Cloning and application of arabidopsis powdery mildew resistance related gene EDR6
A technology for Arabidopsis thaliana and powdery mildew, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problem of not clearly explaining the mechanism of plant disease resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
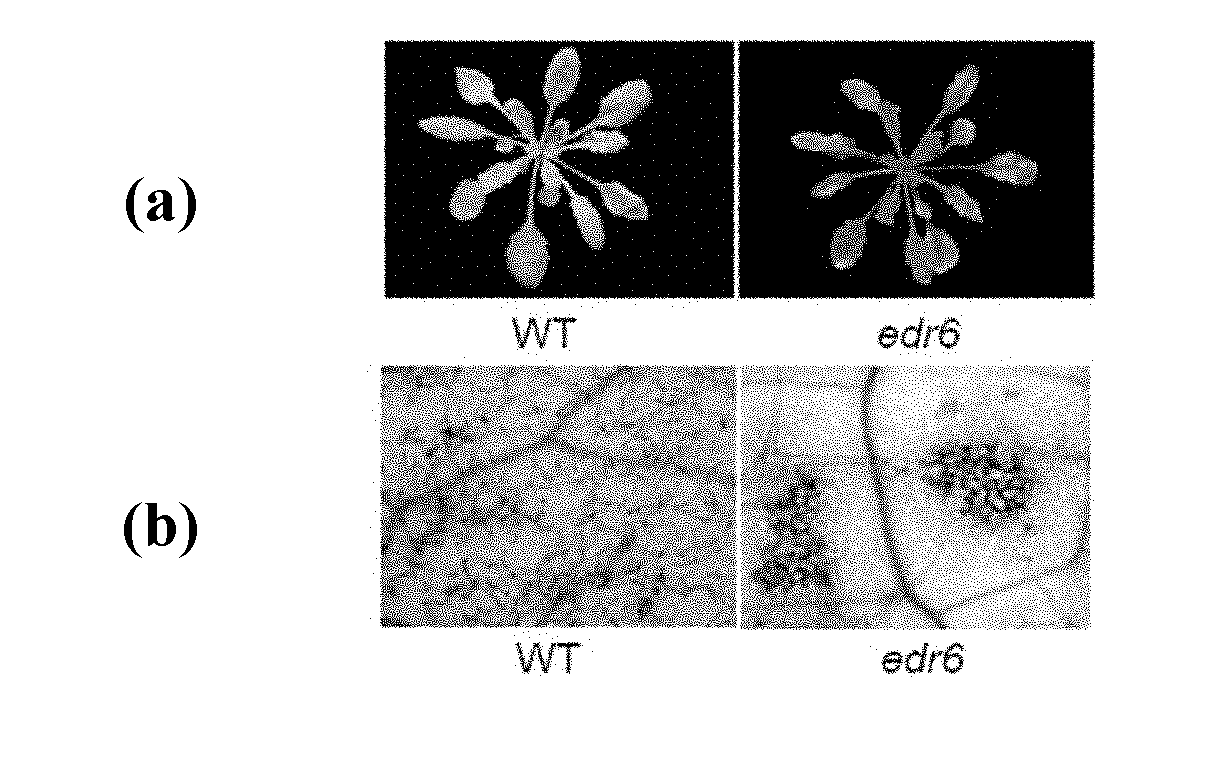
[0031] Example 1. Analysis of edr6 mutant disease resistance phenotype
[0032] Wild-type Col-0 (Weigel D, Glazebrook J, 2002) (purchased from Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC)) was mutagenized with 0.03% EMS (purchased from sigma company), and cells induced by white powder were screened from the mutagenized population A mutant that is dead and powdery mildew resistant was named edr6. Four weeks of wild-type Col-0 and edr6 mutants grown in a short-light (9-hour light / 15-hour dark) light intensity of 8000 lux and a relative humidity of 70% were inoculated with Arabidopsis powdery mildew (G.cichoracearum, Adam et al, 1999). The powdery mildew was maintained with a mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana pad4 (Jirage et al., 1999, commercially available from ABRC) which is susceptible to the powdery mildew. When inoculating, gently scrape the pad4 plants with a large number of powdery mildew spores on the leaves of the plants to be inoculated with white powder, then cover th...
