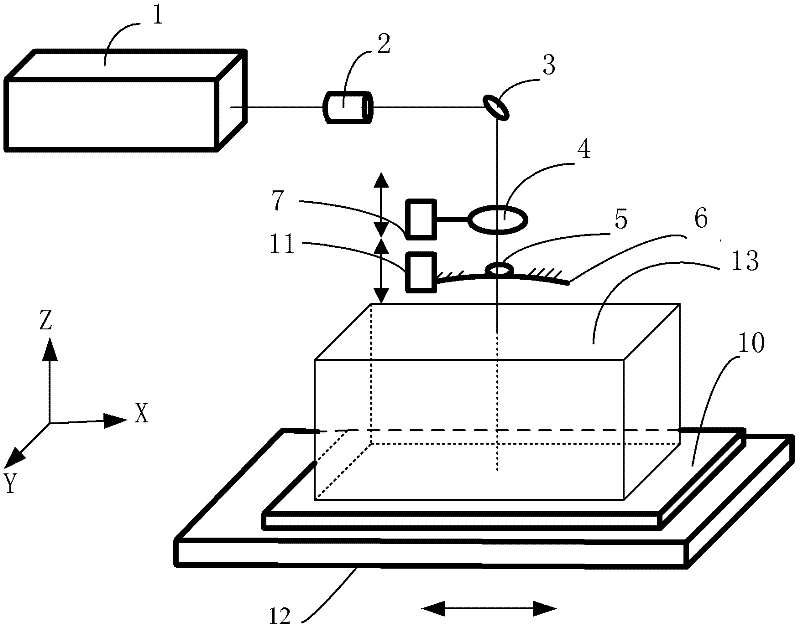
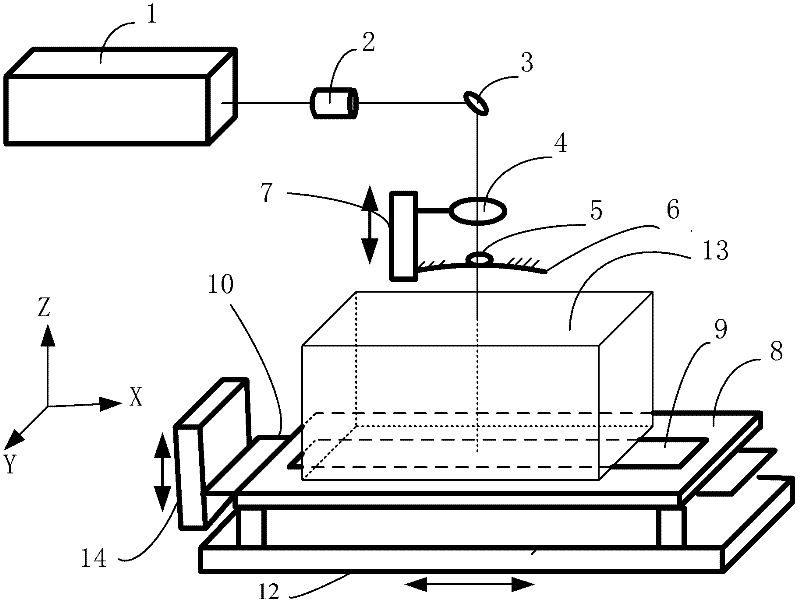
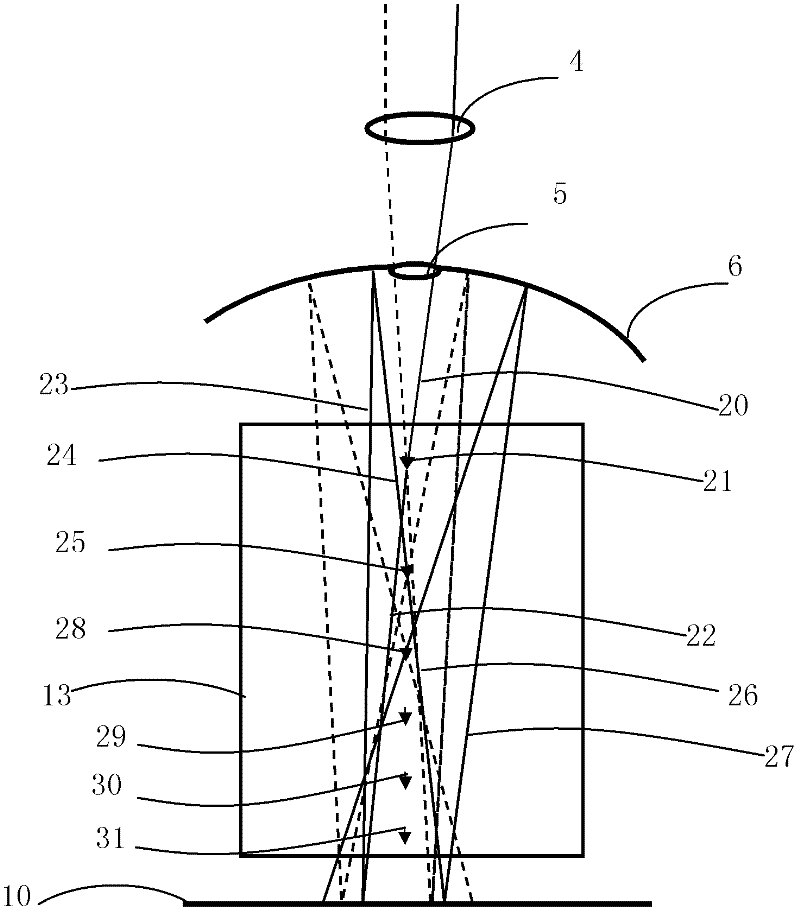
Laser multipoint focusing processing system
A processing system and laser technology, which is applied in the field of laser multi-point focusing processing systems, can solve problems such as uneven absorption of laser energy, difficulty in controlling thermal stress cracks, and out-of-control separation, achieving wide processing range, safe high-quality cutting and separation , The effect of improving the absorption efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031] Adopt one of the specific embodiments of the present invention. The laser source in the single-focus laser processing system is a laser with a pulse width of 25ns, a wavelength of 355nm, an output power of 10W, an output spot diameter of 0.8mm, and a focal length of the focusing lens of 50mm. The first total reflection mirror in the multi-focus derivative system is a spherical mirror with a diameter of 60mm, a mirror focal length of 35mm, and a small hole diameter of 1mm; the second is 50×100mm 2 plane mirror. The transparent material to be processed is quartz glass with a thickness of 10mm and an absorption rate of 15% for a wavelength of 355nm. The distance from the first total reflection mirror to the upper surface of the transparent material to be processed is 40 mm, and the distance from the second total reflection mirror to the lower surface of the material is 8 mm. The table moving speed is 1mm per second. Experimental results: The system produces the first la...
example 2
