Method for water seepage, salt discharge and afforestation of low-humidity saline and alkaline beach and application of method
A saline-alkali beach and landscaping technology, which is applied in the fields of desertification prevention and ecological environment restoration, can solve the problems of unrealistic irrigation and salt washing, poor activity of aerobic microorganisms, and deterioration of soil physical properties, so as to improve saline-alkali land afforestation and greening plants Fewer varieties, better response to uneven deformation performance, improved fertility level and physical and chemical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Traditional saline-alkali land treatment method
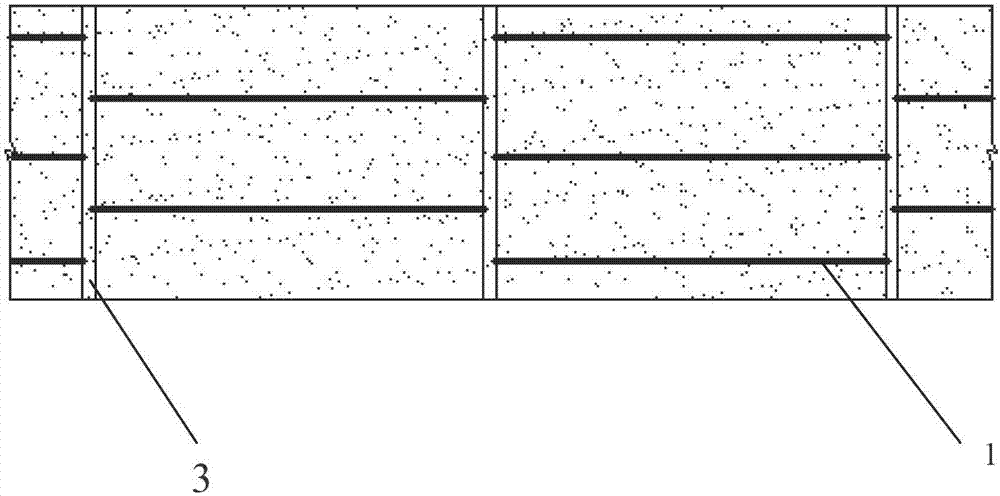
[0042] see figure 1 and Figure 4 .
[0043] 1. Excavate drainage ditches 3 in the direction from high to low on the saline-alkali land to be treated, and the drainage ditches 3 are arranged according to the topography to facilitate drainage. The drainage ditch 3 is 20m apart, and the depth is 1m from the surface.
[0044] 2. After excavating the drainage ditch 3, the surface layer of the plot is covered with compost of livestock and poultry excrement (10m 3 per mu), mechanically plowed, the plowing depth is 30cm, and the organic fertilizer is turned to the bottom.
[0045] 3. In the plowed plot, excavate the buried pipe 4 evenly perpendicular to the drainage ditch, the ditch width is 40cm, the ditch depth is 40cm, the distance between the ditch is 5m, and the longitudinal slope ratio of the ditch bottom is 0.8%.
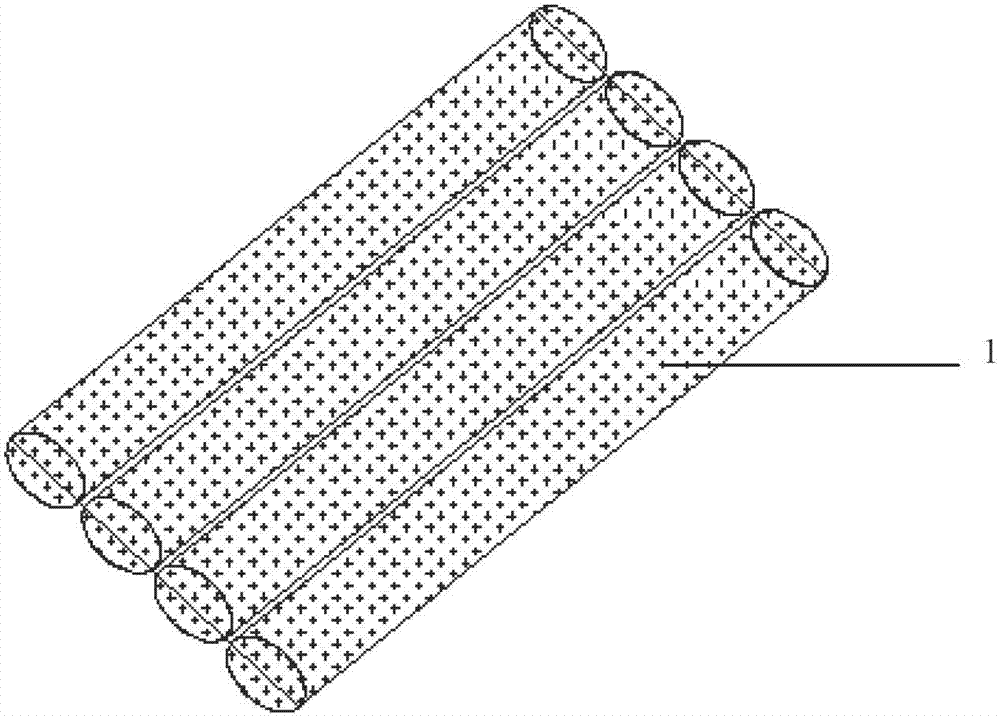
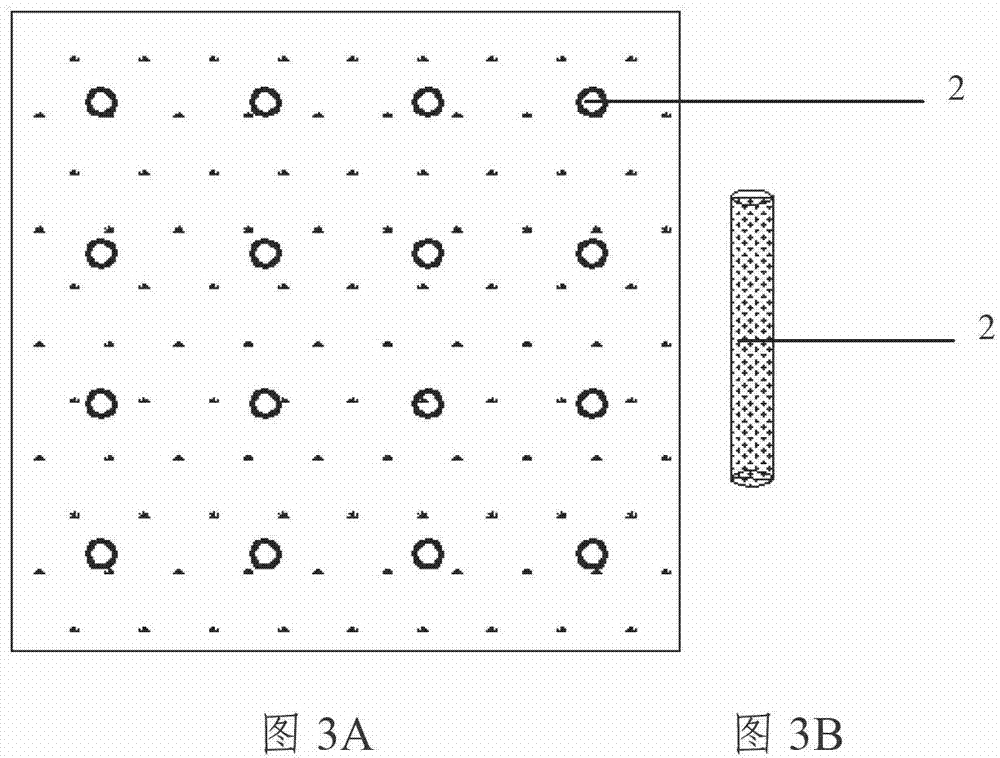
[0046] 4. Use a 5cm gravel cushion at the bottom of the ditch, lay the concealed pipe 5 on the...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2 Scheme 1 of the present invention (Shandong Hekou District Saline-alkali Land Project)
