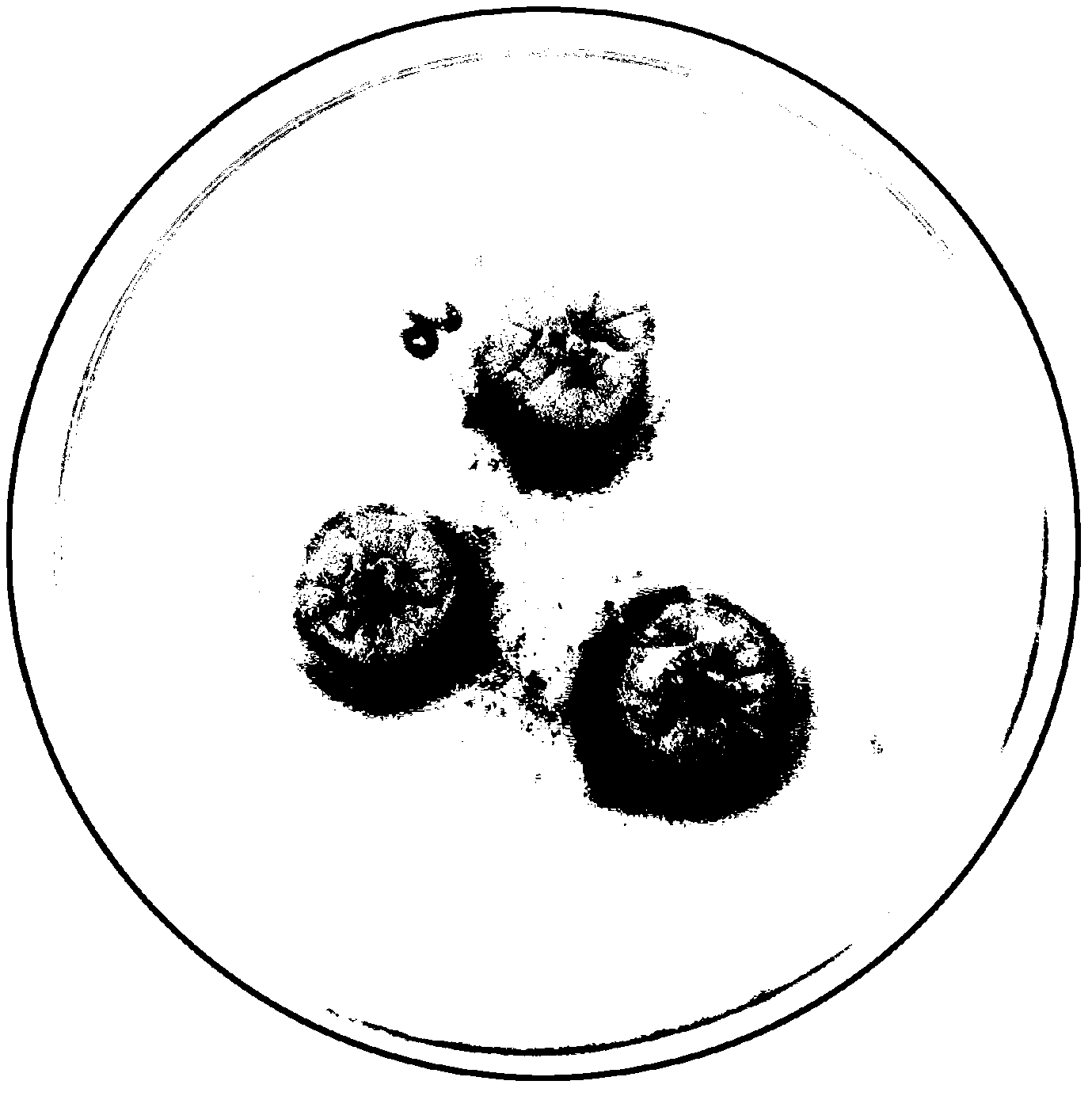
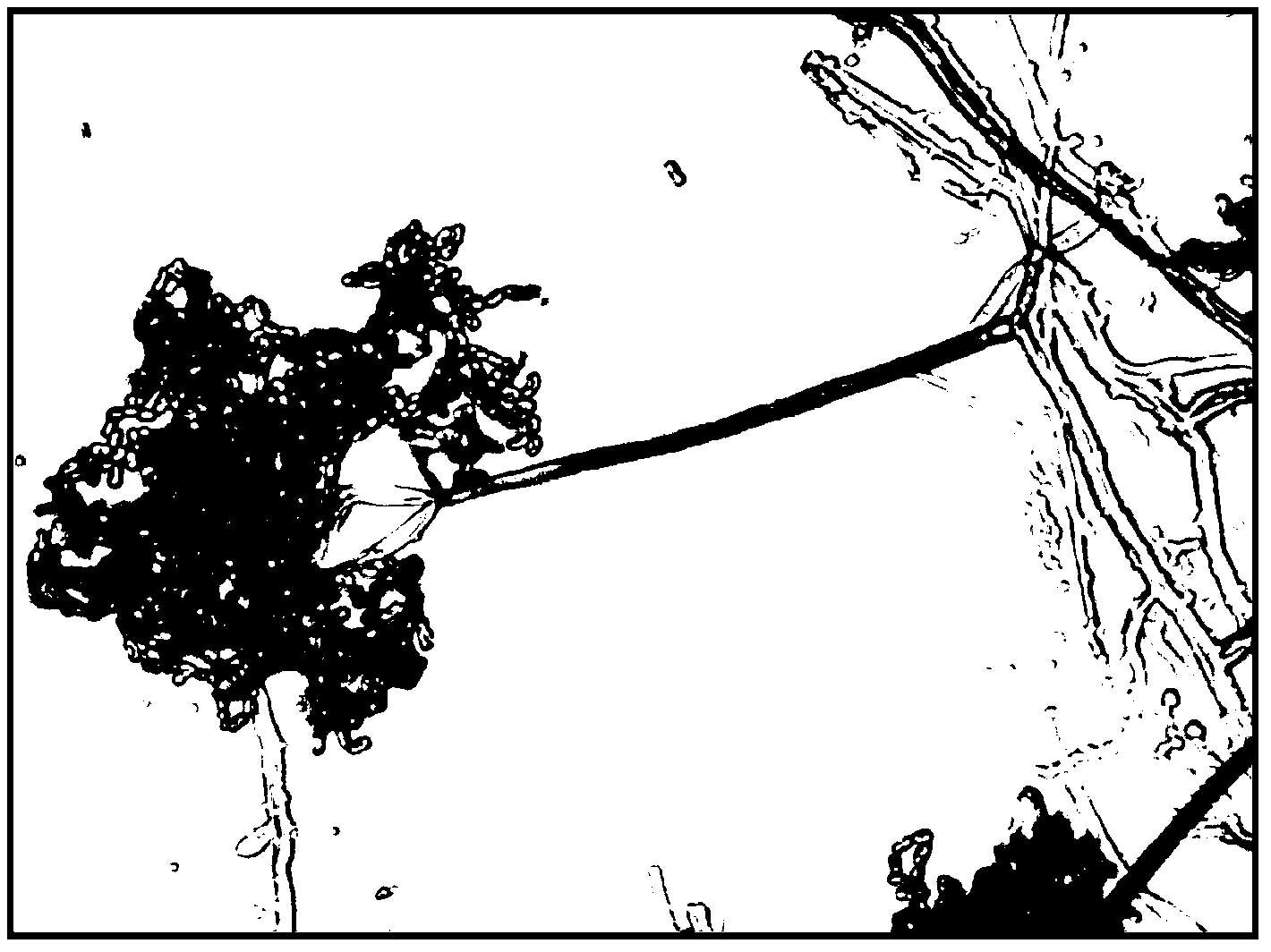
Mycorrhizal fungi strain efficiently growing with rhododendron seedling
A technology of mycorrhizal fungi and strains, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of affecting nutrient absorption of azalea seedlings, slow growth of azalea seedlings, and high mortality, so as to improve the survival rate of seedlings, increase the infection rate of mycorrhizal plants, and promote seedlings. effect of growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Example 1 Isolation and identification of rhododendron mycorrhizal fungi:
[0014] 1. Separation of root materials: Take the living roots of the rhododendron species ‘Purple Crane’ in Shanghai Binjiang Forest Park, put them in an ice bucket together with soil moisture, and store them in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0015] 2. Separation and identification medium:
[0016] (1) Separation medium: Use Martin-Bengal red medium (referred to as MA) to adjust and improve its pH. The formula is: 10 grams of glucose, 5 grams of tryptone, 1 gram of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.5 grams of magnesium sulfate, 0.033 grams of Bengal red, 20 grams of agar, distilled water to 1000 ml, adjust the pH value to 5.0, and then 121 ℃ high pressure Sterilize for 20 minutes, add 0.03 g of streptomycin when cooled to below 60°C, mix well, and pour it into a plate for later use.
[0017] (2) Strain identification medium: use malt extract medium (MEA), the formula is: 20g of malt extra...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The strain of the present invention is isolated from the root system of the rhododendron variety 'Purple Crane' in Shanghai Binjiang Forest Park. It is Ascomycetes Oidiodendron (Oidiodendron) OBJF31. It can be cultured on plates and liquids, using MEA medium, and the formula is: malt Extract 20g, tryptone 1g, glucose 20g, suitable culture medium pH value 5.1, culture temperature 22~24℃.