[0033] The second embodiment of the present invention is adopted. The laser source in the single-focus laser processing system is a laser with a pulse width of 100ns, a wavelength of 1064nm, an output power of 50W, an output spot diameter of 2.5mm, and a focal length of the focusing lens of 60mm. The first total reflection mirror in the multi-focus derivative system is an aspheric mirror with a diameter of 60 mm and a focal length of 48.5 mm. The second total reflection mirror is a plane reflection mirror with a width of 50 mm and a length of 400 mm. The distance from the focusing lens to the first total reflection mirror is 23 mm, and the diameter of the aperture of the first total reflection mirror is 2 mm. The thickness of the transparent material to be processed is 100mm, and the absorption rate of the 1064nm wavelength is 5%. The distance from the first total reflection mirror to the upper surface of the transparent material to be processed is 30 mm, and the distance fr...
example 3
[0035] Adopt the third embodiment of the present invention. The laser source in the single-focus laser processing system is a laser with a pulse width of 50ns, a wavelength of 532nm, an output power of 25W, an output spot diameter of 1.5mm, and a focal length of the focusing lens of 70mm. The first total reflection mirror in the multi-focus derivative system is a spherical mirror with a diameter of 60mm and a focal length of 48.5mm, and the diameter of the small hole is 2mm; the second is an aspheric mirror with a focal length of 200mm. The transparent material to be processed is crystal glass with a thickness of 100mm and an absorption rate of 7% for a wavelength of 1064nm. The distance from the first total reflection mirror to the upper surface of the transparent material to be processed is 30 mm, and the distance from the second total reflection mirror to the lower surface of the material is 10 mm. The table moving speed is 1mm per second. Experimental results: the system...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com