Rice male sterile protein and coding gene and application thereof
A technology that encodes genes and proteins, applied in applications, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as inability to realize three-line matching and limited applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040]Embodiment 1, the phenotype and genetic analysis of rice male sterile mutant mspl
[0041] 1. Phenotype analysis of rice male sterile mutant mspl
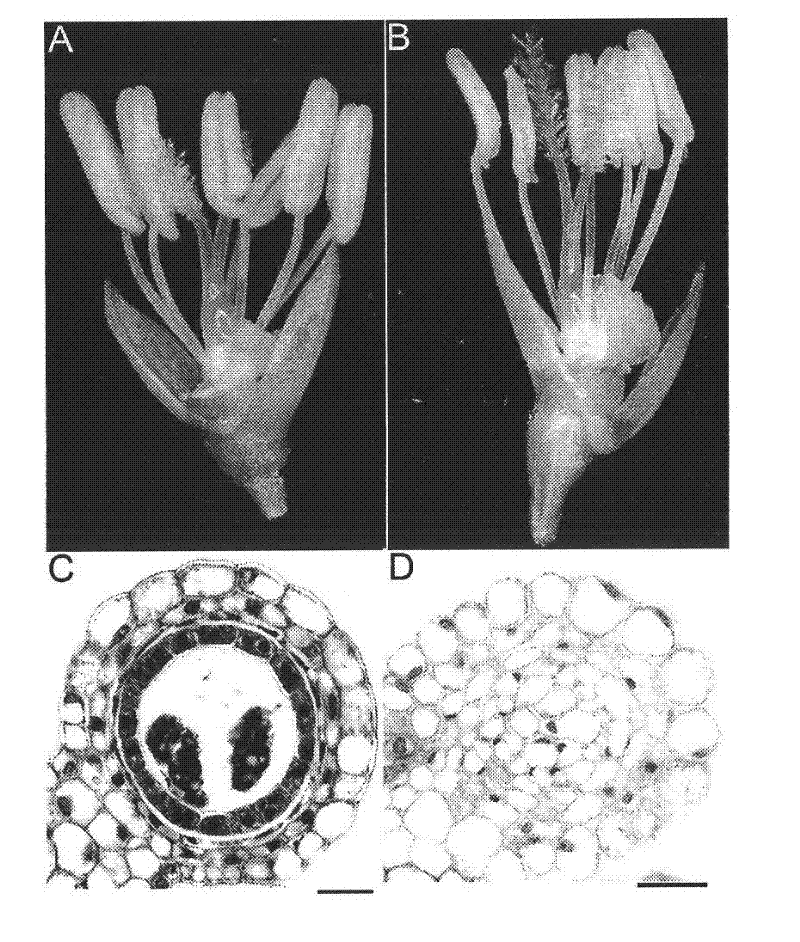
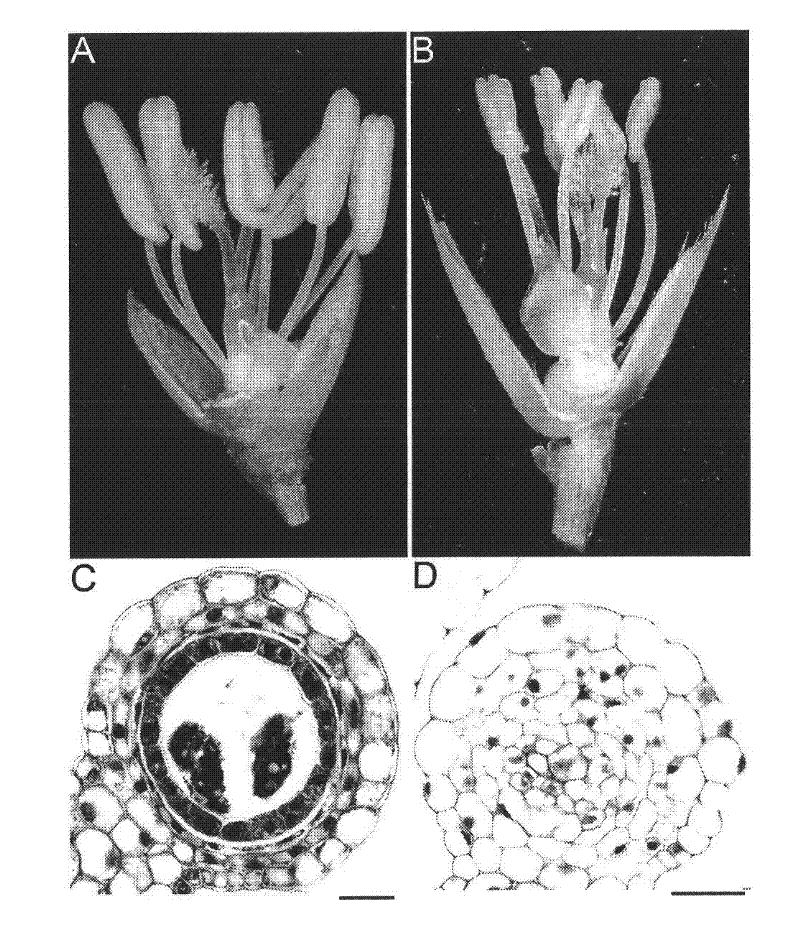
[0042] The rice male sterile mutant mspl is a natural mutant of Zhongxian 3037 (WT, purchased from the Agricultural College of Yangzhou University) found in the field by our laboratory. There was no significant difference between the mspl mutant and the control 3037 in the vegetative growth stage, and the mutant showed a typical male sterile phenotype after heading, which showed that the anthers were white and would not dehisce and release pollen. The results of semi-thin sections showed that there was no pollen in the anthers of the mutant, parenchyma cells of similar size and shape were distributed in the anthers, some anthers were even lignified in the center, and there were tissue differentiations similar to vascular bundles ( figure 1 ).
