Selection breeding method for a Brassica napus-turnip cabbage cytoplasmic male sterility line
A cabbage rape, male sterile line technology, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, application, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in discovering and utilizing restoration genes, far from practical applications, affecting the purity of hybrids, etc. , to achieve the effects of convenient breeding research and utilization, simple breeding procedures and clear breeding goals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
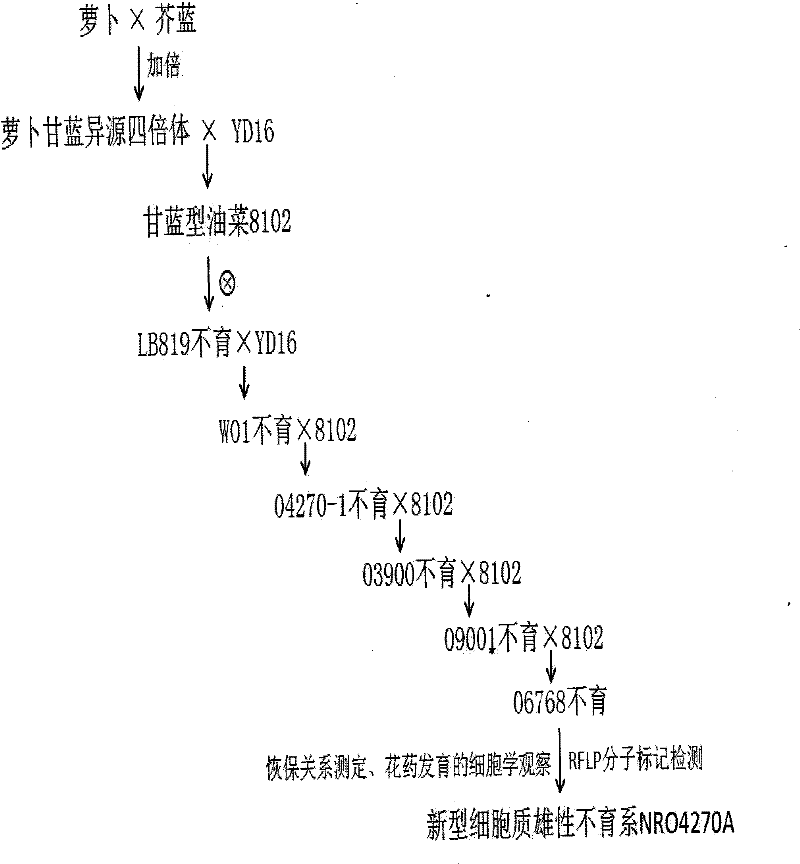
[0029] Example 1: Breeding of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Lines of Brassica oleracea Radish Brassica
[0030] Breeding steps of the cytoplasmic male sterile line NRO4270A of Brassica napus radish and Brassica oleracea:
[0031] Depend on figure 1 Shown:
[0032] (1) Heqing radish (Raphanus sativus L, 2n=18, RR) was used as the female parent and Brassica alboglabra Bailey (2n=18, CC) was used as the male parent to perform hybridization to obtain the first generation of hybrids, and sow the first generation of hybrids, The first generation seedlings of the hybrid were treated with 0.3% colchicine to obtain radish and cabbage allotetraploid (Raphanobrassica, RRCC, 2n=36) (Chen Honggao, Wu Jiangsheng, etc., Synthesis of radish-kale allotetraploid and GISH Analysis of Crops, 2006, 32 (8)); with the radish and cabbage heterotetraploid as the female parent, the Brassica napus variety YD16 (Zhao Heju et al., rapeseed, Chinese cabbage and shepherd's purse cross-breeding new varieties wi...
Embodiment 2
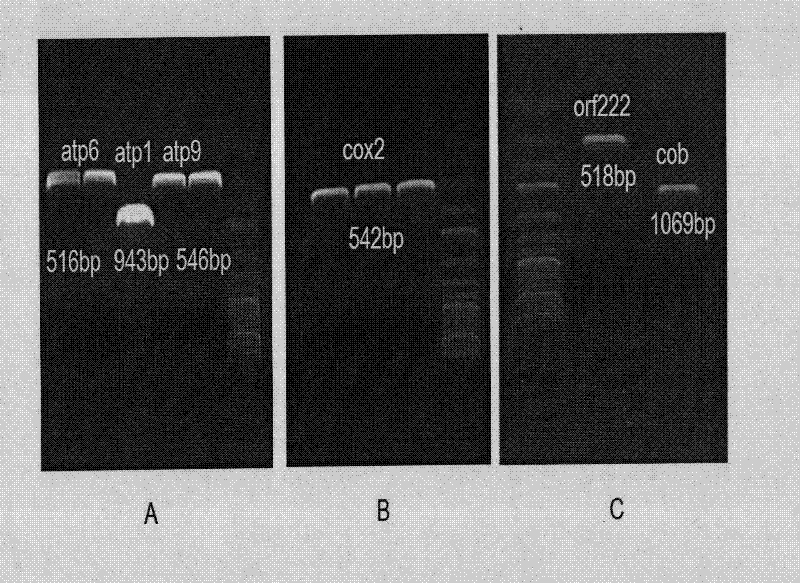
[0039] Example 2: Genetic classification of the cytoplasmic male sterile line NRO4270A of Brassica napus radish
[0040] 1. Determination of recovery relationship:
[0041] (1) Eight representative cultivars or lines were selected for test crossing with pol CMS, ogu CMS, kos CMS, hau CMS and NRO4270A CMS materials in Brassica napus.
[0042] Table 2 Determination results of recovery relationship between NRO4270A CMS and several rapeseed CMS materials
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] Note: (1) S in the table means sterile, and F means fertile.
[0046] (2) The test cross materials listed in Table 2 are the effects of testing the degree of recovery and maintenance of the materials of the present invention, and are not inventions and creations completed by relying on the test cross materials (as long as the existing breeding resources in China have the same genetic characteristics of the above materials as this invention) testcross material for the inventive step, so this examp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com