygen absorbing layer 31 includes one or more of metal and metal nitride. Wherein, the dielec...
Embodiment 2
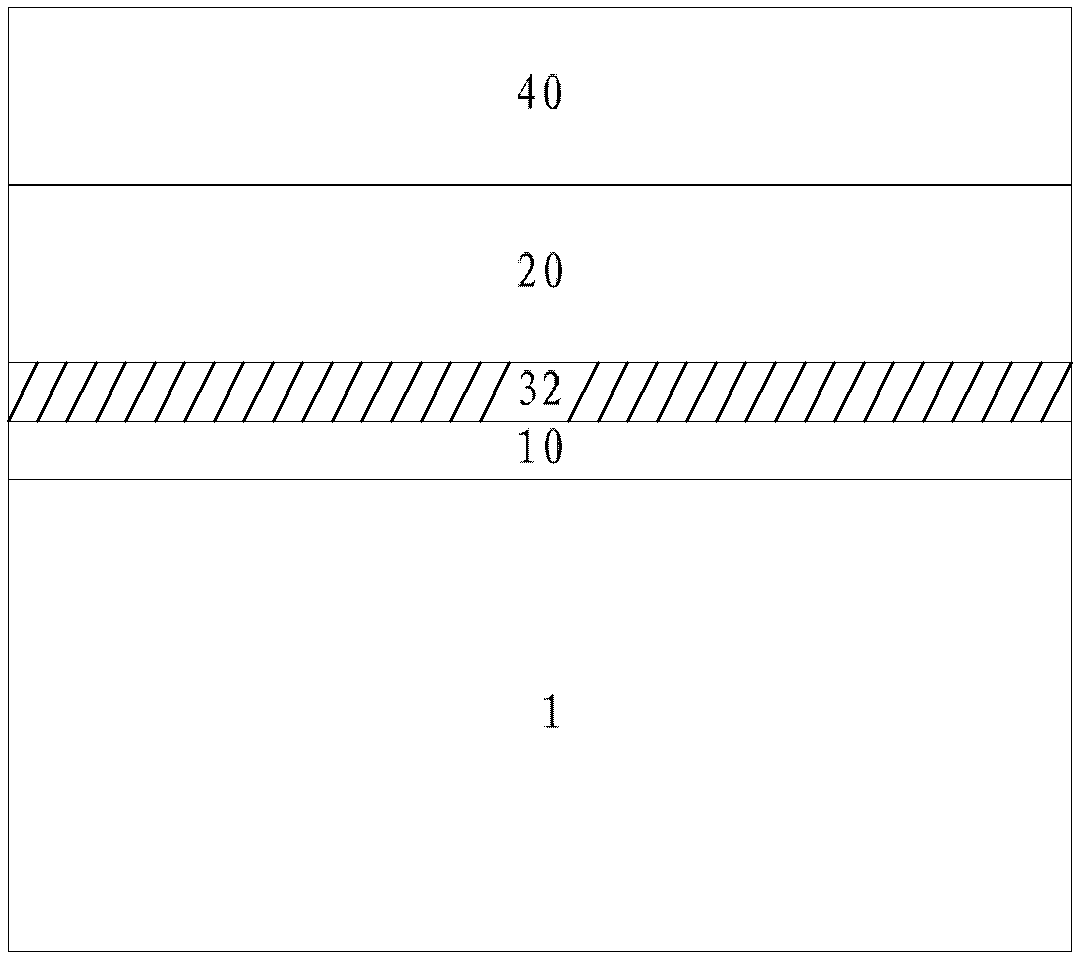
[0037] Such as figure 2 Shown is a schematic diagram of a semiconductor structure according to another embodiment of the present invention. The semiconductor structure includes an interface layer 10 , an oxygen absorbing layer 32 , a gate dielectric layer 20 and a metal gate electrode layer 40 from the substrate 1 to the top.
[0038]The setting of the oxygen absorbing layer 32 in this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here for the sake of simplicity. The difference is that in this embodiment, the oxygen absorbing layer 32 is formed on the interface layer 10, and the absorbing The ability of metal atoms in the oxygen layer 32 to bind oxygen is higher than the ability of atoms in the interface layer 10 below the oxygen absorbing layer 32 to bind oxygen.
[0039] In order to realize Embodiment 2, the present invention also proposes another method for manufacturing a semiconductor structure, comprising the following steps: firstly setting a ...
