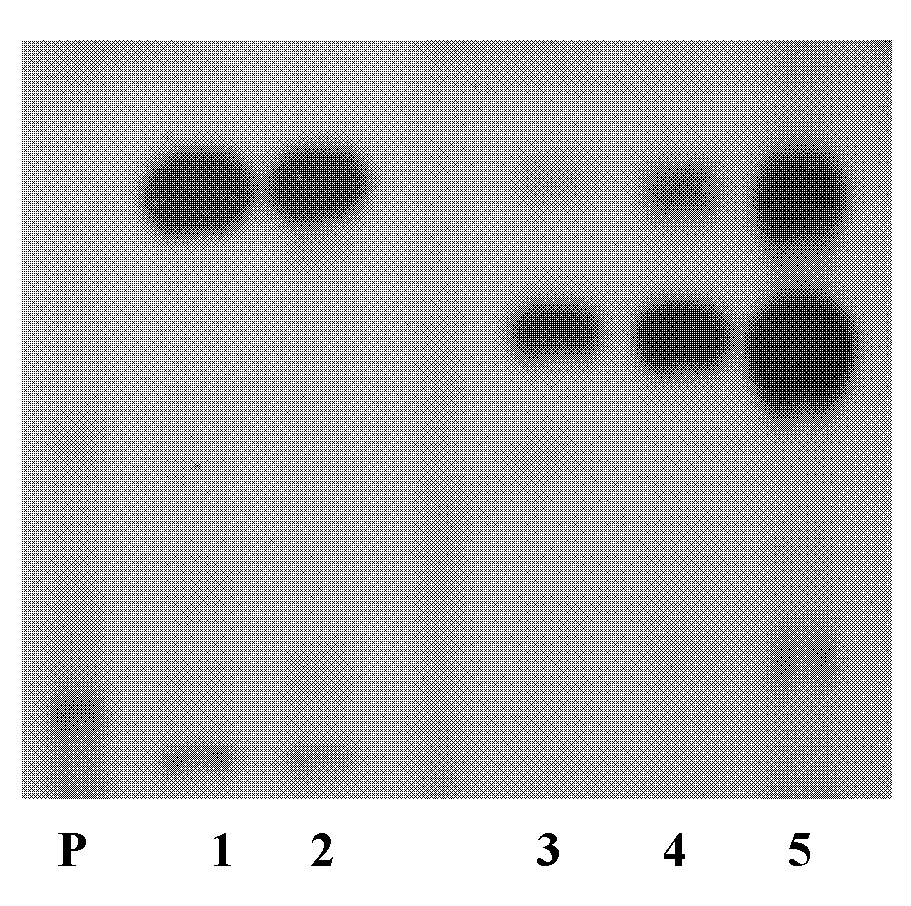GbRPS1 gene for resisting plant fusarium wilt and verticillium wilt and application thereof
A plant resistance technology, applied in the field of broad-spectrum disease resistance protein, can solve the problem of no significant resistance to Fusarium wilt and Verticillium wilt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
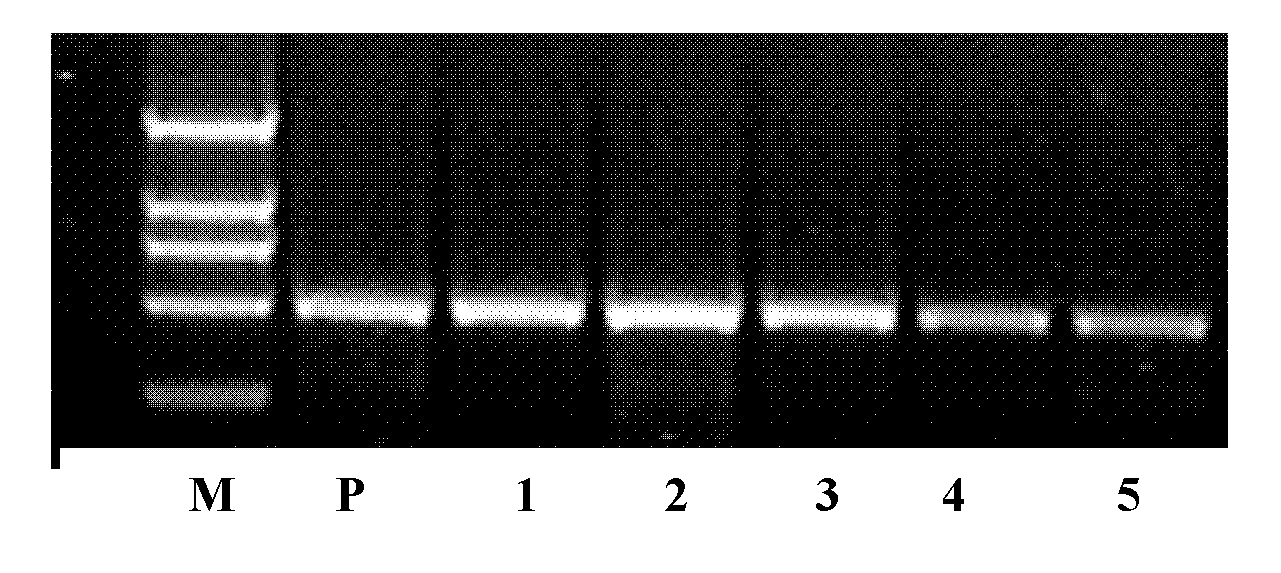
[0070] Example 1 Cloning of GbRPS1 gene against Fusarium wilt
[0071] (1) Construction of the cDNA library of the sea island cotton root
[0072] The library construction method is implemented using Stratagene's cDNA library construction kit. The specific steps of the method are as follows.
