Laser ultrasonic detection method for micro defects
A technology of laser ultrasound and detection method, applied in the direction of optical testing flaws/defects, scattering characteristics measurement, etc., can solve the problems of poor detection accuracy, bulky, affecting the detection effect, etc., to overcome the influence of blind spots, high detection sensitivity, detection simple craftsmanship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
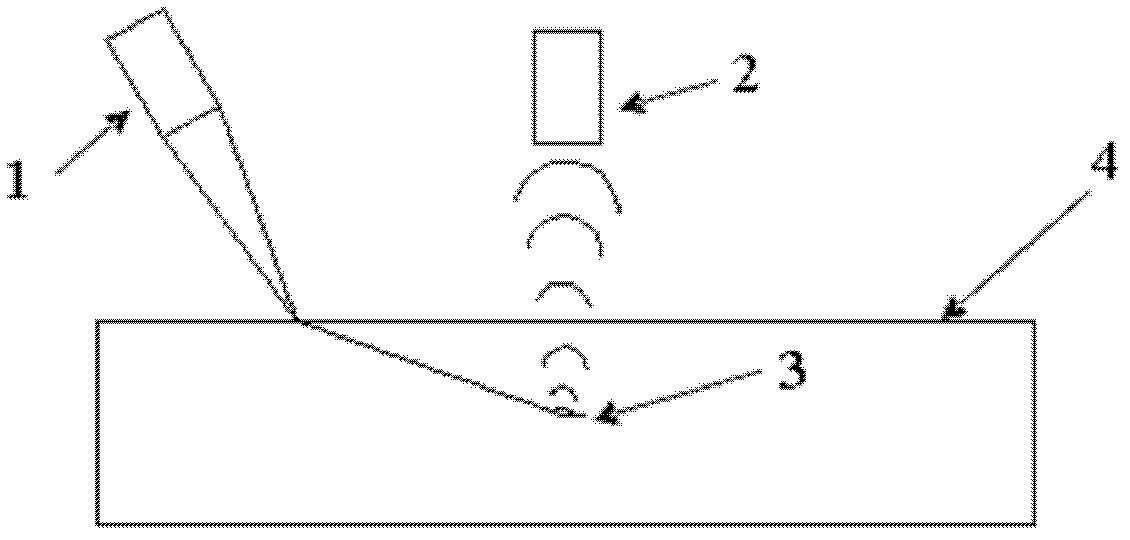
[0025] 1. Select an aluminum alloy sheet workpiece in a factory, with a specification of 100mm×80mm×6mm, and place the aluminum alloy sheet workpiece on figure 1 In the environment, with figure 1 way to detect.
[0026] 2. Adjust the laser probe 1 so that the laser emitted by the laser probe 1 acts on the workpiece 4 to generate ultrasonic waves. When the ultrasonic waves generated in the process 4 meet the defects 3 in the material, a new wave source is formed. The new wave source As a secondary wave source, "scattered waves" are emitted in all directions, and the air-coupled probe 2 is vertically aligned with the workpiece 4, and the two probes are moved synchronously on the same side of the thin plate on the fixed frame.
[0027] 3. Adjust CH1 on the oscilloscope to 500mvΩ, and M to 1.00us. Observe the radio frequency signal on the oscilloscope. When a radio frequency signal wave appears on the oscilloscope, the air-coupled probe receives a radio frequency signal wave. Th...
Embodiment 2
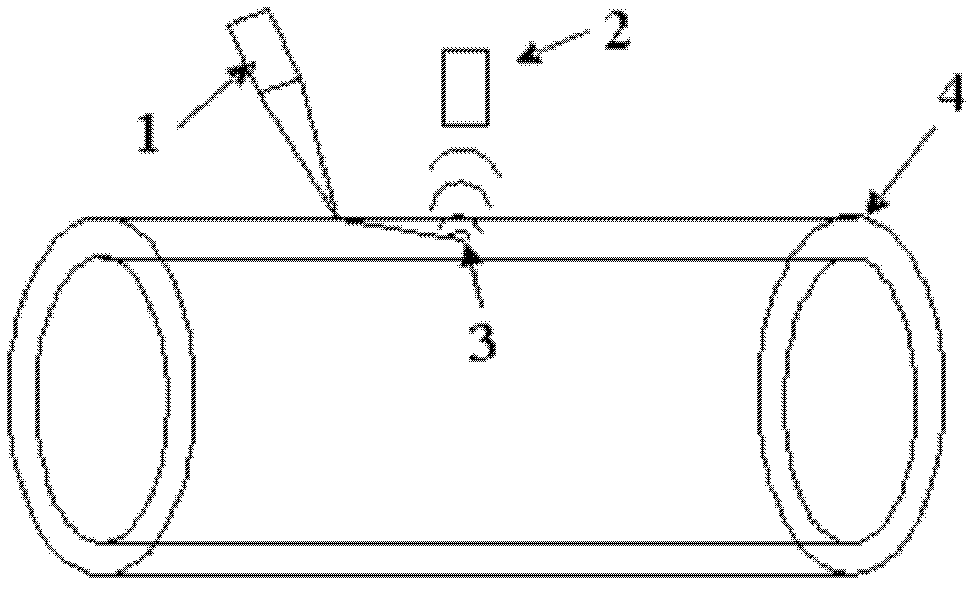
[0030] 1. Select a high-temperature pipe fitting in service in a heating network company, the specification is ¢100×8mm, the pipe temperature is 250°C, and the high-temperature pipe fitting is placed in the image 3 In the environment, with image 3 way to detect.
[0031] 2. Adjust the laser probe 1 so that the laser emitted by the laser probe 1 acts on the pipe 4 to generate ultrasonic waves. When the ultrasonic waves generated in the pipe 4 encounter the defect 3 in the material, a new wave source is formed, and the new wave source is regarded as The secondary wave source emits "scattered waves" in all directions, and the air-coupled probe 2 is aligned vertically with the pipe 4, 10mm away from the surface of the pipe 4, and the two probes are moved synchronously on the same side of the pipe on the fixed frame.
[0032] 3. Adjust CH1 on the oscilloscope to 500mvΩ, and M to 1.00us. Observe the radio frequency signal on the oscilloscope. When the air-coupled probe receives ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com