Magnesium three-layer composite brick and preparation method thereof
A layer composite, magnesia technology, applied in the field of magnesia three-layer composite bricks and its preparation, can solve the problems of increased heat dissipation of the kiln shell, increased heat consumption of clinker, and increased temperature of the supporting wheel tiles, etc., to achieve good refractory insulation Thermal effect, prolonging the service life of equipment and saving energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
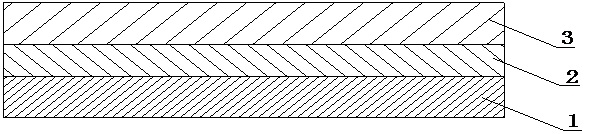
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, the magnesia three-layer composite brick of this embodiment includes a heavy working layer 1, a light heat insulating layer 3, and a transition layer 2 between the heavy working layer 1 and the light heat insulating layer 3.
[0023] in:
[0024] The particle size distribution and mass percentage of the raw materials used in the heavy working layer 1 are: fused magnesia with a particle size greater than 1mm: 45%; fused magnesia with a particle size less than 1mm and greater than 325 mesh: 25%; Fused magnesium powder for 325 mesh: 30%. The binding agent adopted during material preparation is magnesium sulfate solution, and its weight is 3% of the weight of the heavy working layer.
[0025] The particle size distribution and mass percentage of the raw materials used in the transition layer 2 are: sintered spinel with a particle size larger than 1mm: 45%; sintered spinel with a particle size smaller than 1mm and larger than 325 mesh: 25%; Purp...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the magnesia three-layer composite brick of this embodiment includes a heavy working layer 1, a light heat insulating layer 3, and a transition layer 2 between the heavy working layer 1 and the light heat insulating layer 3.
[0035] in:
[0036] The particle size distribution and mass percentage of the raw materials used in the heavy working layer 1 are: fused magnesia with a particle size greater than 1mm: 50%; fused magnesia with a particle size less than 1mm and greater than 325 mesh: 20%; Fused magnesia for 325 mesh: 30%. The binding agent adopted during material preparation is magnesium sulfate solution, and its weight is 2% of the weight of the heavy working layer.
[0037] The particle gradation and mass percentage of the raw materials used in the transition layer 2 are: fused spinel with a particle size greater than 1mm: 50%; fused spinel with a particle size less than 1mm and greater than 325 mesh: 20%; Sintered spinel powder with a...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, the magnesia three-layer composite brick of this embodiment includes a heavy working layer 1, a light heat insulating layer 3, and a transition layer 2 between the heavy working layer 1 and the light heat insulating layer 3.
[0047] in:
[0048] The particle size distribution and mass percentage of the raw materials used in the heavy working layer 1 are as follows: sintered magnesia with a particle size greater than 1mm: 55%; sintered magnesia with a particle size less than 1mm and greater than 325 mesh: 15%; Purpose Sintered magnesium powder: 30%. The binding agent that adopts when preparing materials is yellow dextrin solution, and its weight is 2% of heavy working layer weight.
[0049] The gradation and mass percentage of raw material particles used in the transition layer 2 are: sintered spinel hollow spheres with a particle size of 0.2-5 mm: 55%; sintered spinel powder with a particle size of 325 mesh: 45%. The binding agent that ado...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com