[0073] The sea island cotton variety Pima-90 can be used to extract total RNA from cotton after being treated with Verticillium dahliae (Verticillium dahliae) for 2 hours. Weigh 0.5 g of sea island cotton young roots, grind them into fine powder with liquid nitrogen, and divide them into two 1.5 ml eppendorf tubes. Add 1ml TRIZOL to each tube and shake vigorously to make the mixture uniform, and leave it at room temperature for 5 minutes. After centrifugation at 4°C and 12,000 g for 10 min, the supernatant was sucked into a clean 1.5 ml eppendorf tube. Add 0.2ml chloroform to each tube, shake vigorously for 15s, and leave it at room temperature for 2 to 3 minutes. Then centrifuge for 15 min...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2 Artificial synthesis of GbRPS1 protein gene resistant to Fusarium wilt
[0085] According to the completed nucleotide sequence containing the 2712bp coding region, firstly, it is divided into 8 segments to synthesize a single-stranded oligonucleotide fragment with a length of about 150-200bp and a sticky end according to the sequence of the plus strand and the side strand respectively. The 8 complementary single-stranded oligonucleotide fragments corresponding to each of the positive strand and the secondary strand are annealed separately to form 8 double-stranded oligonucleotide fragments with sticky ends. Mixed double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment, after T 4 DNA ligase catalyzes the assembly into a complete GbRPS1 gene. The synthetic DNA fragment contains the nucleotide sequence at positions 202-2916 in SEQ ID NO:1, and the synthetic gene contains XbaI and SacI sites at both ends.
[0086] The artificially synthesized 5'and 3'end restriction sites are XbaI a...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 Construction of plant expression vector for broad-spectrum resistance GbRPS1 gene
[0088] The specific method for constructing the plant expression vector of the broad-spectrum resistance GbRPS1 gene is as follows:
[0089] A. pBI121 and pCAMBIA2301 were digested with HindIII and EcoRI, and the fragment of pBI121 with p35S-GUS-Nos-ter was connected to pCAMBIA2301 to form the intermediate vector p35S-2301-GUS;
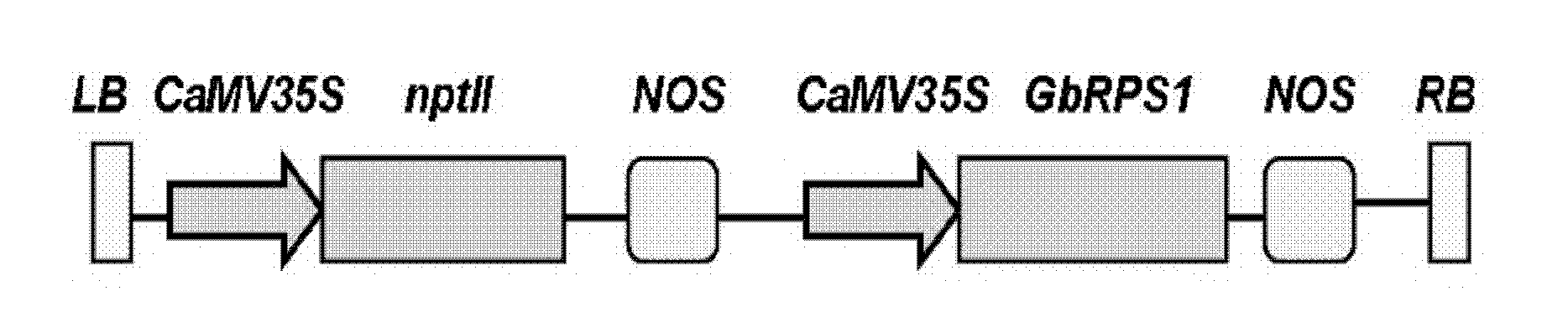
[0090] B. Double cut p35S-2301-GUS and the synthetic GbRPS1 gene with XbaI and SacI, and replace GUS at the corresponding restriction site of p35S-2301-GUS with GbRPS1 to obtain the GbRPS1 gene plant expression vector ( figure 1 ). Then it was transformed into the Agrobacterium line LBA4404 for transformation of cotton.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com