Lactobacillus plantarum R23
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of microbial technology, can solve the problems of low fermentation conditions, reduce the acid-reducing effect of lactic acid bacteria, etc., and achieve the effects of strong probiotic properties, soft taste, and strong aroma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1: the probiotic property of plantarum lactobacillus according to the present invention
[0058] 1. Acid resistance and bile salt resistance
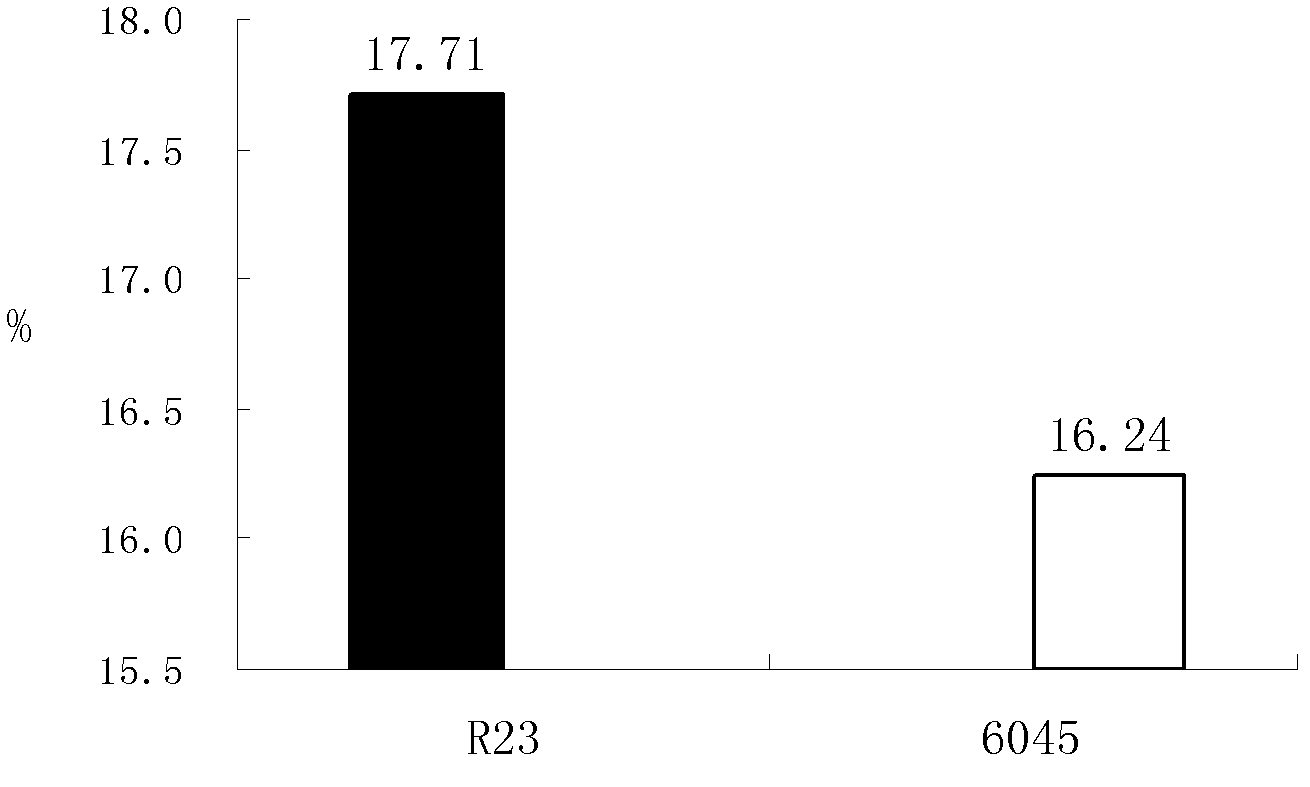
[0059] The collected Lactobacillus plantarum R23 sludge and the control bacteria 6045 were washed twice with sterile saline, and made into suspension bacteria with one-tenth of the original volume, and inoculated with 1% inoculum at pH 3.5, 3.0, 2.5, 2.0, 1.5, and LH18 medium with bile salt concentrations of 0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, and 0.5%, cultured at 25°C for 4 hours, and took samples every 2 hours to count viable bacteria. average value. See Table 1 and Table 2 for the changes in bacterial mass of each strain after being cultured for 4 hours in environments with different pH values and bile salt concentrations: the biomass of Lactobacillus plantarum R23 still reached 10 when cultured for 4 hours in an environment with a pH value of 2.5. 6 CFU / mL, while 6045 can only tolerate the acidity of pH 3.0, and it is dead after ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2: Lactobacillus plantarum R23 produces malate lactic acid enzyme characteristic