Embodiment 3
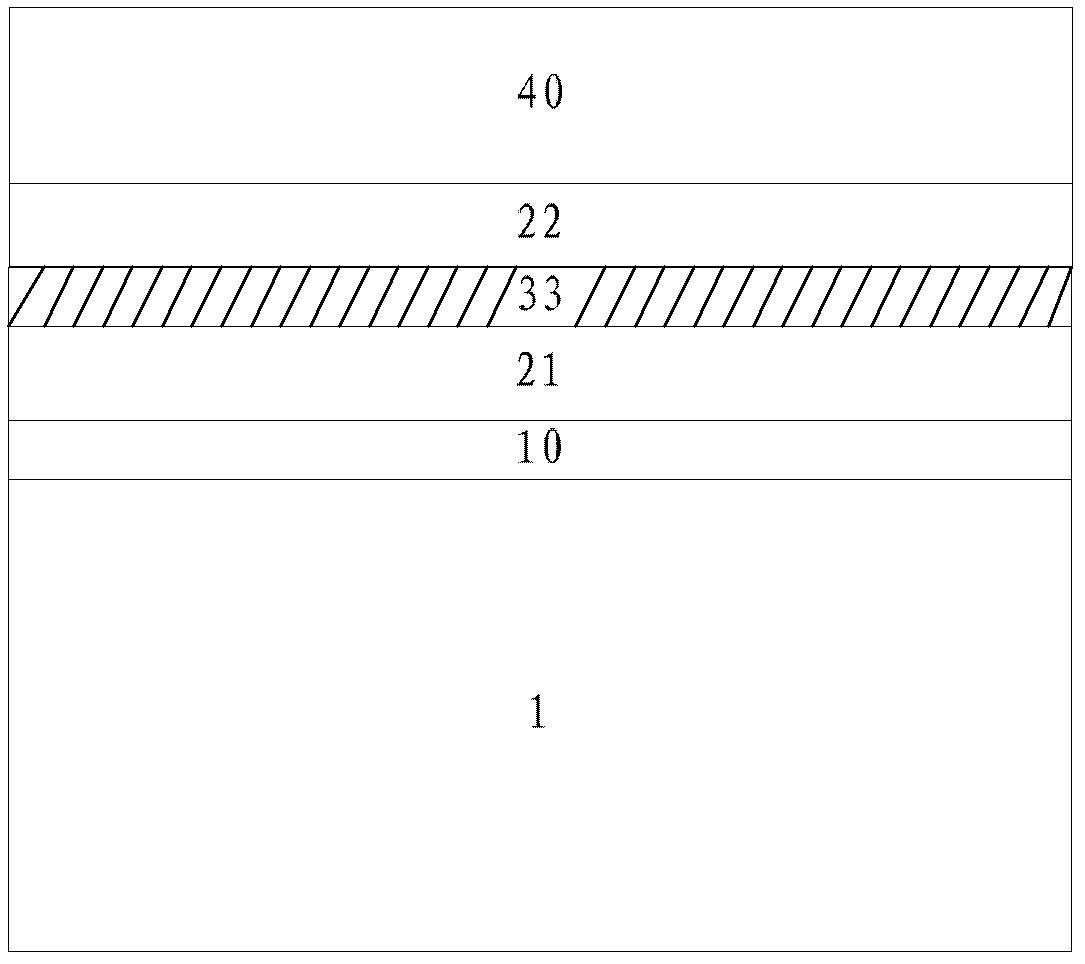
[0041] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of a semiconductor structure according to yet another embodiment of the present invention. The semiconductor structure includes: an interface layer 10, a first gate dielectric layer 21, an oxygen absorbing layer 33, a second gate dielectric layer 22 and Metal gate electrode layer 40 .
[0042] The arrangement of the oxygen absorbing layer 30 in this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here for the sake of simplicity. The difference is that in this embodiment, the oxygen absorbing layer 33 is formed on the first gate dielectric layer 21 and the second gate dielectric layer 22, and the metal atoms in the oxygen absorbing layer 33 have a higher binding ability to oxygen than the interface layer 10 below the oxygen absorbing layer 33 and the first gate dielectric layer 21. , that is, the oxygen absorbing layer 33 needs to have a stronger ability to bind oxygen than the first ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com