Embodiment 2
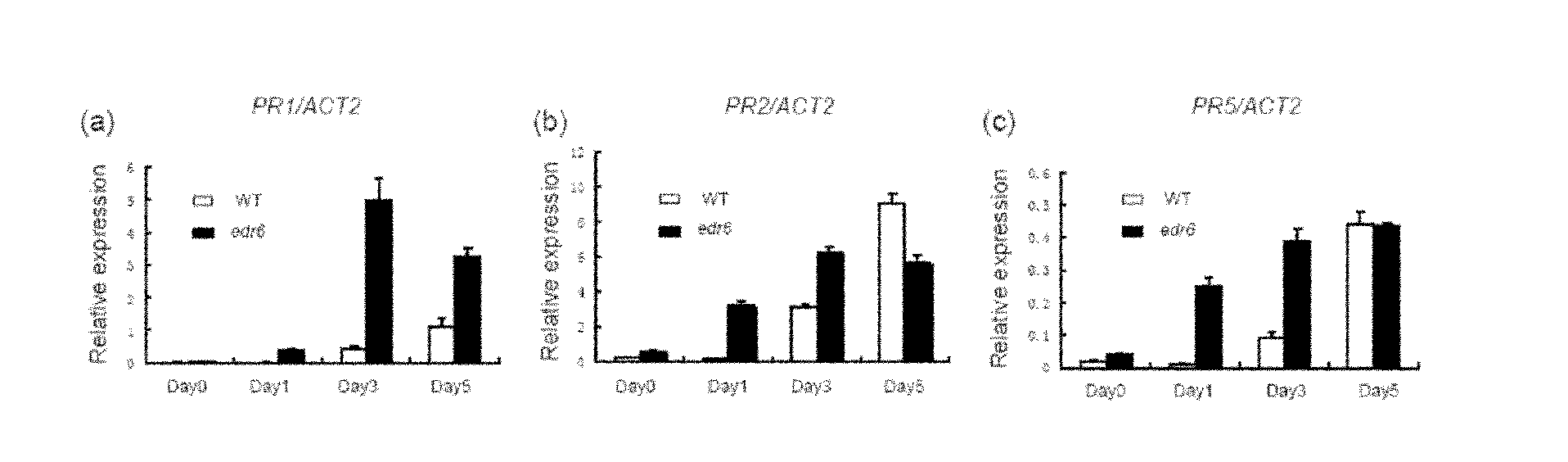
[0049] from figure 2 We saw that the expression levels of PR1 and PR5 were very low in the wild type and mutants before inoculation. After inoculation, the PR1 and PR5 genes in the mutant accumulated rapidly, and reached a high value in 3 to 5 days, while the accumulation of PR1 and PR5 in the wild type was significantly less than that of the mutant, and PR1 in the wild type was significantly less than that in the 3 days after inoculation. The relative expression level is only about 10% of the wild type. After 3 days of inoculation, PR2 was significantly higher in the middle leaves of the mutant than that of the wild type. It shows that the disease resistance response in the mutant is activated faster and stronger. Example 2 Map-position cloning, isolation and identification of the EDR6 gene and its complementation
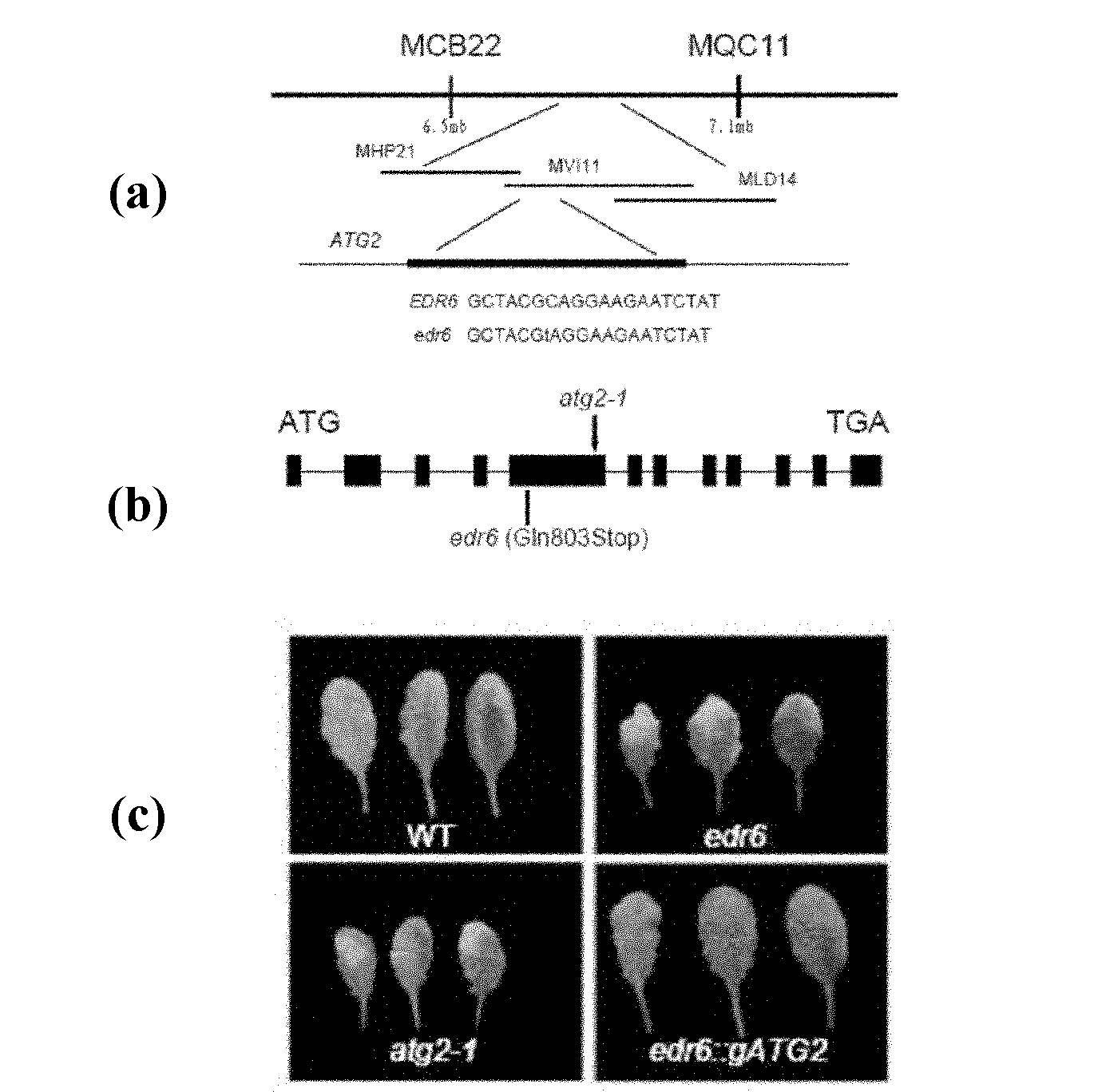
[0050] Using map-based cloning (Jander et al, 2002), we cloned the EDR6 gene. The F1 generation was obtained by crossing the edr6 mutant with another ecotype...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Other autophagy-related protein gene mutants exhibit phenotypes similar to EDR6
[0063] Since EDR6 encodes the ATG2 protein, we also analyzed the functions of other autophagy-related proteins in Arabidopsis. We investigated whether Arabidopsis also exhibits edr6-like powdery mildew resistance after loss of function of these genes. We obtained T-DNA insertion mutants of ATG5, ATG7, ATG9 and ATG10 from the SALK germplasm bank. After identification, homozygous plants were obtained for inoculation experiments. Plants 4 weeks old under light were inoculated with G. cichoracearum (see Example 1 for the method), and the phenotype was observed after 7 days. from Figure 4 As shown, 7 days after inoculation, atg5, atg7, and atg10 all showed resistance to powdery mildew, but they were all weaker than edr6. It shows that other autophagy-related proteins also play an important role in the resistance to mildew.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com