[0071] 1. MLE production and enzyme activity during the growth period
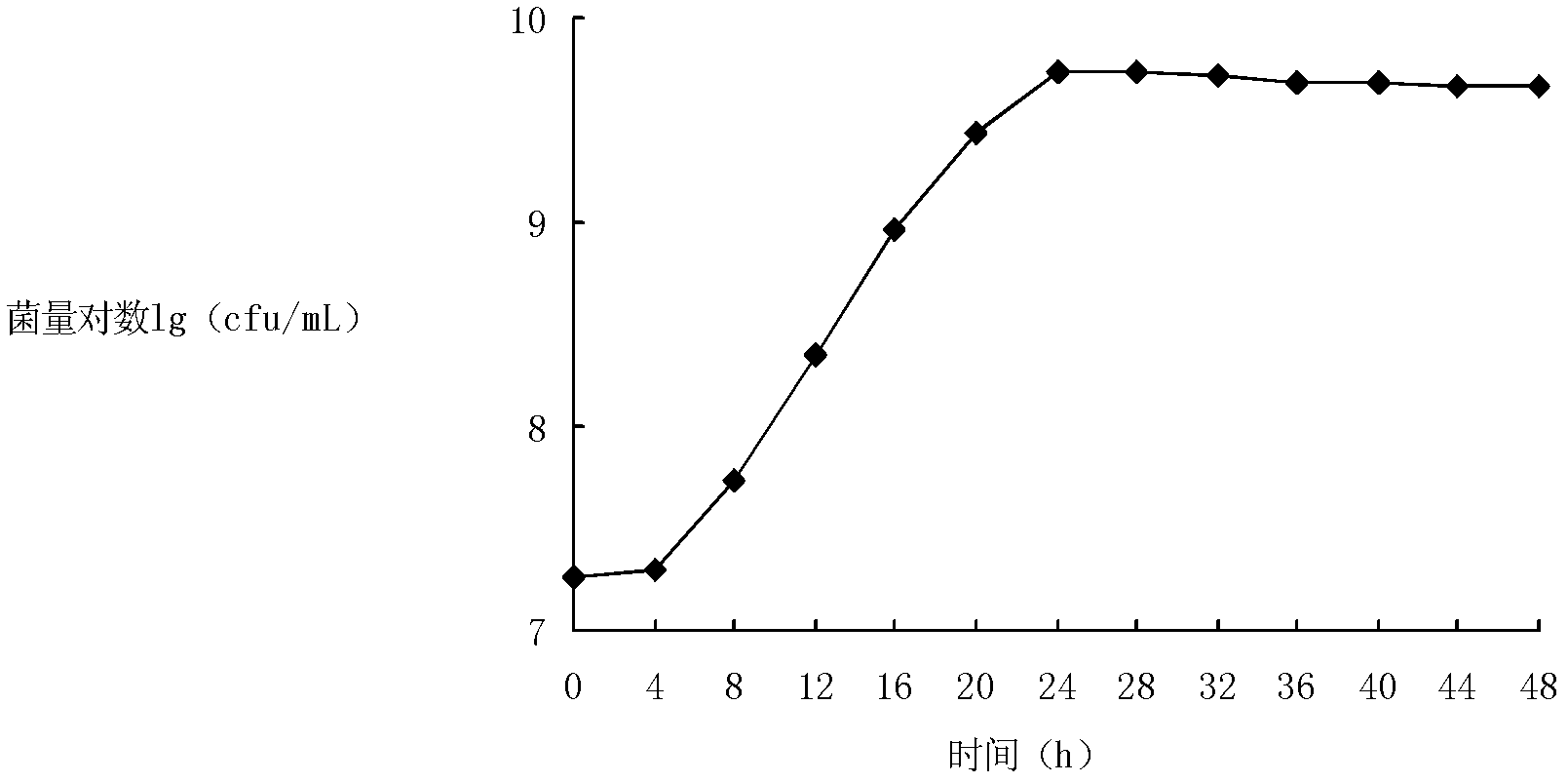
[0072] to 10 7 Insert cfu / mL activated Lactobacillus plantarum R23 into LH18 medium, culture at 25°C for 48 hours, measure the cell density, enzyme production and enzyme activity every 4 hours, and draw the growth curve.
[0073] Such as Figure 3-a As shown, 0h-4h is the lag phase, and the cell density remains basically unchanged, and then enters the logarithmic growth phase, and enters the stable phase after 24 hours of inoculation, and the maximum number of bacteria reaches 5.53×10 9 cfu / mL, and then the bacterial count began to decline slowly. Within 0-28h, the MLE activity and total activity increased rapidly with the increase of the amount of bacteria, and reached the maximum value of 406.9u and 357.67U at 28h, after which the MLE activity and total activity began to decline gradually; after inocul...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3: Application of Lactobacillus plantarum R23 in the brewing of "Chinese" kiwifruit wine
[0089] Plant Lactobacillus R23 at 5.8×10 8 cfu / mL inoculum volume into alcohol 10% (v / v), total acid 14.9g L -1 , The total sulfur concentration is 100mg·L -1 The kiwi fruit wine mash was cultured at a constant temperature of 22±1°C, and the progress of MLF was monitored by paper chromatography. The malic acid disappeared in the paper chromatography after 4 days of cultivation, indicating that the MLF fermentation was over, and the cultivation of Lactobacillus plantarum R23 could be stopped.
