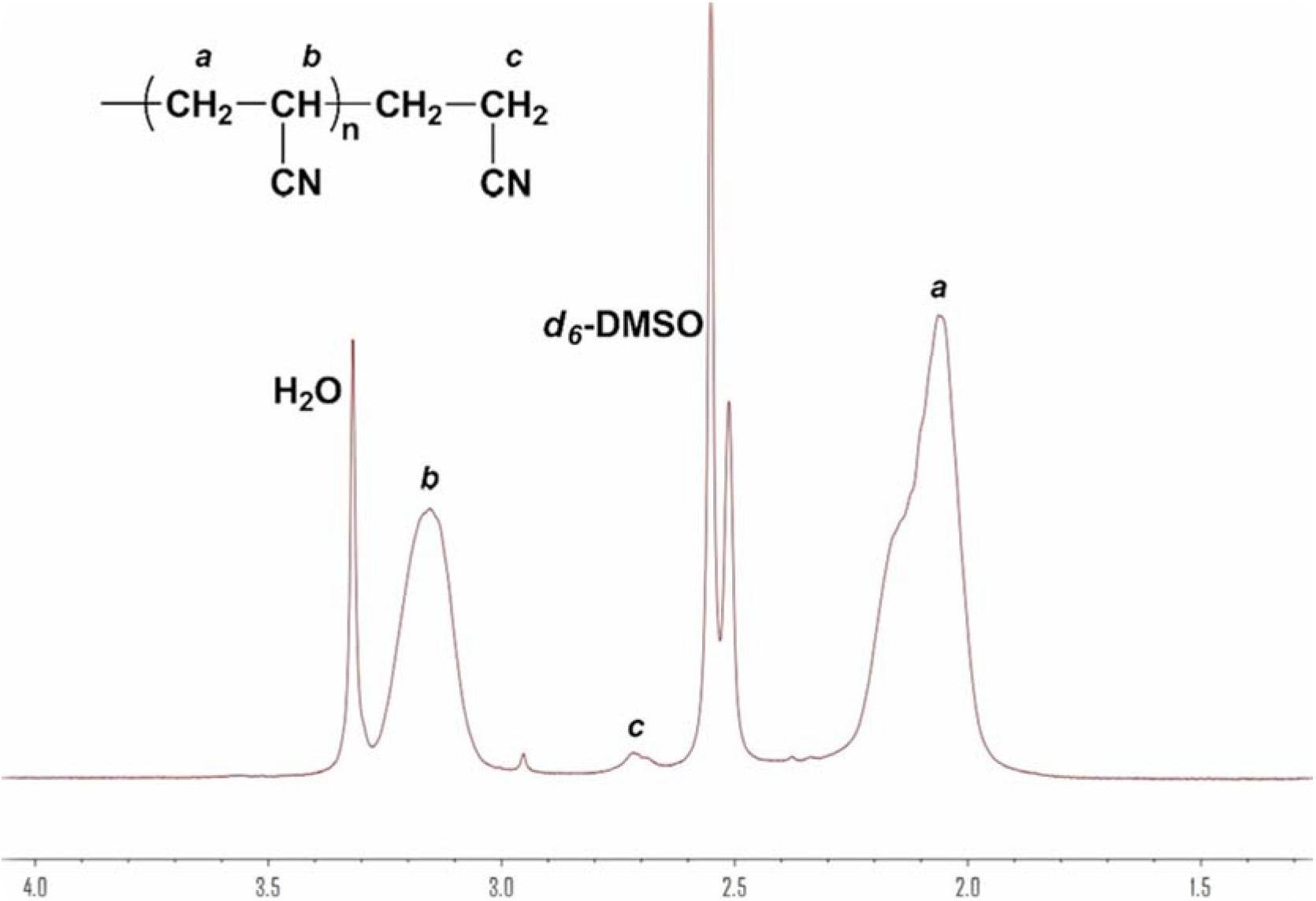
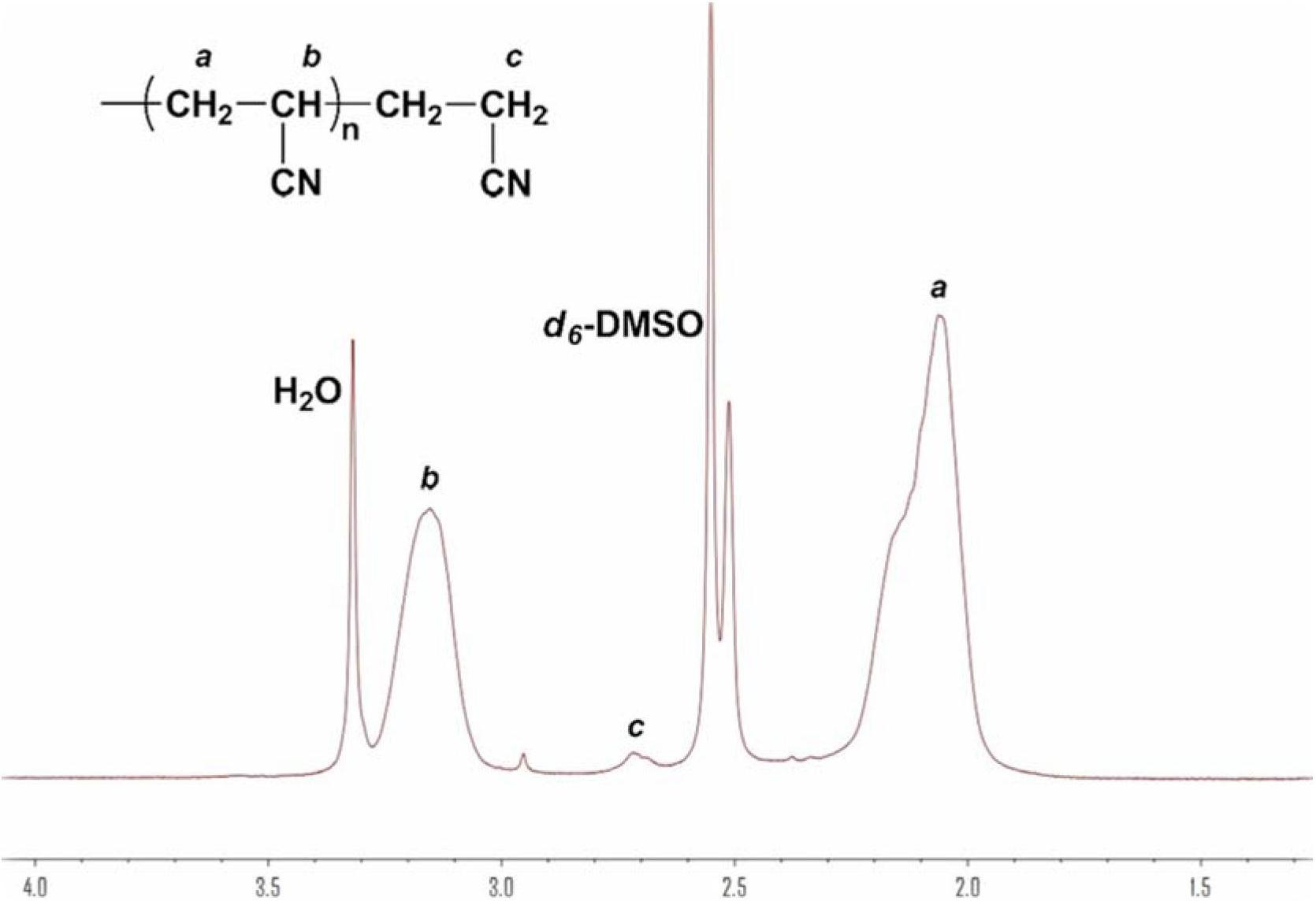
Method for synthesizing polyacrylonitrile by Lewis base
A Lewis base catalysis and polyacrylonitrile technology, which is applied in the field of polyacrylonitrile synthesis, can solve the problems of high cost of atom transfer radical polymerization, low catalytic system activity, and many residual polymerization products, and achieve moderate reaction rate and high reaction rate. Simple system and less side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] All containers and reactors must be vacuum pumped and protected with nitrogen. Add 1 part by mass of DMAP and 36 parts by mass of DMSO to dissolve in the reactor to prepare a solution. Then, 8.5 parts by mass of acrylonitrile were added to the solution, and after being thoroughly mixed in the reactor, the reaction was carried out at 40° C. for 24 hours. The resulting solution is precipitated with ethanol and separated by filtration to obtain an acrylonitrile polymer. Gained polyacrylonitrile weight average molecular weight is 2.8 * 10 4 . After melt spinning, the tensile strength of the obtained product is 22cN / dtex, and the elongation is 30%.
Embodiment 2
[0022] All containers and reactors must be vacuum pumped and protected with nitrogen. Add 1 part by mass of DMAP and 36 parts by mass of DMSO to dissolve in the reactor to prepare a solution. Then, 8.5 parts by mass of acrylonitrile were added to the solution, and after being thoroughly mixed in the reactor, the reaction was carried out at 25° C. for 24 hours. The resulting solution is precipitated with ethanol and separated by filtration to obtain an acrylonitrile polymer. Gained polyacrylonitrile weight average molecular weight is 2.8 * 10 3 . After melt spinning, the resulting product had a tensile strength of 11 cN / dtex and an elongation of 5%.
Embodiment 3
[0024] All containers and reactors must be vacuum pumped and protected with nitrogen. Add 1 part by mass of DMAP and 36 parts by mass of DMSO to dissolve in the reactor to prepare a solution. Further, 8.5 parts by mass of acrylonitrile were added to the solution, and after being thoroughly mixed in the reactor, the reaction was carried out at 60° C. for 8 hours. The resulting solution is precipitated with ethanol and separated by filtration to obtain an acrylonitrile polymer. Gained polyacrylonitrile weight average molecular weight is 2.1 * 10 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com