Reagent for detecting activity of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in tissues or cells
A soluble and oxide-based technology, applied in material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., to achieve fast detection, less sample consumption, and strong operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] The preparation of the detection reagent is as follows:
[0046] 1. Solution preparation
[0047] 1) Lysis solution: hypotonic solution + phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)
[0048] The hypotonic solution is: 55-65 mg of trishydroxymethylaminomethane (Tris), magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) 15-25 mg, ethylene glycol diethyl ether diamine tetraacetic acid (EGTA) 35-40 mg, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) 3-5 mg dissolved in water, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, and dilute the water to 100ml;
[0049] Hypotonic solutions can also be directly used with deionized water.
[0050] 2) Detection buffer: add bovine serum albumin (BSA) at 0.2mg / ml to 50mM Tris, pH=6.8-7.3, store at 4°C;
[0051] 3) Detection substrate: Epoxy Fluor 7 was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to prepare a 5mM stock solution and stored at -20°C;
[0052] 4) sEH inhibitor: 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-n-dodecanoic acid [12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid, AUDA], trans -4-[4-(3-Adaman...
Embodiment 1
[0067] 1. Solution preparation
[0068] 1) Lysis solution 5ml: deionized water 4.95ml+100mM PMSF50ul;
[0069] 2) Assay buffer: 50mM Tris+0.2mg / ml BSA, pH 7.0, stored at 4°C;
[0070] 3) Detection substrate: Epoxy Fluor 7 was dissolved in DMSO to prepare a 5mM stock solution, stored at -20°C;
[0071] 4) sEH inhibitor: t-AUCB was dissolved in DMSO to make a 10mM stock solution and stored at -20°C;
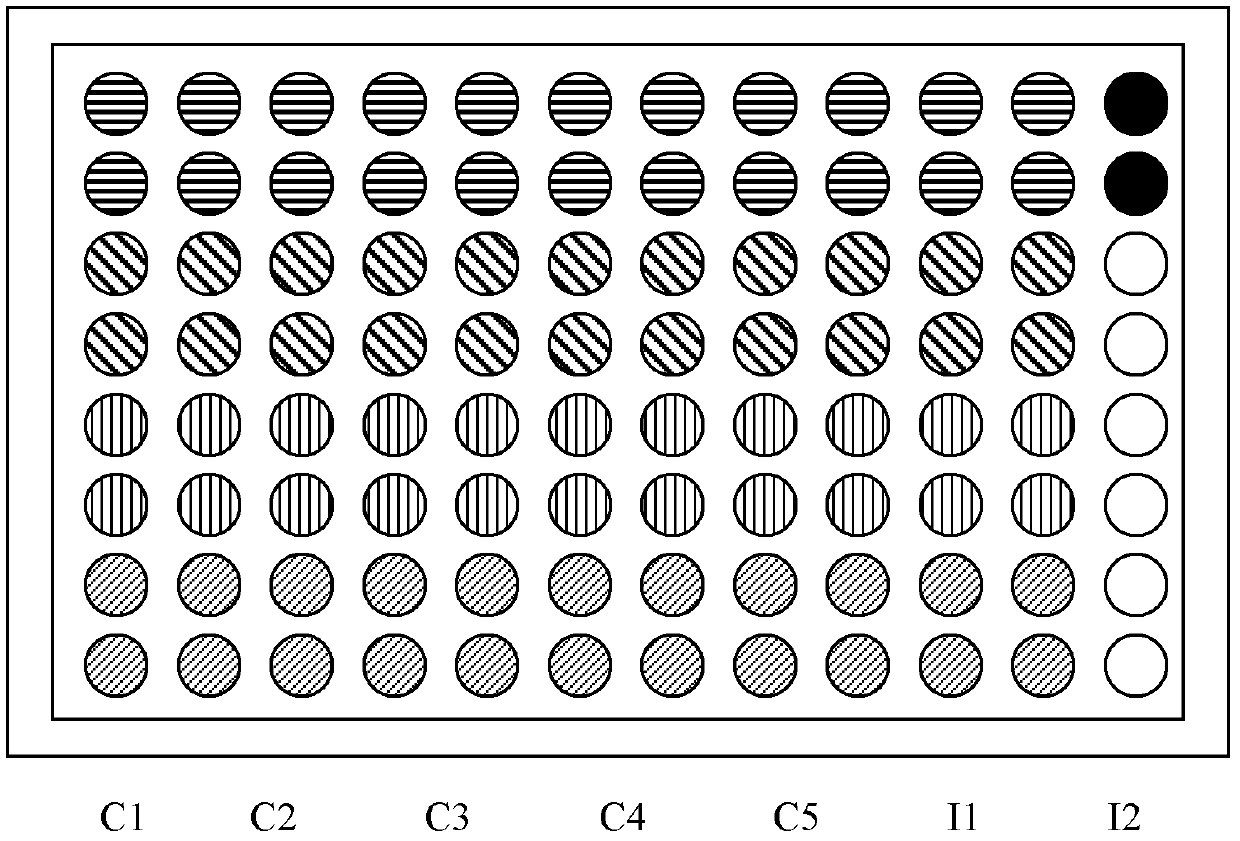
[0072] 2. Sample
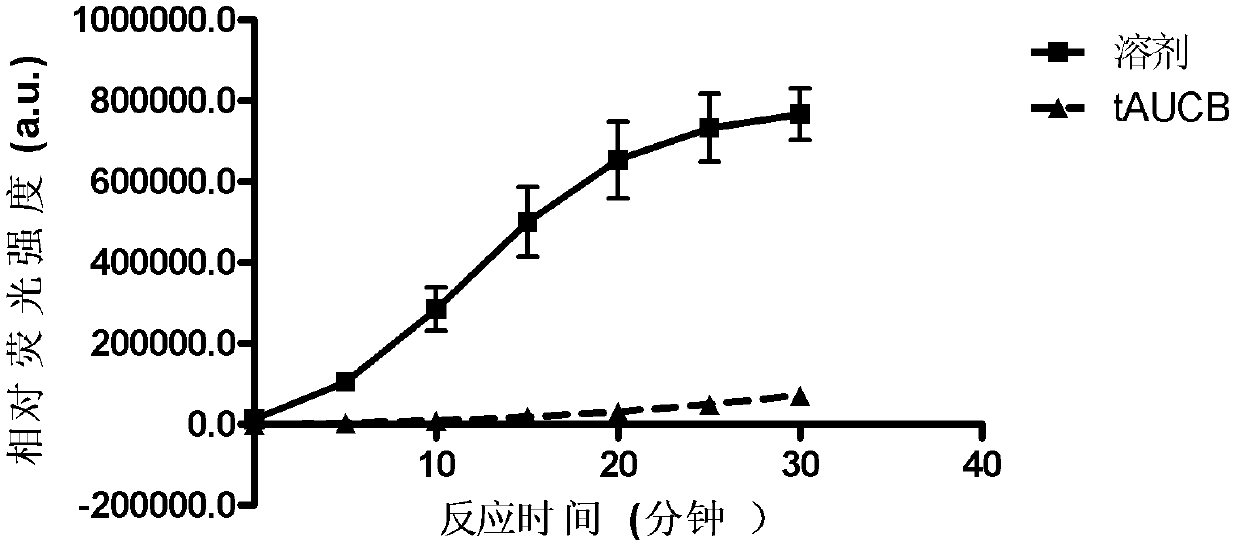
[0073] 1) The sEH inhibitor tAUCB was dissolved in PEG400 to prepare a 4 mg / ml solution. Eleven 8-week-old C57BL / 6 mice were randomly divided into two groups. One group of 6 mice was given the sEH inhibitor tAUCB and added to the drinking water so that the concentration was 20mg / L. The other group of 5 mice was given the same volume of solvent PEG400 to drinking water. The mice had free access to food and water.