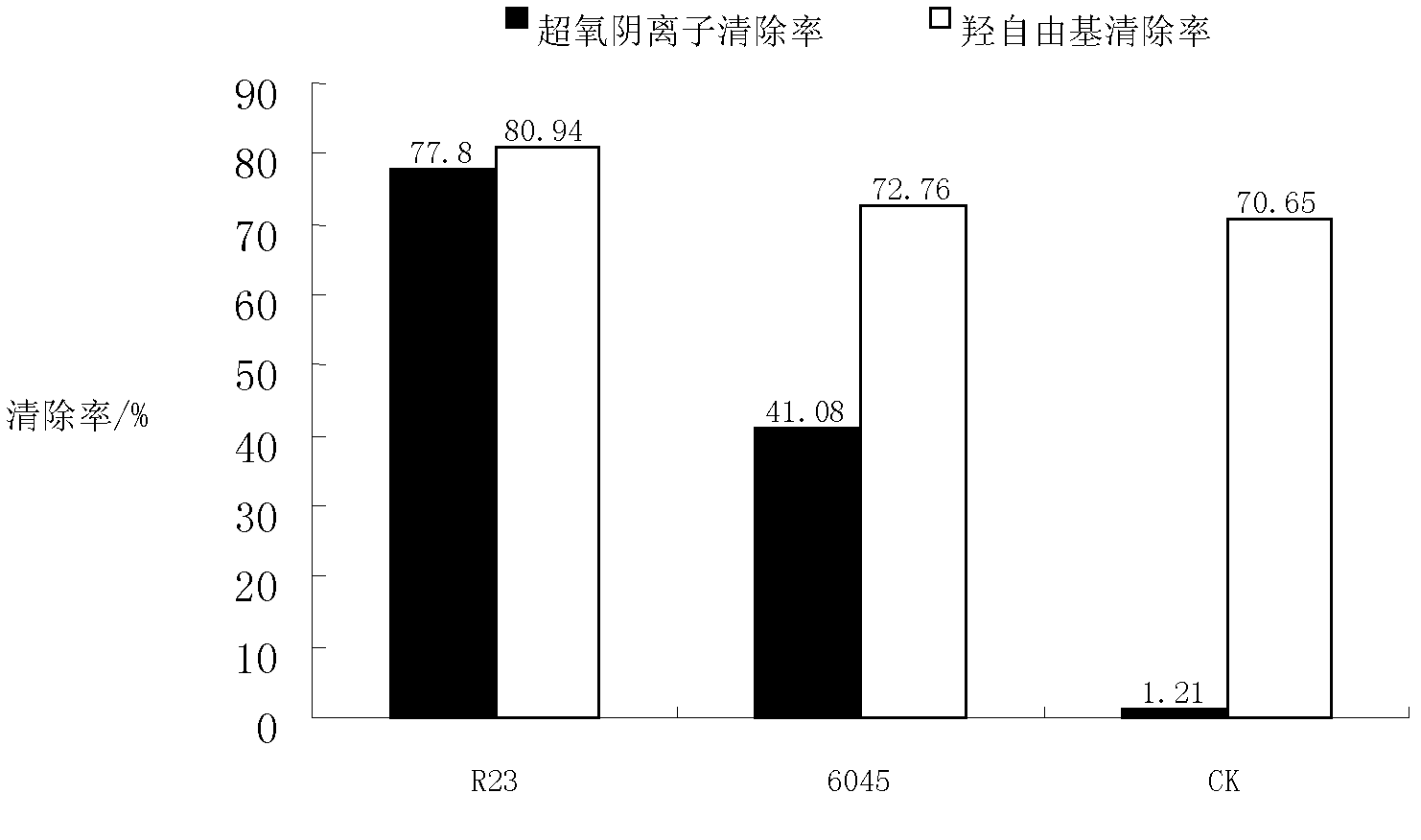
[0090] The changes of the main sensory indicators of "Zhonghua" kiwifruit wine are shown in Table 3. The total acid, pH value, volatile ester and softness index of the kiwifruit wine subjected to MLF reaction with R23 all changed greatly. The malic acid of kiwifruit wine using Lactobacillus plantarum R23 is greatly reduced and the total acid is reduced, which obviously achieves the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com