[0050] 1. In the saline-alkali land to be treated, combined with the natural terrain, in accordance with the requirements of landscape planning and green belt construction, adopt the landscape micro-topography model of low excavation and high filling to form three low-lying water catchment areas for drainage and salt discharge. The catchment surface accounts for the total treatment 12.7% of the area. Drainage ditches shall be excavated in the direction from high to low and lead to the low-lying catchment area for easy drainage. The distance between drainage ditches 3 is 40m, and the depth is 1.2m from the ground surface.
[0051] 2. After the excavation of the drainage ditches, the surface layer of the plot is covered with compost of livestock and poultry excrement (10m 3 per mu) and then mechanically plowed to a depth of 20 cm, and the organic fertilizer was turned t...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3 The present invention scheme 2 Hekou District, Shandong Province
[0059] This example is a supplement to Example 2, that is, the shallow dense seepage and salt discharge method, which improves the energy efficiency of the overall system seepage and salt discharge. Change the flexible water seepage and salt drainage belt composed of 3 groups of cells in the ground 4 step in Example 2 to a single seepage and salt discharge pipe composed of 1 cell, and the layout distance is reduced from 6m to 2m, forming a shallow layer Intensive seepage and salt discharge method.
[0060] Compared with Example 2, on the basis of the same investment, the distance of the drainage belt is shortened by 3 times, and the seepage and salt discharge efficiency is increased by nearly 20% on the original basis.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com