[0074] 2) After 4 days of administration, the mice were anesthetized, blood was taken from the right ventricle, and perfused with normal saline f...
Embodiment 2
[0084] 1. Solution preparation
[0085] 1) Prepare a hypotonic solution first: dissolve 55-65 mg of trishydroxymethylaminomethane, 15-25 mg of magnesium chloride, 35-40 mg of ethylene glycol diethyl ether diamine tetraacetic acid, and 3-5 mg of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid In water, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, and dilute the water to 100ml;
[0086] Take 2.475ml of hypotonic solution and add 25ul of PMSF with a concentration of 100mM to make 5ml of lysate;
[0087] 2) Assay buffer: 50mM Tris+0.2mg / ml BSA, pH 7.0, stored at 4°C;
[0088] 3) Detection substrate: Epoxy Fluor 7 was dissolved in DMSO to prepare a 5mM stock solution, stored at -20°C
[0089] 4) sEH inhibitor: t-AUCB was dissolved in DMSO to make a 10mM stock solution, stored at -20°C
[0090] 2. Sample
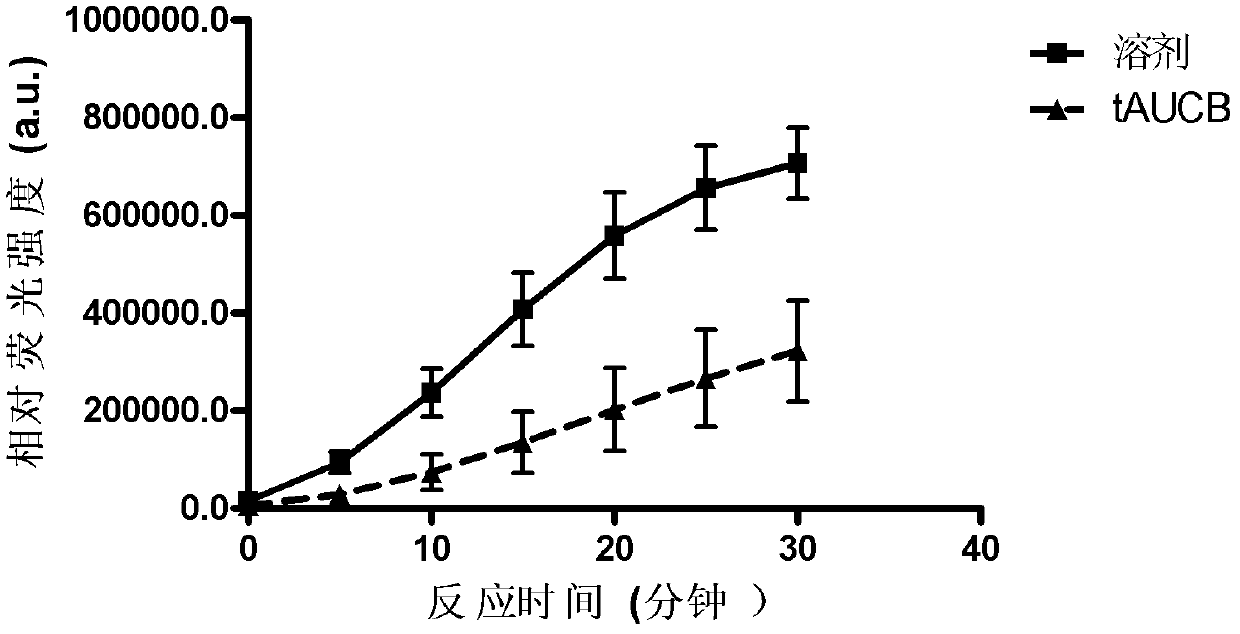
[0091] 1) Cell culture and treatment: the human embryonic kidney 293 cell line was spread in a 6cm cell culture dish, the cells were 80% confluent, the medium was changed, and treatment was given. Divided int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com