Two color-related mutations in apple MdMYB1 gene and detection method thereof
An apple and gene technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as inability to detect, and achieve the effects of reduced experimental cost, simple and practical identification method, and shortened electrophoresis time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Detection of mutations and identification of plant coloring traits of apple cultivars by CAPS marker method
[0031] Step 1, test materials: leaves or flowers of 8 common apple varieties: Fuji, Gala, Jinshuai, Guoguang, Hongxing, Hongyu, India, and Green Banana.
[0032] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0033] Step 3, PCR amplification: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
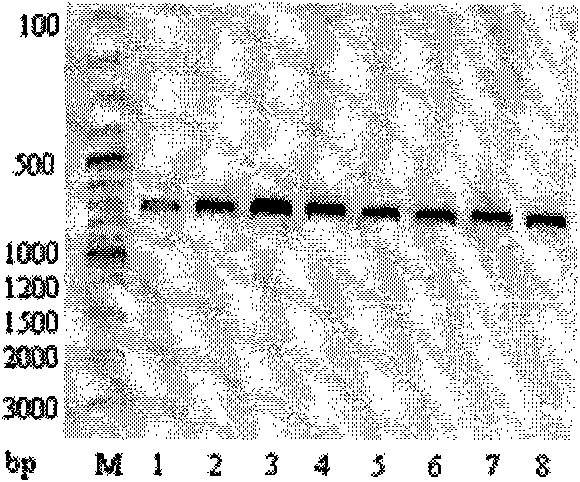
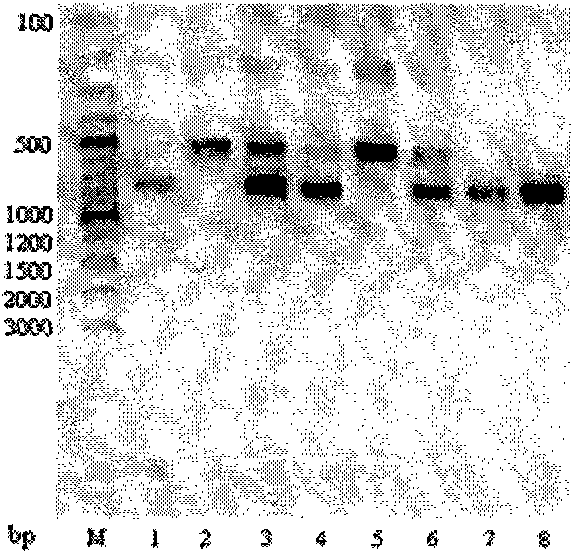
[0034] Step 4, enzyme digestion experiment: Take 5 μL of the PCR product and add it to a test tube, then add 2 μL of reaction buffer (10x), 1 μL (10 U) of restriction endonuclease Pml I and 12 μL of water, and carry out enzyme digestion in a 37°C water bath for 2-3 hours. Mix 20 μL of digested products with 5 μL of loading dye, stain with ethidium bromide, and perform electrophoresis on 1.2% agarose gel at 120V to check the digested products. The results are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0035] Step 5, analysis of coloring trait...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Detection of mutations and identification of coloring traits of apple hybrid offspring by CAPS marker method
[0037] Step 1, test material: use Fuji and Gala apples as parents to cross to obtain seeds, and the leaves of apple hybrid progeny plants obtained after the seeds are sown are used as test materials.
[0038] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0039] Step 3, PCR amplification: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0040] Step 4, enzyme digestion experiment: Take 5 μL of the PCR product and add it to a test tube, then add 2 μL of reaction buffer (10x), 1 μL (10 U) of restriction endonuclease Pml I and 12 μL of water, and carry out enzyme digestion in a 37°C water bath for 2-3 hours. 20 μL of digested products were mixed with 5 μL of loading dye, stained with ethidium bromide, and checked by electrophoresis on 1.2% agarose gel at 120V.
[0041] Step 5, analysis of coloring traits of apple hybri...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Using Mutation Site 206 to Identify Plant Coloring Traits of Apple Varieties
[0043] Step 1, test material: the same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0044] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0045] Step 3, PCR amplification: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0046] Step 4, electrophoresis inspection: the same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
[0047] Step 5, PCR product sequencing: same as the aforementioned sequencing method.
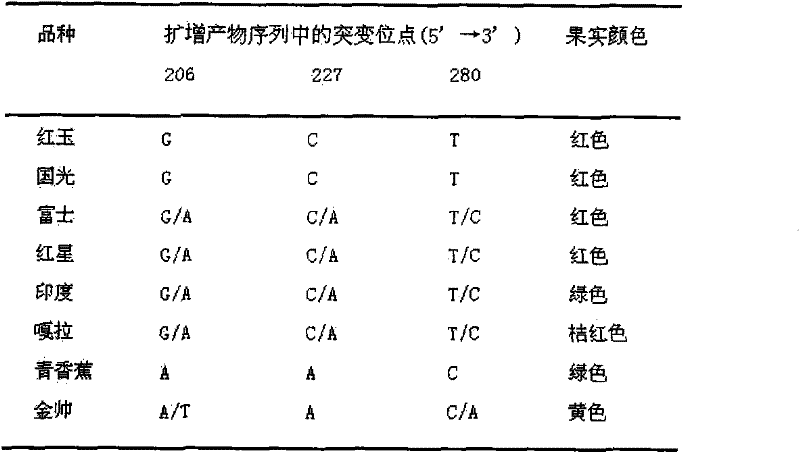
[0048] Step 6, analysis of coloring traits of apple cultivars: In view of the fact that the newly found mutation site 206 (that is, at -1624bp upstream of the transcription start point of MdMYB1-1 gene) can provide the same mutation site as the former apple coloring traits dCAPS molecular marker mutation site The information shows that the base information of the newly obtained mutation site 206 is the same as the previous apple coloring traits dCAPS m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com