Method for controlling critical size of graph on uneven silicon slice surface
A critical dimension, silicon wafer surface technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, photolithography process exposure devices, electrical components, etc. Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving the excellent rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The following will combine Figure 5 ˜ FIG. 8 further describes in detail the method for controlling the critical dimensions of the graphics on the surface of the uneven silicon wafer according to the present invention.
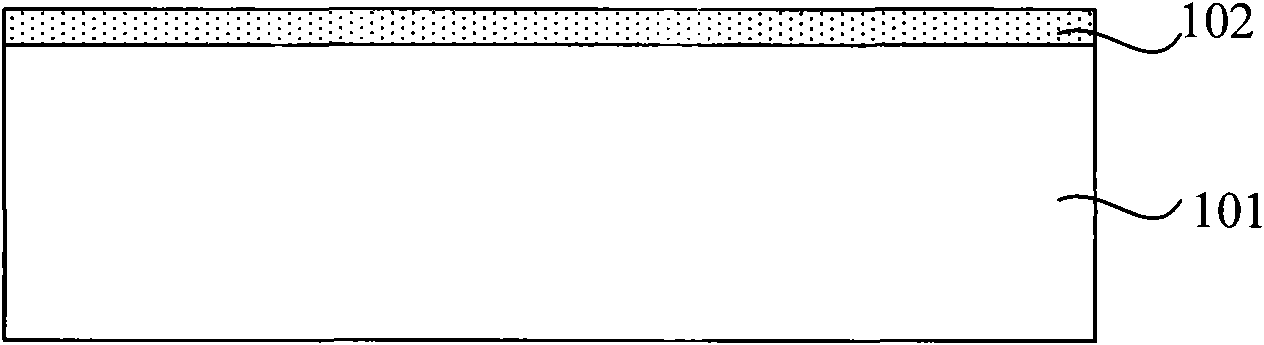
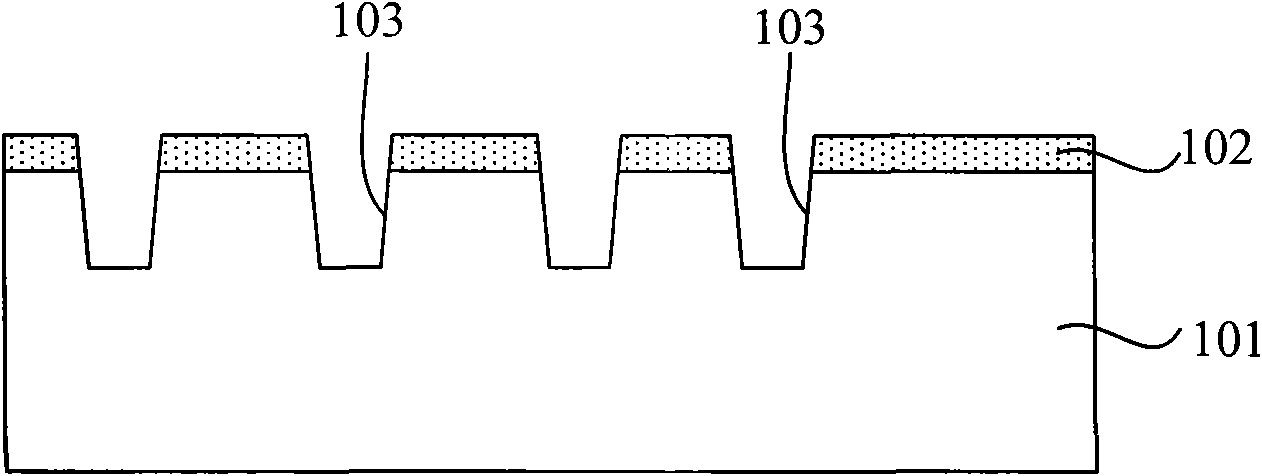
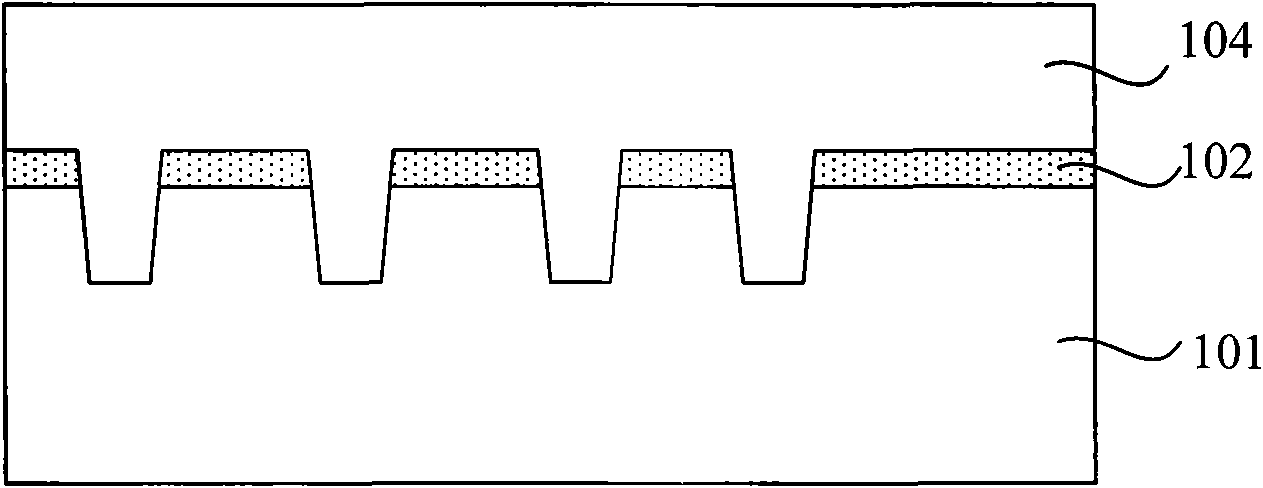
[0037] In order to characterize the unevenness of the surface of the silicon wafer, a physical concept-step height is introduced. The definition of the step height is the distance between the highest point and the lowest point on the surface of the silicon wafer. For example, as Figure 1D As shown, when fabricating the tunneling injection mask layer, the height difference H between the top of the isolation trench and the surface of the substrate is the step height.
[0038]The manufacture of semiconductor devices is performed step by step according to preset process conditions, for example, when making a tunneling injection mask layer, the thickness of the deposited barrier layer, the depth of the etched trench, the thickness of the deposited oxide, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com