[0033] The macroscopic characteristics of the culture of the strain are as follows: the colony grows slowly, and it is off-white at first. After 10 days, the color of the center of the colony becomes darker and brown. cm. Microscopic characteristics: Mycelia diameter 2.0~3.0μm, with unicellular conidia, oval, smooth surface, size 2.5~3.5μm*1.5~2.0μm, with conidiophores, length 80~120μm. According to the ITS sequence comparison of the strain, the closest species is the fungus of the genus Oidiodendron, which is consistent with the identification results of the morphological characteris...
Embodiment 3
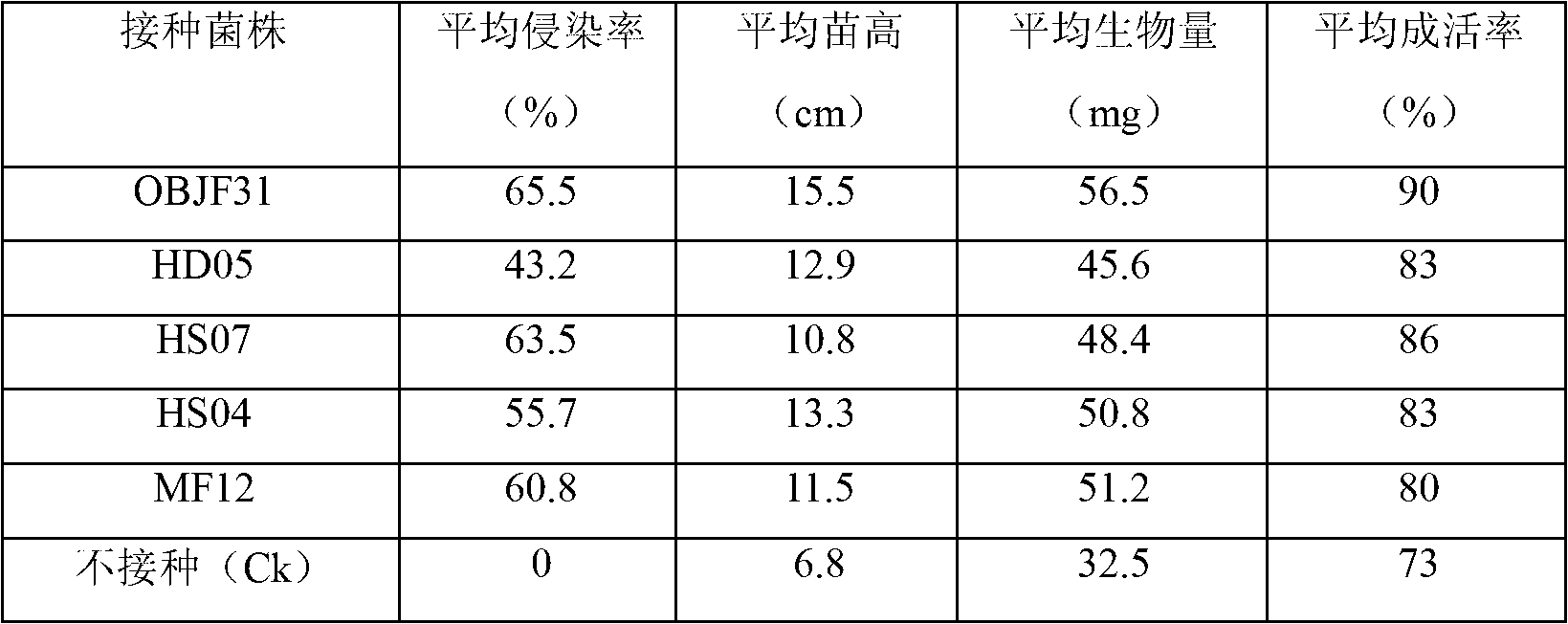
[0038] Seedlings of Rhododendron yunnanensis cultured for 9 weeks in aseptic culture, with a height of about 2-4 cm, were transplanted in substrates with different pH values that were sterilized. The adjustment method of the pH value of the cultivation medium: based on the original pH value of the cultivation medium, a certain amount of CaCO is added according to the volume ratio of the substrate. 3 (addition ratio according to 0, 3, 5kg / m 3 ), adjust the pH value of the cultivation substrate to 5.5, 6.8, 7.2 respectively. Seedlings were inoculated after transplanting. The inoculated strains were OBJF31 (preservation number: CGMCC No.6010) and HS04. The inoculation method and seedling culture conditions were the same as in Example 1. 30 plants were inoculated for each treatment, and no inoculation controls were set respectively. After 20 weeks of inoculation, the infection rate and biomass of the seedlings were detected (Table 2). The biomass and survival rate of the inocul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com