[0043] We granted the mspl mutant to the pollen of the wild type, and found that...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2, the acquisition of MSPL and its coding gene MSPL
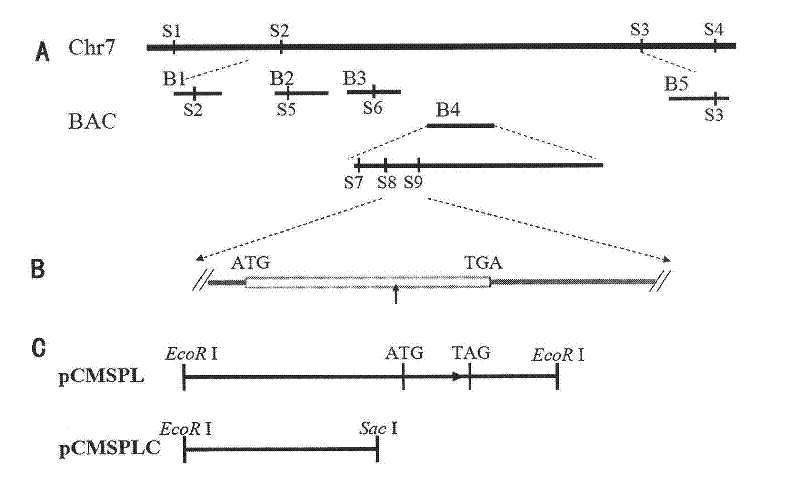
[0049] 1. Map-based cloning of the genomic gene of MSPL
[0050] In order to clone the MSPL gene, we will cross the homozygous male sterile mutant mspl and Nipponbare and obtain the F 1 F 2 In the population, 236 F2 recessive individuals (F2 individuals with male sterility phenotype) were initially mapped for the MSPL gene. Using STS (Sequence-Tagged Site) molecular markers and PCR method, we found that the STS markers S1, S2, S3 and S4 on chromosome 7 had obvious linkage with the mutation site. Most of the exchanged plants between the mutation site and S2 were also exchanged between the mutation site and S1, and most of the exchanged plants between the mutation site and S3 were included in the mutation site and S4 in exchange among individual plants. At the same time, the exchanged individual plants between the mutation site and S3 were different from those between the mutation site and S2, so it was ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, complementation experiment of male sterile mutant MSPL phenotype
[0060] 1. Construction of complementary vector pCMSPL and complementary control vector pCMSPLC
[0061] BAC OsJNBa0057C01 (purchased from Shanghai National Gene Research Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. OsJNBa0057C01) was digested with EcoRI to obtain the full length of 3870 bases upstream of the start codon ATG of MSPL and 1306 bases after the stop codon TGA The DNA fragment (5360bp) of the sequence was cloned into the EcoRI site of pCAMBIA1300 (DingGuo, MCV033), and the complementary expression vector pCMSPL was constructed. The constructed complementary vector pCMSPL was digested with SacI to remove part of the promoter region, the entire coding region and the 3' regulatory region of the MSPL gene, and retain the part of the promoter region at the 5' end, thus constructing the complementary control vector pCMSPLC( figure 2 Middle C).
[0062] 2. Acquisition and phenotypic iden...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com