Auxiliary identification method of geographical origin of beef
A beef and origin technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problem of lack of beef origin fatty acid fingerprint analysis technology and other problems, and achieve the effect of simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
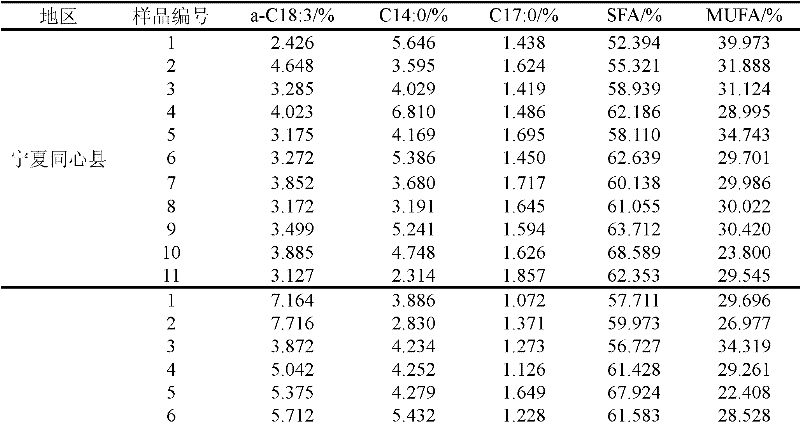
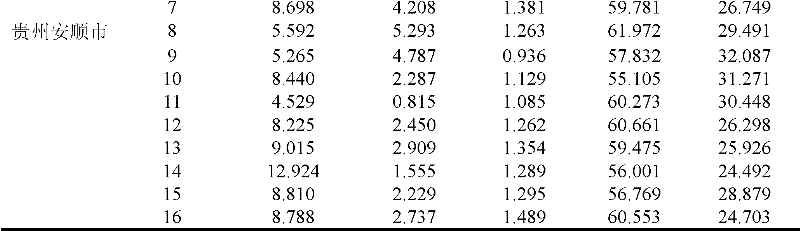
[0024] Embodiment 1, the identification of the place of origin of beef
[0025] (1) Beef sample collection, mincing, drying, crushing, fat extraction
[0026] Beef samples from 27 cows were collected from Anshun City, Guizhou Province, and Tongxin County, Ningxia Province. The beef samples were ground into meat paste by a meat grinder, dried at a constant temperature of 70°C for 48 hours, and crushed into a powder with a particle size of 100 mesh by a grinder. ;Put beef powder in a beaker and add petroleum ether with a boiling range of 30-60°C for leaching, centrifugation and filtration for three times, the first leaching for 6 hours, the second leaching overnight (about 12h), and the third leaching After 8 hours, the supernatant was placed in a rotary evaporator, and petroleum ether was recovered at 35° C. under a vacuum of 0.08 MPa to obtain a crude fat sample for later use.
[0027] (2) Fatty acid methylation
[0028] Weigh 50 mg of crude fat sample, place it in a 25 mL s...
Embodiment 2
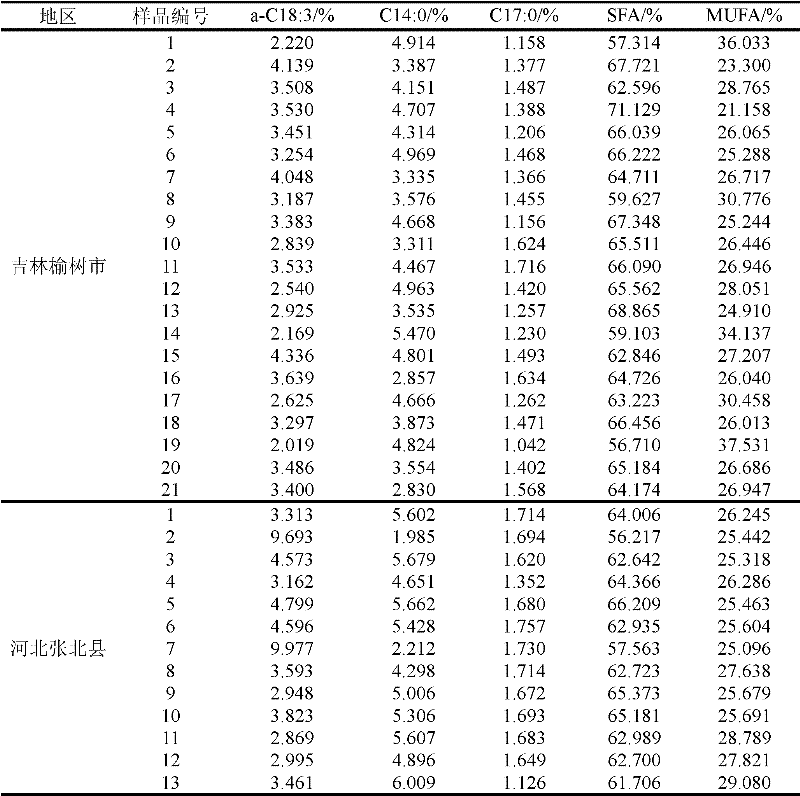
[0041] Embodiment 2, the identification of beef origin
[0042] (1) Beef sample collection, mincing, drying, crushing, fat extraction
[0043]Beef samples from 34 cows were collected from Yushu City, Jilin Province, and Zhangbei County, Hebei Province. The beef samples were ground by a meat grinder, dried at a constant temperature of 60°C for 36 hours, and crushed into a powder with a particle size of 200 mesh by a pulverizer. Put beef powder in a beaker and add petroleum ether with a boiling range of 30-60°C to extract, centrifuge, and filter three times. The first extraction is 3 hours, the second extraction is overnight (about 12 hours), and the third extraction is 3 hours. , the supernatant was placed in a rotary evaporator, and petroleum ether was recovered under the condition of a vacuum of 0.08 MPa at 35° C. to obtain a crude fat sample for later use.
[0044] (2) Fatty acid methylation
[0045] Weigh 50 mg of crude fat sample, place it in a 25 mL stoppered test tube,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com